
Info
William Morris
William Blake Richmond
1880s
National Portrait Gallery


Edgar Albert Guest (20 August 1881 in Birmingham, England – 5 August 1959 in Detroit, Michigan) (aka Eddie Guest) was a prolific English-born American poet who was popular in the first half of the 20th century and became known as the People’s Poet. In 1891, Guest moved with his family to the United States from England. After he began at the Detroit Free Press as a copy boy and then a reporter, his first poem appeared 11 December 1898. He became a naturalized citizen in 1902. For 40 years, Guest was widely read throughout North America, and his sentimental, optimistic poems were in the same vein as the light verse of Nick Kenny, who wrote syndicated columns during the same decades. Guest’s most famous poem is the oft-quoted “Home”: It don’t make a difference how rich ye get t’ be’ How much yer chairs and tables cost, how great the luxury; It ain’t home t’ ye, though it be the palace of a king, Until somehow yer soul is sort o’ wrapped round everything. Within the hi how are you there’s got t’ be some babies born an’ then... Right there ye’ve got t’ bring em up t’ women good, an’ men; Home ain’t a place that gold can buy or get up in a minute; Afore it’s home there’s got t’ be a heap o’ living in it.” —Excerpt from “Home,” It takes A Heap o’ Livin’ (1916) When you’re up against a trouble, Meet it squarely, face to face, Lift your chin, and set your shoulders, Plant your feet and take a brace, When it’s vain to try to dodge it, Do the best that you can do. You may fail, but you may conquer— See it through! —Excerpt from “See It Through” Guest’s most motivating poem: You can do as much as you think you can, But you'll never accomplish more; If you're afraid of yourself, young man, There's little for you in store. For failure comes from the inside first, It's there, if we only knew it, And you can win, though you face the worst, If you feel that you're going to do it. —Excerpt from “The Secret of the Ages” (1926)

Robert William Service (January 16, 1874 – September 11, 1958) was a poet and writer who has often been called "the Bard of the Yukon". He was born in Preston, Lancashire, England and he is best known for his poems "The Shooting of Dan McGrew" and "The Cremation of Sam McGee", from his first book, Songs of a Sourdough (1907; also published as The Spell of the Yukon and Other Verses).
#English #XIXCentury #XXCentury

George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron FRS; 22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), simply known as Lord Byron, was an English poet and peer. One of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, Byron is regarded as one of the greatest English poets. He remains widely read and influential. Among his best-known works are the lengthy narrative poems Don Juan and Childe Harold's Pilgrimage; many of his shorter lyrics in Hebrew Melodies also became popular. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, and later travelled extensively across Europe, especially in Italy, where he lived for seven years in Venice, Ravenna, and Pisa after he was forced to flee England due to lynching threats. During his stay in Italy, he frequently visited his friend and fellow poet Percy Bysshe Shelley. Later in life Byron joined the Greek War of Independence fighting the Ottoman Empire and died leading a campaign during that war, for which Greeks revere him as a folk hero. He died in 1824 at the age of 36 from a fever contracted after the First and Second Sieges of Missolonghi.
#English #Romanticism #XIXCentury


William Shakespeare (baptised 26 April 1564; died 23 April 1616) was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon". His surviving works, including some collaborations, consist of about 38 plays, 154 sonnets, two long narrative poems, and several other poems. His plays have been translated into every major living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Authorship Around 230 years after Shakespeare’s death, doubts began to be expressed about the authorship of the works attributed to him. Proposed alternative candidates include Francis Bacon, Christopher Marlowe, and Edward de Vere, 17th Earl of Oxford. Several “group theories” have also been proposed. All but a few Shakespeare scholars and literary historians consider it a fringe theory, with only a small minority of academics who believe that there is reason to question the traditional attribution, but interest in the subject, particularly the Oxfordian theory of Shakespeare authorship, continues into the 21st century.
#English #XVICentury #XVIICentury

Joseph Rudyard Kipling (30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936) was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work. Kipling was one of the most popular writers in England, in both prose and verse, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Henry James said: “Kipling strikes me personally as the most complete man of genius (as distinct from fine intelligence) that I have ever known.”
#English #Victorians #XIXCentury #XXCentury


William Wordsworth (7 April 1770 – 23 April 1850) was a major English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with the 1798 joint publication Lyrical Ballads. Wordsworth's magnum opus is generally considered to be The Prelude, a semiautobiographical poem of his early years which he revised and expanded a number of times. It was posthumously titled and published, prior to which it was generally known as the poem "To Coleridge". Wordsworth was Britain's Poet Laureate from 1843 until his death in 1850.
#English #Romanticism #XIXCentury #XVIIICentury


Percy Bysshe Shelley (4 August 1792 – 8 July 1822) was one of the major English Romantic poets and is critically regarded as among the finest lyric poets in the English language. Shelley was famous for his association with John Keats and Lord Byron. The novelist Mary Shelley (née Godwin) was his second wife. Shelley's unconventional life and uncompromising idealism, combined with his strong disapproving voice, made him a marginalized figure during his life, important in a fairly small circle of admirers, and opened him to criticism as well as praise afterward.
#English #Romanticism #XIXCentury


In 1830, Christina Rossetti was born in London, one of four children of Italian parents. Her father was the poet Gabriele Rossetti; her brother Dante Gabriel Rossetti also became a poet and a painter. Rossetti’s first poems were written in 1842 and printed in the private press of her grandfather. In 1850, under the pseudonym Ellen Alleyne, she contributed seven poems to the Pre-Raphaelite journal The Germ, which had been founded by her brother William Michael and his friends.
#English #Victorians #Women #XIXCentury


Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. While his works typically belong to the Naturalism movement, several poems display elements of the previous Romantic and Enlightenment periods of literature, such as his fascination with the supernatural. While he regarded himself primarily as a poet who composed novels mainly for financial gain, he became and continues to be widely regarded for his novels, such as Tess of the d'Urbervilles and Far from the Madding Crowd. Hardy's poetry, first published in his fifties, has come to be as well regarded as his novels and has had a significant influence over modern English poetry, especially after The Movement poets of the 1950s and 1960s cited Hardy as a major figure.
#English #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Isaac Watts (17 July 1674 – 25 November 1748) was an English Christian minister, hymnwriter, theologian and logician. A prolific and popular hymn writer, his work was part of evangelization. He was recognized as the “Father of English Hymnody”, credited with some 750 hymns. Many of his hymns remain in use today and have been translated into numerous languages.
#English #XVIICentury #XVIIICentury


Robert Laurence Binyon (10 August 1869– 10 March 1943) was an English poet, dramatist and art scholar. His most famous work, For the Fallen, is well known for being used in Remembrance Sunday services. Laurence Binyon was born in Lancaster, Lancashire, England. His parents were Frederick Binyon, and Mary Dockray. Mary’s father, Robert Benson Dockray, was the main engineer of the London and Birmingham Railway. The family were Quakers. Binyon studied at St Paul’s School, London. Then he read Classics (Honour Moderations) at Trinity College, Oxford, where he won the Newdigate Prize for poetry in 1891.
#Decadents #English #XIXCentury #XXCentury


English Romantic poet John Keats was born on October 31, 1795, in London. The oldest of four children, he lost both his parents at a young age. His father, a livery-stable keeper, died when Keats was eight; his mother died of tuberculosis six years later. After his mother's death, Keats's maternal grandmother appointed two London merchants, Richard Abbey and John Rowland Sandell, as guardians. Abbey, a prosperous tea broker, assumed the bulk of this responsibility, while Sandell played only a minor role. When Keats was fifteen, Abbey withdrew him from the Clarke School, Enfield, to apprentice with an apothecary-surgeon and study medicine in a London hospital. In 1816 Keats became a licensed apothecary, but he never practiced his profession, deciding instead to write poetry.
#English #Romanticism #XIXCentury


Dante Gabriel Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882) was an English poet, illustrator, painter and translator. He founded the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood in 1848 with William Holman Hunt and John Everett Millais, and was later to be the main inspiration for a second generation of artists and writers influenced by the movement, most notably William Morris and Edward Burne-Jones. His work also influenced the European Symbolists and was a major precursor of the Aesthetic movement.
#English #Victorians #XIXCentury


Richard Le Gallienne (20 January 1866 – 15 September 1947) was an English author and poet. The American actress Eva Le Gallienne (1899–1991) was his daughter, by his second marriage. He was born in Liverpool. He started work in an accountant’s office, but abandoned this job to become a professional writer. The book My Ladies’ Sonnets appeared in 1887, and in 1889 he became, for a brief time, literary secretary to Wilson Barrett.
#English #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Philip Arthur Larkin (9 August 1922 – 2 December 1985) was an English poet and novelist. His first book of poetry, The North Ship, was published in 1945, followed by two novels, Jill (1946) and A Girl in Winter (1947), but he came to prominence in 1955 with the publication of his second collection of poems, The Less Deceived, followed by The Whitsun Weddings (1964) and High Windows (1974). He was the recipient of many honours, including the Queen's Gold Medal for Poetry. He was offered, but declined, the position of poet laureate in 1984, following the death of John Betjeman.


Robert Herrick (baptized 24 August 1591 – buried 15 October 1674) was a 17th-century English poet. The Victorian poet Swinburne described Herrick as the greatest song writer ever born of English race. It is certainly true that despite his use of classical allusions and names, his poems are easier for modern readers to understand than those of many of his contemporaries. The over-riding message of Herrick’s work is that life is short, the world is beautiful, love is splendid, and we must use the short time we have to make the most of it. This message can be seen clearly in To the Virgins, to make much of Time, To Daffodils, To Blossoms and Corinna going a-Maying, where the warmth and exuberance of what seems to have been a kindly and jovial personality comes over strongly. The opening stanza in one of his more famous poems, "To the Virgins, to Make Much of Time", is as follows: Gather ye rosebuds while ye may, Old Time is still a-flying; And this same flower that smiles today, Tomorrow will be dying.
#English #XVICentury #XVIICentury


Wystan Hugh Auden (21 February 1907 – 29 September 1973), who published as W. H. Auden, was an Anglo-American poet, born in England, later an American citizen, regarded by many as one of the greatest writers of the 20th century. His work is noted for its stylistic and technical achievements, its engagement with moral and political issues, and its variety of tone, form and content. The central themes of his poetry are love, politics and citizenship, religion and morals, and the relationship between unique human beings and the anonymous, impersonal world of nature. Auden grew up in Birmingham in a professional middle class family and read English literature at Christ Church, Oxford. His early poems, written in the late 1920s and early 1930s, alternated between telegraphic modern styles and fluent traditional ones, were written in an intense and dramatic tone, and established his reputation as a left-wing political poet and prophet. He became uncomfortable in this role in the later 1930s, and abandoned it after he moved to the United States in 1939, where he became an American citizen in 1946. His poems in the 1940s explored religious and ethical themes in a less dramatic manner than his earlier works, but still combined traditional forms and styles with new forms devised by Auden himself. In the 1950s and 1960s many of his poems focused on the ways in which words revealed and concealed emotions, and he took a particular interest in writing opera librettos, a form ideally suited to direct expression of strong feelings.


George Meredith, OM (12 February 1828 – 18 May 1909) was an English novelist and poet of the Victorian era. Meredith was born in Portsmouth, England, a son and grandson of naval outfitters. His mother died when he was five. At the age of 14 he was sent to a Moravian School in Neuwied, Germany, where he remained for two years. He read law and was articled as a solicitor, but abandoned that profession for journalism and poetry. He collaborated with Edward Gryffydh Peacock, son of Thomas Love Peacock in publishing a privately circulated literary magazine, the Monthly Observer. He married Edward Peacock’s widowed sister Mary Ellen Nicolls in 1849 when he was twenty-one years old and she was twenty-eight.
#English #Victorians #XIXCentury


On July 24, 1895, Robert Graves was born in Wimbledon, near London. His father, Alfred Perceval Graves, was a Gaelic scholar and minor Irish poet. His mother, Amalie von Ranke Graves, was a relation of Leopold von Ranke, one of the founding fathers of modern historical studies. One of ten children, Robert was greatly influenced by his mother's puritanical beliefs and his father's love of Celtic poetry and myth. As a young man, he was more interested in boxing and mountain climbing than studying, although poetry later sustained him through a turbulent adolescence. In 1913 Graves won a scholarship to continue his studies at St. John's College, Oxford, but in August 1914 he enlisted as a junior officer in the Royal Welch Fusiliers. He fought in the Battle of Loos and was injured in the Somme offensive in 1916. While convalescing, he published his first collection of poetry, Over the Brazier. By 1917, though still an active serviceman, Graves had published three volumes. In 1918, he spent a year in the trenches, where he was again severely wounded. In January 1918, at the age of twenty-two, he married eighteen-year-old Nancy Nicholson, with whom he was to have four children. Traumatized by the war, he went to Oxford with his wife and took a position at St. John's College. Graves's early volumes of poetry, like those of his contemporaries, deal with natural beauty and bucolic pleasures, and with the consequences of the First World War. Over the Brazier and Fairies and Fusiliers earned for Graves the reputation as an accomplished war poet. After meeting the American poet and theorist Laura Riding in 1926, Graves's poetry underwent a significant transformation. Douglas Day has written that the "influence of Laura Riding is quite possibly the most important single element in [Graves's] poetic career: she persuaded him to curb his digressiveness and his rambling philosophizing and to concentrate instead on terse, ironic poems written on personal themes." In 1927, Graves and his first wife separated permanently, and in 1929 he published Goodbye to All That, an autobiography that announced his psychological accommodation with the residual horror of his war experiences. Shortly afterward, he departed to Majorca with Laura Riding. In addition to completing many books of verse while in Majorca, Graves also wrote several volumes of criticism, some in collaboration with Riding. The couple cofounded Seizin Press in 1928 and Epilogue, a semiannual magazine, in 1935. During that period, he evolved his theory of poetry as spiritually cathartic to both the poet and the reader. Although Graves claimed that he wrote novels only to earn money, it was through these that he attained status as a major writer in 1934, with the publication of the historical novel I, Claudius, and its sequel, Claudius the God and His Wife Messalina. (During the 1970's, the BBC adapted the novels into an internationally popular television series.) At the onset of the Spanish Civil War in 1936, Graves and Riding fled Majorca, eventually settling in America. In 1939, Laura Riding left Graves for the writer Schuyler Jackson; one year later Graves began a relationship with Beryl Hodge that was to last until his death. It was in the 1940s, after his break with Riding, that Graves formulated his personal mythology of the White Goddess. Inspired by late nineteenth-century studies of matriarchal societies and goddess cults, this mythology was to pervade all of his later work. After World War II, Graves returned to Majorca, where he lived with Hodge and continued to write. By the 1950s, Graves had won an enormous international reputation as a poet, novelist, literary scholar, and translator. In 1962, W. H. Auden went as far as to assert that Graves was England's "greatest living poet." In 1968, he received the Queen's Gold Medal for Poetry. During his lifetime he published more than 140 books, including fifty-five collections of poetry (he reworked his Collected Poems repeatedly during his career), fifteen novels, ten translations, and forty works of nonfiction, autobiography, and literary essays. From 1961 to 1966, Graves returned to England to serve as a professor of poetry at Oxford. In the 1970s his productivity fell off; and the last decade of his life was lost in silence and senility. Robert Graves died in Majorca in 1985, at the age of ninety.


William Cowper (26 November 1731 – 25 April 1800) was an English poet and hymnodist. One of the most popular poets of his time, Cowper changed the direction of 18th century nature poetry by writing of everyday life and scenes of the English countryside. In many ways, he was one of the forerunners of Romantic poetry. Samuel Taylor Coleridge called him “the best modern poet”, whilst William Wordsworth particularly admired his poem Yardley-Oak. He was a nephew of the poet Judith Madan.


Siegfried Loraine Sassoon (8 September 1886 – 1 September 1967) was an English poet, author and soldier. Decorated for bravery on the Western Front, he became one of the leading poets of the First World War. His poetry both described the horrors of the trenches, and satirised the patriotic pretensions of those who, in Sassoon's view, were responsible for a vainglorious war. He later won acclaim for his prose work, notably his three-volume fictionalised autobiography, collectively known as the "Sherston Trilogy". Motivated by patriotism, Sassoon joined the British Army just as the threat of World War I was realised, and was in service with the Sussex Yeomanry on the day the United Kingdom declared war (4 August 1914). He broke his arm badly in a riding accident and was put out of action before even leaving England, spending the spring of 1915 convalescing.

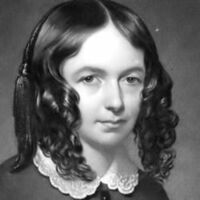
Elizabeth Barrett Browning (6 March 1806 – 29 June 1861) was one of the most prominent poets of the Victorian era. Her poetry was widely popular in both England and the United States during her lifetime. A collection of her last poems was published by her husband, Robert Browning, shortly after her death. Barrett Browning opposed slavery and published two poems highlighting the barbarity of slavers and her support for the abolitionist cause. The poems opposing slavery include "The Runaway Slave at Pilgrim's Point" and "A Curse for a Nation"; in the first she describes the experience of a slave woman who is whipped, raped, and made pregnant as she curses the slavers. She declared herself glad that the slaves were "virtually free" when the Emancipation Act abolishing slavery in British colonies was passed in 1833, despite the fact that her father believed that Abolitionism would ruin his business.


Alfred Tennyson, 1st Baron Tennyson, FRS (6 August 1809 – 6 October 1892) was Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom during much of Queen Victoria's reign and remains one of the most popular poets in the English language. A number of phrases from Tennyson’s work have become commonplaces of the English language, including “Nature, red in tooth and claw”, “'Tis better to have loved and lost / Than never to have loved at all”, “Theirs not to reason why, / Theirs but to do and die”, “My strength is as the strength of ten, / Because my heart is pure”, “Knowledge comes, but Wisdom lingers”, and “The old order changeth, yielding place to new”. He is the ninth most frequently quoted writer in The Oxford Dictionary of Quotations.
#English #Victorians #XIXCentury


Wilfrid Scawen Blunt (17 August 1840 – 10 September 1922, sometimes spelled “Wilfred”) was an English poet and writer. He and his wife, Lady Anne Blunt, travelled in the Middle East and were instrumental in preserving the Arabian horse bloodlines through their farm, the Crabbet Arabian Stud. He was best known for his poetry, which was published in a collected edition in 1914, but also wrote a number of political essays and polemics. Blunt is also known for his views against imperialism, viewed as relatively enlightened for his time.
#English #XIXCentury #XXCentury


John Clare (13 July 1793 – 20 May 1864) was an English poet, the son of a farm labourer, who came to be known for his celebratory representations of the English countryside and his lamentation of its disruption. His poetry underwent a major re-evaluation in the late 20th century and he is often now considered to be among the most important 19th-century poets. His biographer Jonathan Bate states that Clare was "the greatest labouring-class poet that England has ever produced. No one has ever written more powerfully of nature, of a rural childhood, and of the alienated and unstable self”. Early life Clare was born in Helpston, six miles to the north of the city of Peterborough. In his life time, the village was in the Soke of Peterborough in Northamptonshire and his memorial calls him "The Northamptonshire Peasant Poet". Helpston now lies in the Peterborough unitary authority of Cambridgeshire. He became an agricultural labourer while still a child; however, he attended school in Glinton church until he was twelve. In his early adult years, Clare became a pot-boy in the Blue Bell public house and fell in love with Mary Joyce; but her father, a prosperous farmer, forbade her to meet him. Subsequently he was a gardener at Burghley House. He enlisted in the militia, tried camp life with Gypsies, and worked in Pickworth as a lime burner in 1817. In the following year he was obliged to accept parish relief. Malnutrition stemming from childhood may be the main culprit behind his 5-foot stature and may have contributed to his poor physical health in later life. Early poems Clare had bought a copy of Thomson's Seasons and began to write poems and sonnets. In an attempt to hold off his parents' eviction from their home, Clare offered his poems to a local bookseller named Edward Drury. Drury sent Clare's poetry to his cousin John Taylor of the publishing firm of Taylor & Hessey, who had published the work of John Keats. Taylor published Clare's Poems Descriptive of Rural Life and Scenery in 1820. This book was highly praised, and in the next year his Village Minstrel and other Poems were published. Midlife He had married Martha ("Patty") Turner in 1820. An annuity of 15 guineas from the Marquess of Exeter, in whose service he had been, was supplemented by subscription, so that Clare became possessed of £45 annually, a sum far beyond what he had ever earned. Soon, however, his income became insufficient, and in 1823 he was nearly penniless. The Shepherd's Calendar (1827) met with little success, which was not increased by his hawking it himself. As he worked again in the fields his health temporarily improved; but he soon became seriously ill. Earl FitzWilliam presented him with a new cottage and a piece of ground, but Clare could not settle in his new home. Clare was constantly torn between the two worlds of literary London and his often illiterate neighbours; between the need to write poetry and the need for money to feed and clothe his children. His health began to suffer, and he had bouts of severe depression, which became worse after his sixth child was born in 1830 and as his poetry sold less well. In 1832, his friends and his London patrons clubbed together to move the family to a larger cottage with a smallholding in the village of Northborough, not far from Helpston. However, he felt only more alienated. His last work, the Rural Muse (1835), was noticed favourably by Christopher North and other reviewers, but this was not enough to support his wife and seven children. Clare's mental health began to worsen. As his alcohol consumption steadily increased along with his dissatisfaction with his own identity, Clare's behaviour became more erratic. A notable instance of this behaviour was demonstrated in his interruption of a performance of The Merchant of Venice, in which Clare verbally assaulted Shylock. He was becoming a burden to Patty and his family, and in July 1837, on the recommendation of his publishing friend, John Taylor, Clare went of his own volition (accompanied by a friend of Taylor's) to Dr Matthew Allen's private asylum High Beach near Loughton, in Epping Forest. Taylor had assured Clare that he would receive the best medical care. Later life and death During his first few asylum years in Essex (1837–1841), Clare re-wrote famous poems and sonnets by Lord Byron. His own version of Child Harold became a lament for past lost love, and Don Juan, A Poem became an acerbic, misogynistic, sexualised rant redolent of an aging Regency dandy. Clare also took credit for Shakespeare's plays, claiming to be the Renaissance genius himself. "I'm John Clare now," the poet claimed to a newspaper editor, "I was Byron and Shakespeare formerly." In 1841, Clare left the asylum in Essex, to walk home, believing that he was to meet his first love Mary Joyce; Clare was convinced that he was married with children to her and Martha as well. He did not believe her family when they told him she had died accidentally three years earlier in a house fire. He remained free, mostly at home in Northborough, for the five months following, but eventually Patty called the doctors in. Between Christmas and New Year in 1841, Clare was committed to the Northampton General Lunatic Asylum (now St Andrew's Hospital). Upon Clare's arrival at the asylum, the accompanying doctor, Fenwick Skrimshire, who had treated Clare since 1820, completed the admission papers. To the enquiry "Was the insanity preceded by any severe or long-continued mental emotion or exertion?", Dr Skrimshire entered: "After years of poetical prosing." He remained here for the rest of his life under the humane regime of Dr Thomas Octavius Prichard, encouraged and helped to write. Here he wrote possibly his most famous poem, I Am. He died on 20 May 1864, in his 71st year. His remains were returned to Helpston for burial in St Botolph’s churchyard. Today, children at the John Clare School, Helpston's primary, parade through the village and place their 'midsummer cushions' around Clare's gravestone (which has the inscriptions "To the Memory of John Clare The Northamptonshire Peasant Poet" and "A Poet is Born not Made") on his birthday, in honour of their most famous resident. The thatched cottage where he was born was bought by the John Clare Education & Environment Trust in 2005 and is restoring the cottage to its 18th century state. Poetry In his time, Clare was commonly known as "the Northamptonshire Peasant Poet". Since his formal education was brief, Clare resisted the use of the increasingly standardised English grammar and orthography in his poetry and prose. Many of his poems would come to incorporate terms used locally in his Northamptonshire dialect, such as 'pooty' (snail), 'lady-cow' (ladybird), 'crizzle' (to crisp) and 'throstle' (song thrush). In his early life he struggled to find a place for his poetry in the changing literary fashions of the day. He also felt that he did not belong with other peasants. Clare once wrote "I live here among the ignorant like a lost man in fact like one whom the rest seemes careless of having anything to do with—they hardly dare talk in my company for fear I should mention them in my writings and I find more pleasure in wandering the fields than in musing among my silent neighbours who are insensible to everything but toiling and talking of it and that to no purpose.” It is common to see an absence of punctuation in many of Clare's original writings, although many publishers felt the need to remedy this practice in the majority of his work. Clare argued with his editors about how it should be presented to the public. Clare grew up during a period of massive changes in both town and countryside as the Industrial Revolution swept Europe. Many former agricultural workers, including children, moved away from the countryside to over-crowded cities, following factory work. The Agricultural Revolution saw pastures ploughed up, trees and hedges uprooted, the fens drained and the common land enclosed. This destruction of a centuries-old way of life distressed Clare deeply. His political and social views were predominantly conservative ("I am as far as my politics reaches 'King and Country'—no Innovations in Religion and Government say I."). He refused even to complain about the subordinate position to which English society relegated him, swearing that "with the old dish that was served to my forefathers I am content." His early work delights both in nature and the cycle of the rural year. Poems such as Winter Evening, Haymaking and Wood Pictures in Summer celebrate the beauty of the world and the certainties of rural life, where animals must be fed and crops harvested. Poems such as Little Trotty Wagtail show his sharp observation of wildlife, though The Badger shows his lack of sentiment about the place of animals in the countryside. At this time, he often used poetic forms such as the sonnet and the rhyming couplet. His later poetry tends to be more meditative and use forms similar to the folks songs and ballads of his youth. An example of this is Evening. His knowledge of the natural world went far beyond that of the major Romantic poets. However, poems such as I Am show a metaphysical depth on a par with his contemporary poets and many of his pre-asylum poems deal with intricate play on the nature of linguistics. His 'bird's nest poems', it can be argued, illustrate the self-awareness, and obsession with the creative process that captivated the romantics. Clare was the most influential poet, aside from Wordsworth to practice in an older style. Revival of interest in the twentieth century Clare was relatively forgotten during the later nineteenth century, but interest in his work was revived by Arthur Symons in 1908, Edmund Blunden in 1920 and John and Anne Tibble in their ground-breaking 1935 2-volume edition. Benjamin Britten set some of 'May' from A Shepherd's Calendar in his Spring Symphony of 1948, and included a setting of The Evening Primrose in his Five Flower Songs Copyright to much of his work has been claimed since 1965 by the editor of the Complete Poetry (OUP, 9 vols., 1984–2003), Professor Eric Robinson though these claims were contested. Recent publishers have refused to acknowledge the claim (especially in recent editions from Faber and Carcanet) and it seems the copyright is now defunct. The John Clare Trust purchased Clare Cottage in Helpston in 2005, preserving it for future generations. In May 2007 the Trust gained £1.m of funding from the Heritage Lottery Fund and commissioned Jefferson Sheard Architects to create the new landscape design and Visitor Centre, including a cafe, shop and exhibition space. The Cottage has been restored using traditional building methods and opened to the public. The largest collection of original Clare manuscripts are housed at Peterborough Museum, where they are available to view by appointment. Since 1993, the John Clare Society of North America has organised an annual session of scholarly papers concerning John Clare at the annual Convention of the Modern Language Association of America. Poetry collections by Clare (chronological) * Poems Descriptive of Rural Life and Scenery. London, 1820. * The Village Minstrel, and Other Poems. London, 1821. * The Shepherd's Calendar with Village Stories and Other Poems. London, 1827 * The Rural Muse. London, 1835. * Sonnet. London 1841 * First Love * Snow Storm. * The Firetail. * The Badger – Time unknown References Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Clare


William Barnes (22 February 1801– 7 October 1886) was an English writer, poet, Church of England priest, and philologist. He wrote over 800 poems, some in Dorset dialect, and much other work, including a comprehensive English grammar quoting from more than 70 different languages. Barnes was born at Rushay in the parish of Bagber, Dorset, the son of a farmer. His formal education finished when he was 13 years old. Between 1818 and 1823 he worked in Dorchester, the county town, as a solicitor’s clerk, then moved to Mere in neighbouring Wiltshire and opened a school. During his time here he began writing poetry in the Dorset dialect, as well as studying several languages (Italian, Persian, German and French, in addition to Greek and Latin), playing musical instruments (violin, piano and flute) and practising wood-engraving. He married Julia Miles, the daughter of an exciseman from Dorchester, in 1827, then in 1835 moved back to the county town, where again he ran a school. The school was initially in Durngate Street, then was moved to South Street. A second move to another South Street site made the school a neighbour of an architect’s practice where Thomas Hardy was an apprentice. The architect, John Hicks, was interested in literature and the classics, and when disputes about grammar occurred in the practice, Hardy would visit Barnes next door for an authoritative opinion.


Edward James (Ted) Hughes was born in Mytholmroyd, in the West Riding district of Yorkshire, on August 17, 1930. His childhood was quiet and dominately rural. When he was seven years old, his family moved to the small town of Mexborough in South Yorkshire, and the landscape of the moors of that area informed his poetry throughout his life. Hughes graduated from Cambridge in 1954. A few years later, in 1956, he co-founded the literary magazine St. Botolph’s Review with a handful of other editors. At the launch party for the magazine, he met Sylvia Plath. A few short months later, on June 16, 1956, they were married.


Robert Browning was born on May 7, 1812, in Camberwell, England. His mother was an accomplished pianist and a devout evangelical Christian. His father, who worked as a bank clerk, was also an artist, scholar, antiquarian, and collector of books and pictures. His rare book collection of more than 6,000 volumes included works in Greek, Hebrew, Latin, French, Italian, and Spanish. Much of Browning's education came from his well-read father. It is believed that he was already proficient at reading and writing by the age of five. A bright and anxious student, Browning learned Latin, Greek, and French by the time he was fourteen. From fourteen to sixteen he was educated at home, attended to by various tutors in music, drawing, dancing, and horsemanship.
#English #Victorians #XIXCentury

Edmund Spenser (c. 1552 – 13 January 1599) was an English poet best known for The Faerie Queene, an epic poem and fantastical allegory celebrating the Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I. He is recognised as one of the premier craftsmen of Modern English verse in its infancy, and is considered one of the greatest poets in the English language.
#English #Renaissance #XVICentury


Samuel Taylor Coleridge (21 October 1772 – 25 July 1834) was an English poet, Romantic, literary critic and philosopher who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets. He is probably best known for his poems The Rime of the Ancient Mariner and Kubla Khan, as well as for his major prose work Biographia Literaria. His critical work, especially on Shakespeare, was highly influential, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking culture. He coined many familiar words and phrases, including the celebrated suspension of disbelief. He was a major influence, via Emerson, on American transcendentalism. Throughout his adult life, Coleridge suffered from crippling bouts of anxiety and depression; it has been speculated by some that he suffered from bipolar disorder, a condition as yet unidentified during his lifetime. Coleridge suffered from poor health that may have stemmed from a bout of rheumatic fever and other childhood illnesses. He was treated for these concerns with laudanum, which fostered a lifelong opium addiction.
#English #Romanticism #XIXCentury #XVIIICentury


Joseph Skipsey (1832– 1903) was a Northumberland born poet and songwriter in the middle and late 19th century. His best known work is arguably “The Hartley Calamity” about the Hartley Colliery Disaster, a devastating mining accident in Hartley, Northumberland, England in 1862 in which 204 lives were lost. He was known as “The Pitman Poet”.
#English #Victorians #XIXCentury


Alfred Austin DL (30 May 1835 – 2 June 1913) was an English poet who was appointed Poet Laureate in 1896, after an interval following the death of Tennyson, when the other candidates had either caused controversy or refused the honour. It was claimed that he was being rewarded for his support for the Conservative leader Lord Salisbury in the General Election of 1895. Austin’s poems are little-remembered today, his most popular work being prose idylls celebrating nature.
#English #XIXCentury #XXCentury


David Herbert Richards Lawrence (11 September 1885 – 2 March 1930) was an English novelist, poet, playwright, essayist, literary critic and painter who published as D. H. Lawrence. His collected works represent an extended reflection upon the dehumanising effects of modernity and industrialisation. In them, Lawrence confronts issues relating to emotional health and vitality, spontaneity, and instinct. Lawrence’s opinions earned him many enemies and he endured official persecution, censorship, and misrepresentation of his creative work throughout the second half of his life, much of which he spent in a voluntary exile which he called his “savage pilgrimage”. At the time of his death, his public reputation was that of a pornographer who had wasted his considerable talents. E. M. Forster, in an obituary notice, challenged this widely held view, describing him as, “The greatest imaginative novelist of our generation”. Later, the influential Cambridge critic F. R. Leavis championed both his artistic integrity and his moral seriousness, placing much of Lawrence's fiction within the canonical “great tradition” of the English novel. Lawrence is now valued by many as a visionary thinker and significant representative of modernism in English literature.
#English Modern


William Ernest Henley (23 August 1849 – 11 July 1903) was an English poet, critic and editor, best remembered for his 1875 poem “Invictus”. Henley was born in Gloucester and was the oldest of a family of six children, five sons and a daughter. His father, William, a bookseller and stationer, died in 1868 and was survived by young children and creditors. His mother, Mary Morgan, was descended from the poet and critic Joseph Wharton. Between 1861 and 1867, Henley was a pupil at the Crypt Grammar School (founded 1539).


Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950), better known by his pen name George Orwell, was an English novelist and journalist. His work is marked by clarity, intelligence and wit, awareness of social injustice, opposition to totalitarianism, and belief in democratic socialism. Considered perhaps the 20th century's best chronicler of English culture, Orwell wrote literary criticism, poetry, fiction and polemical journalism. He is best known for the dystopian novel Nineteen Eighty-Four (1949) and the allegorical novella Animal Farm (1945), which together have sold more copies than any two books by any other 20th-century author. His book Homage to Catalonia (1938), an account of his experiences in the Spanish Civil War, is widely acclaimed, as are his numerous essays on politics, literature, language and culture. In 2008, The Times ranked him second on a list of "The 50 greatest British writers since 1945”.


Frances Anne “Fanny” Kemble (27 November 1809– 15 January 1893) was a notable British actress from a theatre family in the early and mid-19th century. She was a well-known and popular writer, whose published works included plays, poetry, eleven volumes of memoirs, travel writing and works about the theatre.


Gilbert Keith Chesterton (29 May 1874 – 14 June 1936) was an English writer, philosopher, Christian apologist, and literary and art critic. He has been referred to as the "prince of paradox". Of his writing style, Time observed: "Whenever possible Chesterton made his points with popular sayings, proverbs, allegories—first carefully turning them inside out." Chesterton created the fictional priest-detective Father Brown, and wrote on apologetics. Even some of those who disagree with him have recognised the wide appeal of such works as Orthodoxy and The Everlasting Man. Chesterton routinely referred to himself as an "orthodox" Christian, and came to identify this position more and more with Catholicism, eventually converting to Roman Catholicism from high church Anglicanism. Biographers have identified him as a successor to such Victorian authors as Matthew Arnold, Thomas Carlyle, John Henry Newman and John Ruskin.


John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet, polemicist, a scholarly man of letters, and a civil servant for the Commonwealth (republic) of England under Oliver Cromwell. He wrote at a time of religious flux and political upheaval, and is best known for his epic poem Paradise Lost. Milton's poetry and prose reflect deep personal convictions, a passion for freedom and self determination, and the urgent issues and political turbulence of his day. Writing in English, Latin, and Italian, he achieved international renown within his lifetime, and his celebrated Areopagitica, (written in condemnation of pre-publication censorship) is among history’s most influential and impassioned defenses of free speech and freedom of the press.


Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by the pseudonym Lewis Carroll, was an English author, mathematician, logician, Anglican deacon and photographer. His most famous writings are Alice's Adventures in Wonderland and its sequel Through the Looking-Glass, as well as the poems "The Hunting of the Snark" and "Jabberwocky", all examples of the genre of literary nonsense. He is noted for his facility at word play, logic, and fantasy, and there are societies in many parts of the world (including the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, and New Zealand) dedicated to the enjoyment and promotion of his works and the investigation of his life. Antecedents Dodgson's family was predominantly northern English, with Irish connections. Conservative and High Church Anglican, most of Dodgson's ancestors were army officers or Church of England clergy. His great-grandfather, also named Charles Dodgson, had risen through the ranks of the church to become the Bishop of Elphin. His grandfather, another Charles, had been an army captain, killed in action in Ireland in 1803 when his two sons were hardly more than babies. His mother's name was Frances Jane Lutwidge. The elder of these sons – yet another Charles Dodgson – was Carroll's father. He reverted to the other family tradition and took holy orders. He went to Westminster School, and then to Christ Church, Oxford. He was mathematically gifted and won a double first degree, which could have been the prelude to a brilliant academic career. Instead he married his first cousin in 1827 and became a country parson. Dodgson was born in the little parsonage of Daresbury in Cheshire near the towns of Warrington and Runcorn, the eldest boy but already the third child of the four-and-a-half-year-old marriage. Eight more children were to follow. When Charles was 11, his father was given the living of Croft-on-Tees in North Yorkshire, and the whole family moved to the spacious rectory. This remained their home for the next twenty-five years. Young Charles' father was an active and highly conservative cleric of the Church of England who later became the Archdeacon of Richmond and involved himself, sometimes influentially, in the intense religious disputes that were dividing the church. He was High Church, inclining to Anglo-Catholicism, an admirer of John Henry Newman and the Tractarian movement, and did his best to instill such views in his children. Young Charles was to develop an ambiguous relationship with his father's values and with the Church of England as a whole. Education Home life During his early youth, Dodgson was educated at home. His "reading lists" preserved in the family archives testify to a precocious intellect: at the age of seven the child was reading The Pilgrim's Progress. He also suffered from a stammer – a condition shared by most of his siblings – that often influenced his social life throughout his years. At age twelve he was sent to Richmond Grammar School (now part of Richmond School) at nearby Richmond. Rugby In 1846, young Dodgson moved on to Rugby School, where he was evidently less happy, for as he wrote some years after leaving the place: I cannot say ... that any earthly considerations would induce me to go through my three years again ... I can honestly say that if I could have been ... secure from annoyance at night, the hardships of the daily life would have been comparative trifles to bear. Scholastically, though, he excelled with apparent ease. "I have not had a more promising boy at his age since I came to Rugby", observed R.B. Mayor, then Mathematics master. Oxford He left Rugby at the end of 1849 and matriculated at Oxford in May 1850 as a member of his father's old college, Christ Church. After waiting for rooms in college to become available, he went into residence in January 1851. He had been at Oxford only two days when he received a summons home. His mother had died of "inflammation of the brain" – perhaps meningitis or a stroke – at the age of forty-seven. His early academic career veered between high promise and irresistible distraction. He did not always work hard, but was exceptionally gifted and achievement came easily to him. In 1852 he obtained first-class honours in Mathematics Moderations, and was shortly thereafter nominated to a Studentship by his father's old friend, Canon Edward Pusey. In 1854 he obtained first-class honours in the Final Honours School of Mathematics, graduating Bachelor of Arts. He remained at Christ Church studying and teaching, but the next year he failed an important scholarship through his self-confessed inability to apply himself to study. Even so, his talent as a mathematician won him the Christ Church Mathematical Lectureship in 1855, which he continued to hold for the next twenty-six years. Despite early unhappiness, Dodgson was to remain at Christ Church, in various capacities, until his death. Character and appearance Health challenges The young adult Charles Dodgson was about six feet tall, slender, and had curling brown hair and blue or grey eyes (depending on the account). He was described in later life as somewhat asymmetrical, and as carrying himself rather stiffly and awkwardly, though this may be on account of a knee injury sustained in middle age. As a very young child, he suffered a fever that left him deaf in one ear. At the age of seventeen, he suffered a severe attack of whooping cough, which was probably responsible for his chronically weak chest in later life. Another defect he carried into adulthood was what he referred to as his "hesitation", a stammer he acquired in early childhood and which plagued him throughout his life. The stammer has always been a potent part of the conceptions of Dodgson; it is part of the belief that he stammered only in adult company and was free and fluent with children, but there is no evidence to support this idea. Many children of his acquaintance remembered the stammer while many adults failed to notice it. Dodgson himself seems to have been far more acutely aware of it than most people he met; it is said he caricatured himself as the Dodo in Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, referring to his difficulty in pronouncing his last name, but this is one of the many "facts" often-repeated, for which no firsthand evidence remains. He did indeed refer to himself as the dodo, but that this was a reference to his stammer is simply speculation. Although Dodgson's stammer troubled him, it was never so debilitating that it prevented him from applying his other personal qualities to do well in society. At a time when people commonly devised their own amusements and when singing and recitation were required social skills, the young Dodgson was well-equipped to be an engaging entertainer. He reportedly could sing tolerably well and was not afraid to do so before an audience. He was adept at mimicry and storytelling, and was reputedly quite good at charades. Social connections In the interim between his early published writing and the success of the Alice books, Dodgson began to move in the Pre-Raphaelite social circle. He first met John Ruskin in 1857 and became friendly with him. He developed a close relationship with Dante Gabriel Rossetti and his family, and also knew William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, and Arthur Hughes, among other artists. He also knew the fairy-tale author George MacDonald well – it was the enthusiastic reception of Alice by the young MacDonald children that convinced him to submit the work for publication. Politics, religion and philosophy In broad terms, Dodgson has traditionally been regarded as politically, religiously, and personally conservative. Martin Gardner labels Dodgson as a Tory who was "awed by lords and inclined to be snobbish towards inferiors." The Revd W. Tuckwell, in his Reminiscences of Oxford (1900), regarded him as "austere, shy, precise, absorbed in mathematical reverie, watchfully tenacious of his dignity, stiffly conservative in political, theological, social theory, his life mapped out in squares like Alice's landscape." However, Dodgson also expressed interest in philosophies and religions that seem at odds with this assessment. For example, he was a founding member of the Society for Psychical Research. It has been argued by the proponents of the 'Carroll Myth' that these factors require a reconsideration of Gardner's diagnosis, and that perhaps, Dodgson's true outlook was more complex than previously believed (see 'the Carroll Myth' below). Dodgson wrote some studies of various philosophical arguments. In 1895, he developed a philosophical regressus-argument on deductive reasoning in his article "What the Tortoise Said to Achilles", which appeared in one of the early volumes of the philosophical journal Mind. The article was reprinted in the same journal a hundred years later, in 1995, with a subsequent article by Simon Blackburn titled Practical Tortoise Raising. Artistic activities Literature From a young age, Dodgson wrote poetry and short stories, both contributing heavily to the family magazine Mischmasch and later sending them to various magazines, enjoying moderate success. Between 1854 and 1856, his work appeared in the national publications, The Comic Times and The Train, as well as smaller magazines like the Whitby Gazette and the Oxford Critic. Most of this output was humorous, sometimes satirical, but his standards and ambitions were exacting. "I do not think I have yet written anything worthy of real publication (in which I do not include the Whitby Gazette or the Oxonian Advertiser), but I do not despair of doing so some day," he wrote in July 1855. Sometime after 1850, he did write puppet plays for his siblings' entertainment, of which one has survived, La Guida di Bragia. In 1856 he published his first piece of work under the name that would make him famous. A romantic poem called "Solitude" appeared in The Train under the authorship of "Lewis Carroll." This pseudonym was a play on his real name; Lewis was the anglicised form of Ludovicus, which was the Latin for Lutwidge, and Carroll an Irish surname similar to the Latin name Carolus, from which the name Charles comes. Alice In the same year, 1856, a new Dean, Henry Liddell, arrived at Christ Church, bringing with him his young family, all of whom would figure largely in Dodgson's life and, over the following years, greatly influence his writing career. Dodgson became close friends with Liddell's wife, Lorina, and their children, particularly the three sisters: Lorina, Edith and Alice Liddell. He was for many years widely assumed to have derived his own "Alice" from Alice Liddell. This was given some apparent substance by the fact the acrostic poem at the end of Through the Looking Glass spells out her name, and that there are many superficial references to her hidden in the text of both books. It has been pointed out that Dodgson himself repeatedly denied in later life that his "little heroine" was based on any real child, and frequently dedicated his works to girls of his acquaintance, adding their names in acrostic poems at the beginning of the text. Gertrude Chataway's name appears in this form at the beginning of The Hunting of the Snark, and no one has ever suggested this means any of the characters in the narrative are based on her. Though information is scarce (Dodgson's diaries for the years 1858–1862 are missing), it does seem clear that his friendship with the Liddell family was an important part of his life in the late 1850s, and he grew into the habit of taking the children (first the boy, Harry, and later the three girls) on rowing trips accompanied by an adult friend to nearby Nuneham Courtenay or Godstow. It was on one such expedition, on 4 July 1862, that Dodgson invented the outline of the story that eventually became his first and largest commercial success. Having told the story and been begged by Alice Liddell to write it down, Dodgson eventually (after much delay) presented her with a handwritten, illustrated manuscript entitled Alice's Adventures Under Ground in November 1864. Before this, the family of friend and mentor George MacDonald read Dodgson's incomplete manuscript, and the enthusiasm of the MacDonald children encouraged Dodgson to seek publication. In 1863, he had taken the unfinished manuscript to Macmillan the publisher, who liked it immediately. After the possible alternative titles Alice Among the Fairies and Alice's Golden Hour were rejected, the work was finally published as Alice's Adventures in Wonderland in 1865 under the Lewis Carroll pen-name, which Dodgson had first used some nine years earlier. The illustrations this time were by Sir John Tenniel; Dodgson evidently thought that a published book would need the skills of a professional artist. The overwhelming commercial success of the first Alice book changed Dodgson's life in many ways. The fame of his alter ego "Lewis Carroll" soon spread around the world. He was inundated with fan mail and with sometimes unwanted attention. Indeed, according to one popular story, Queen Victoria herself enjoyed Alice In Wonderland so much that she suggested he dedicate his next book to her, and was accordingly presented with his next work, a scholarly mathematical volume entitled An Elementary Treatise on Determinants. Dodgson himself vehemently denied this story, commenting "...It is utterly false in every particular: nothing even resembling it has occurred"; and it is unlikely for other reasons: as T.B. Strong comments in a Times article, "It would have been clean contrary to all his practice to identify [the] author of Alice with the author of his mathematical works". He also began earning quite substantial sums of money but continued with his seemingly disliked post at Christ Church. Late in 1871, a sequel – Through the Looking-Glass and What Alice Found There – was published. (The title page of the first edition erroneously gives "1872" as the date of publication.) Its somewhat darker mood possibly reflects the changes in Dodgson's life. His father had recently died (1868), plunging him into a depression that lasted some years. The Hunting of the Snark In 1876, Dodgson produced his last great work, The Hunting of the Snark, a fantastical "nonsense" poem, exploring the adventures of a bizarre crew of tradesmen, and one beaver, who set off to find the eponymous creature. The painter Dante Gabriel Rossetti reputedly became convinced the poem was about him. Photography In 1856, Dodgson took up the new art form of photography, first under the influence of his uncle Skeffington Lutwidge, and later his Oxford friend Reginald Southey. He soon excelled at the art and became a well-known gentleman-photographer, and he seems even to have toyed with the idea of making a living out of it in his very early years. A recent study by Roger Taylor and Edward Wakeling exhaustively lists every surviving print, and Taylor calculates that just over fifty percent of his surviving work depicts young girls, though this may be a highly distorted figure as approximately 60% of his original photographic portfolio is now missing, so any firm conclusions are difficult. Dodgson also made many studies of men, women, male children and landscapes; his subjects also include skeletons, dolls, dogs, statues and paintings, and trees. His pictures of children were taken with a parent in attendance and many of the pictures were taken in the Liddell garden, because natural sunlight was required for good exposures. He also found photography to be a useful entrée into higher social circles. During the most productive part of his career, he made portraits of notable sitters such as John Everett Millais, Ellen Terry, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, Julia Margaret Cameron, Michael Faraday and Alfred, Lord Tennyson. Dodgson abruptly ceased photography in 1880. Over 24 years, he had completely mastered the medium, set up his own studio on the roof of Tom Quad, and created around 3, images. Fewer than 1, have survived time and deliberate destruction. He reported that he stopped taking photographs because keeping his studio working was difficult (he used the wet collodion process) and commercial photographers (who started using the dry plate process in the 1870s) took pictures more quickly. With the advent of Modernism, tastes changed, and his photography was forgotten from around 1920 until the 1960s. Inventions To promote letter writing, Dodgson invented The Wonderland Postage-Stamp Case in 1889. This was a cloth-backed folder with twelve slots, two marked for inserting the then most commonly used penny stamp, and one each for the other current denominations to one shilling. The folder was then put into a slip case decorated with a picture of Alice on the front and the Cheshire Cat on the back. All could be conveniently carried in a pocket or purse. When issued it also included a copy of Carroll's pamphletted lecture, Eight or Nine Wise Words About Letter-Writing. Reconstructed nyctograph, with scale demonstrated by a 5 euro cent. Another invention is a writing tablet called the nyctograph for use at night that allowed for note-taking in the dark; thus eliminating the trouble of getting out of bed and striking a light when one wakes with an idea. The device consisted of a gridded card with sixteen squares and system of symbols representing an alphabet of Dodgson's design, using letter shapes similar to the Graffiti writing system on a Palm device. Among the games he devised outside of logic there are a number of word games, including an early version of what today is known as Scrabble. He also appears to have invented, or at least certainly popularised, the Word Ladder (or "doublet" as it was known at first); a form of brain-teaser that is still popular today: the game of changing one word into another by altering one letter at a time, each successive change always resulting in a genuine word. For instance, CAT is transformed into DOG by the following steps: CAT, COT, DOT, DOG. Other items include a rule for finding the day of the week for any date; a means for justifying right margins on a typewriter; a steering device for a velociam (a type of tricycle); new systems of parliamentary representation; more nearly fair elimination rules for tennis tournaments; a new sort of postal money order; rules for reckoning postage; rules for a win in betting; rules for dividing a number by various divisors; a cardboard scale for the college common room he worked in later in life, which, held next to a glass, ensured the right amount of liqueur for the price paid; a double-sided adhesive strip for things like the fastening of envelopes or mounting things in books; a device for helping a bedridden invalid to read from a book placed sideways; and at least two ciphers for cryptography. Mathematical work Within the academic discipline of mathematics, Dodgson worked primarily in the fields of geometry, matrix algebra, mathematical logic and recreational mathematics, producing nearly a dozen books under his real name. Dodgson also developed new ideas in the study of elections (e.g., Dodgson's method) and committees; some of this work was not published until well after his death. He worked as a mathematics tutor at Oxford, an occupation that gave him some financial security. Later years Over the remaining twenty years of his life, throughout his growing wealth and fame, his existence remained little changed. He continued to teach at Christ Church until 1881, and remained in residence there until his death. His last novel, the two-volume Sylvie and Bruno, was published in 1889 and 1893 respectively. It achieved nowhere near the success of the Alice books. Its intricacy was apparently not appreciated by contemporary readers. The reviews and its sales, only 13, copies, were disappointing. The only occasion on which (as far as is known) he travelled abroad was a trip to Russia in 1867 as an ecclesiastical together with the Reverend Henry Liddon. He recounts the travel in his "Russian Journal", which was first commercially published in 1935. On his way to Russia and back Lewis Carroll also saw different cities in Belgium, Germany, the partitioned Poland, and France. He died on 14 January 1898 at his sisters' home, "The Chestnuts" in Guildford, of pneumonia following influenza. He was two weeks away from turning 66 years old. He is buried in Guildford at the Mount Cemetery. Controversies and mysteries "Carroll Myth” Since 1999 a group of scholars, notably Karoline Leach, Hugues Lebailly and Sherry L. Ackerman, John Tufail, Douglas Nickel and others, argue that what Leach terms the "Carroll Myth" has wildly distorted biographical perception of his life and his work. Leach's book, In the Shadow of the Dreamchild, raised a considerable amount of controversy. In brief the claim is that: * In general terms Dodgson's life has been simplified and 'infantilised' by a combination of inaccurate biography and the longstanding unavailability of key evidence, which allowed legends to proliferate unchecked. * By the time the evidence did become available the 'mythic' image of the man had become so embedded in scholastic and popular thinking it remained unquestioned, despite the fact the evidence failed to support it. * If the evidence is examined dispassionately it shows many of the most famous legends about the man (e.g. his 'paedophilia', and his exclusive adoration of small girls) are untrue, or at least grossly simplified. In more detail, Lebailly has endeavoured to set Dodgson's child-photography within the "Victorian Child Cult", which perceived child-nudity as essentially an expression of innocence. Lebailly claims that studies of child nudes were mainstream and fashionable in Dodgson's time and that most photographers, including Oscar Gustave Rejlander and Julia Margaret Cameron, made them as a matter of course. Lebailly continues that child nudes even appeared on Victorian Christmas cards, implying a very different social and aesthetic assessment of such material. Lebailly concludes that it has been an error of Dodgson's biographers to view his child-photography with 20th or 21st century eyes, and to have presented it as some form of personal idiosyncrasy, when it was in fact a response to a prevalent aesthetic and philosophical movement of the time. Leach's reappraisal of Dodgson focused in particular on his controversial sexuality. She argues that the allegations of paedophilia rose initially from a misunderstanding of Victorian morals, as well as the mistaken idea, fostered by Dodgson's various biographers, that he had no interest in adult women. She termed the traditional image of Dodgson "the Carroll Myth". She drew attention to the large amounts of evidence in his diaries and letters that he was also keenly interested in adult women, married and single, and enjoyed several scandalous (by the social standards of his time) relationships with them. She also pointed to the fact that many of those he described as "child-friends" were girls in their late teens and even twenties. She argues that suggestions of paedophilia evolved only many years after his death, when his well-meaning family had suppressed all evidence of his relationships with women in an effort to preserve his reputation, thus giving a false impression of a man interested only in little girls. Similarly, Leach traces the claim that many of Carroll's female friendships ended when the girls reached the age of 14 to a 1932 biography by Langford Reed. The concept of the Carroll Myth has produced polarised reactions from Carroll scholars. In 2004 Contrariwise, the Association for new Lewis Carroll studies. was established, and those such as Carolyn Sigler and Cristopher Hollingsworth have joined the ranks of those calling for a major reassessment. But the concept of the Myth has been opposed by some leading Carroll scholars, in particular Morton N. Cohen and Martin Gardner (their comments, and those of more positive reviewers, can be found on Karoline Leach's own page). Biographer Jenny Woolf, while agreeing that Carroll's image has been comprehensively misrepresented in the past, believes that this can be attributed partly to Carroll's own behaviour and in particular his tendency to self-caricature in later life. Ordination Dodgson had been groomed for the ordained ministry in the Anglican Church from a very early age and was expected, as a condition of his residency at Christ Church, to take holy orders within four years of obtaining his master's degree. He delayed the process for some time but eventually took deacon's orders on 22 December 1861. But when the time came a year later to progress to priestly orders, Dodgson appealed to the dean for permission not to proceed. This was against college rules and initially Dean Liddell told him he would have to consult the college ruling body, which would almost undoubtedly have resulted in his being expelled. For unknown reasons, Dean Liddell changed his mind overnight and permitted Dodgson to remain at the college in defiance of the rules. Uniquely amongst senior students of his time Dodgson never became a priest. There is currently no conclusive evidence about why Dodgson rejected the priesthood. Some have suggested his stammer made him reluctant to take the step, because he was afraid of having to preach. Wilson quotes letters by Dodgson describing difficulty in reading lessons and prayers rather than preaching in his own words. But Dodgson did indeed preach in later life, even though not in priest's orders, so it seems unlikely his impediment was a major factor affecting his choice. Wilson also points out that the then Bishop of Oxford, Samuel Wilberforce, who ordained Dodgson, had strong views against clergy going to the theatre, one of Dodgson's great interests. Others have suggested that he was having serious doubts about Anglicanism. He was interested in minority forms of Christianity (he was an admirer of F.D. Maurice) and "alternative" religions (theosophy). Dodgson became deeply troubled by an unexplained sense of sin and guilt at this time (the early 1860s) and frequently expressed the view in his diaries that he was a "vile and worthless" sinner, unworthy of the priesthood, and this sense of sin and unworthiness may well have affected his decision to abandon being ordained to the priesthood. Missing diaries At least four complete volumes and around seven pages of text are missing from Dodgson's 13 diaries. The loss of the volumes remains unexplained; the pages have been deliberately removed by an unknown hand. Most scholars assume the diary material was removed by family members in the interests of preserving the family name, but this has not been proven. Except for one page, the period of his diaries from which material is missing is between 1853 and 1863 (when Dodgson was 21–31 years old). This was a period when Dodgson began suffering great mental and spiritual anguish and confessing to an overwhelming sense of his own sin. This was also the period of time when he composed his extensive love poetry, leading to speculation that the poems may have been autobiographical. Many theories have been put forward to explain the missing material. A popular explanation for one particular missing page (27 June 1863) is that it might have been torn out to conceal a proposal of marriage on that day by Dodgson to the 11-year-old Alice Liddell; there has never been any evidence to suggest this was so, and a paper discovered by Karoline Leach in the Dodgson family archive in 1996 offers some evidence to the contrary. This paper, known as the "cut pages in diary document", was compiled by various members of Carroll's family after his death. Part of it may have been written at the time the pages were destroyed, though this is unclear. The document offers a brief summary of two diary pages that are now missing, including the one for 27 June 1863. The summary for this page states that Mrs. Liddell told Dodgson there was gossip circulating about him and the Liddell family's governess, as well as about his relationship with "Ina", presumably Alice's older sister, Lorina Liddell. The "break" with the Liddell family that occurred soon after was presumably in response to this gossip. An alternative interpretation has been made regarding Carroll's rumoured involvement with "Ina": Lorina was also the name of Alice Liddell's mother. What is deemed most crucial and surprising is that the document seems to imply Dodgson's break with the family was not connected with Alice at all. Until a primary source is discovered, the events of 27 June 1863 remain inconclusive. Migraine and epilepsy In his diary for 1880, Dodgson recorded experiencing his first episode of migraine with aura, describing very accurately the process of 'moving fortifications' that are a manifestation of the aura stage of the syndrome. Unfortunately there is no clear evidence to show whether this was his first experience of migraine per se, or if he may have previously suffered the far more common form of migraine without aura, although the latter seems most likely, given the fact that migraine most commonly develops in the teens or early adulthood. Another form of migraine aura, Alice in Wonderland Syndrome, has been named after Dodgson's little heroine, because its manifestation can resemble the sudden size-changes in the book. Also known as micropsia and macropsia, it is a brain condition affecting the way objects are perceived by the mind. For example, an afflicted person may look at a larger object, like a basketball, and perceive it as if it were the size of a golf ball. Some authors have suggested that Dodgson may have suffered from this type of aura, and used it as an inspiration in his work, but there is no evidence that he did. Dodgson also suffered two attacks in which he lost consciousness. He was diagnosed by three different doctors; a Dr. Morshead, Dr. Brooks, and Dr. Stedman, believed the attack and a consequent attack to be an "epileptiform" seizure (initially thought to be fainting, but Brooks changed his mind). Some have concluded from this he was a lifetime sufferer of this condition, but there is no evidence of this in his diaries beyond the diagnosis of the two attacks already mentioned. Some authors, in particular Sadi Ranson, have suggested Carroll may have suffered from temporal lobe epilepsy in which consciousness is not always completely lost, but altered, and in which the symptoms mimic many of the same experiences as Alice in Wonderland. Carroll had at least one incidence in which he suffered full loss of consciousness and awoke with a bloody nose, which he recorded in his diary and noted that the episode left him not feeling himself for "quite sometime afterward". This attack was diagnosed as possibly "epileptiform" and Carroll himself later wrote of his "seizures" in the same diary. Most of the standard diagnostic tests of today were not available in the nineteenth century. Recently, Dr Yvonne Hart, consultant neurologist at the Radcliffe Hospital, Oxford, considered Dodgson's symptoms. Her conclusion, quoted in Jenny Woolf's The Mystery of Lewis Carroll, is that Dodgson very likely had migraine, and may have had epilepsy, but she emphasises that she would have considerable doubt about making a diagnosis of epilepsy without further information. Suggestions of paedophilia Stuart Dodgson Collingwood (Dodgson's nephew and biographer) wrote: And now as to the secondary causes which attracted him to children. First, I think children appealed to him because he was pre-eminently a teacher, and he saw in their unspoiled minds the best material for him to work upon. In later years one of his favourite recreations was to lecture at schools on logic; he used to give personal attention to each of his pupils, and one can well imagine with what eager anticipation the children would have looked forward to the visits of a schoolmaster who knew how to make even the dullest subjects interesting and amusing. Despite comments like this, Dodgson's friendships with young girls and psychological readings of his work – especially his photographs of nude or semi-nude girls – have all led to speculation that he was a paedophile. This possibility has underpinned numerous modern interpretations of his life and work, particularly Dennis Potter's play Alice and his screenplay for the motion picture, Dreamchild, Robert Wilson's Alice, and a number of recent biographies, including Michael Bakewell's Lewis Carroll: A Biography (1996), Donald Thomas's Lewis Carroll: A Portrait with Background (1995), and Morton N. Cohen's Lewis Carroll: A Biography (1995). All of these works more or less unequivocally assume that Dodgson was a paedophile, albeit a repressed and celibate one. Cohen claims Dodgson's "sexual energies sought unconventional outlets", and further writes: We cannot know to what extent sexual urges lay behind Charles's preference for drawing and photographing children in the nude. He contended the preference was entirely aesthetic. But given his emotional attachment to children as well as his aesthetic appreciation of their forms, his assertion that his interest was strictly artistic is naïve. He probably felt more than he dared acknowledge, even to himself. Cohen notes that Dodgson "apparently convinced many of his friends that his attachment to the nude female child form was free of any eroticism", but adds that "later generations look beneath the surface" (p. 229). Cohen and other biographers argue that Dodgson may have wanted to marry the 11-year-old Alice Liddell, and that this was the cause of the unexplained "break" with the family in June 1863. There has never been significant evidence to support the idea, however, and the 1996 discovery of the "cut pages in diary document" (see above) seems to make it highly probable that the 1863 "break" had nothing to do with Alice, but was perhaps connected with rumours involving her older sister Lorina (born 11 May 1849, so she would have been 14 at the time), her governess, or her mother who was also nicknamed "Ina". Some writers, e.g., Derek Hudson and Roger Lancelyn Green, stop short of identifying Dodgson as a paedophile, but concur that he had a passion for small female children and next to no interest in the adult world. The basis for Dodgson's interest in female children has been challenged in the last ten years by several writers and scholars (see the 'Carroll Myth' above). Literary works * La Guida di Bragia, a Ballad Opera for the Marionette Theatre (around 1850) * A Tangled Tale * Alice's Adventures in Wonderland (1865) * Facts * Rhyme? And Reason? (also published as Phantasmagoria) * Pillow Problems * Sylvie and Bruno * Sylvie and Bruno Concluded * The Hunting of the Snark (1876) * Three Sunsets and Other Poems * Through the Looking-Glass, and What Alice Found There (includes "Jabberwocky" and "The Walrus and the Carpenter") (1871) * What the Tortoise Said to Achilles Mathematical works * A Syllabus of Plane Algebraic Geometry (1860) * The Fifth Book of Euclid Treated Algebraically (1858 and 1868) * An Elementary Treatise on Determinants, With Their Application to Simultaneous Linear Equations and Algebraic Equations * Euclid and his Modern Rivals (1879), both literary and mathematical in style * Symbolic Logic Part I * Symbolic Logic Part II (published posthumously) * The Alphabet Cipher (1868) * The Game of Logic * Some Popular Fallacies about Vivisection * Curiosa Mathematica I (1888) * Curiosa Mathematica II (1892) * The Theory of Committees and Elections, collected, edited, analysed, and published in 1958, by Duncan Black References Wikipedia - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lewis_Carroll


Thomas Hood (23 May 1799 – 3 May 1845) was an English poet, author and humourist, best known for poems such as “The Bridge of Sighs” and “The Song of the Shirt”. Hood wrote regularly for The London Magazine, the Athenaeum, and Punch. He later published a magazine largely consisting of his own works. Hood, never robust, lapsed into invalidism by the age of 41 and died at the age of 45. William Michael Rossetti in 1903 called him “the finest English poet” between the generations of Shelley and Tennyson. Hood was the father of playwright and humourist Tom Hood (1835–1874).


Matthew Prior (21 July 1664– 18 September 1721) was an English poet and diplomat. He is also known as a contributor to The Examiner. Early life Prior was probably born in Middlesex. He was the son of a Nonconformist joiner at Wimborne Minster, East Dorset. His father moved to London, and sent him to Westminster School, under Dr. Busby. On his father’s death, he left school, and was cared for by his uncle, a vintner in Channel Row. Here Lord Dorset found him reading Horace, and set him to translate an ode. He did so well that the Earl offered to contribute to the continuation of his education at Westminster. One of his schoolfellows and friends was Charles Montagu, 1st Earl of Halifax. It was to avoid being separated from Montagu and his brother James that Prior accepted, against his patron’s wish, a scholarship recently founded at St John’s College, Cambridge. He took his B.A. degree in 1686, and two years later became a fellow. In collaboration with Montagu he wrote in 1687 the City Mouse and Country Mouse, in ridicule of John Dryden’s The Hind and the Panther. Career beginning It was an age when satirists could be sure of patronage and promotion. Montagu was promoted at once, and Prior, three years later, became secretary to the embassy at the Hague. After four years of this, he was appointed a gentleman of the King’s bedchamber. Apparently he acted as one of the King’s secretaries, and in 1697 he was secretary to the plenipotentiaries who concluded the Peace of Ryswick. Prior’s talent for affairs was doubted by Pope, who had no special means of judging, but it is not likely that King William would have employed in this important business a man who had not given proof of diplomatic skill and grasp of details. The poet’s knowledge of French is specially mentioned among his qualifications, and this was recognized by his being sent in the following year to Paris in attendance on the English ambassador. At this period Prior could say with good reason that “he had commonly business enough upon his hands, and was only a poet by accident.” To verse, however, which had laid the foundation of his fortunes, he still occasionally trusted as a means of maintaining his position. His occasional poems during this period include an elegy on Queen Mary in 1695; a satirical version of Boileau’s Ode sur le prise de Namur (1695); some lines on William’s escape from assassination in 1696; and a brief piece called The Secretary. After his return from France Prior became under-secretary of state and succeeded John Locke as a commissioner of trade. In 1701 he sat in Parliament for East Grinstead. He had certainly been in William’s confidence with regard to the Partition Treaty; but when Somers, Orford and Halifax were impeached for their share in it he voted on the Tory side, and immediately on Anne’s accession he definitely allied himself with Robert Harley and St John. Perhaps in consequence of this for nine years there is no mention of his name in connection with any public transaction. But when the Tories came into power in 1710 Prior’s diplomatic abilities were again called into action, and until the death of Anne he held a prominent place in all negotiations with the French court, sometimes as secret agent, sometimes in an equivocal position as ambassador’s companion, sometimes as fully accredited but very unpunctually paid ambassador. His share in negotiating the Treaty of Utrecht, of which he is said to have disapproved personally, led to its popular nickname of “Matt’s Peace.” Prior is also known as a contributor to The Examiner newspaper. Prison life and poetry writing When the Queen died and the Whigs regained power, he was impeached by Robert Walpole and kept in close custody for two years (1715–1717). In 1709, he had already published a collection of verse. During this imprisonment, maintaining his cheerful philosophy, he wrote his longest humorous poem, Alma; or, The Progress of the Mind. This, along with his most ambitious work, Solomon, and other Poems on several Occasions, was published by subscription in 1718. The sum received for this volume (4000 guineas), with a present of £4000 from Lord Harley, enabled him to live in comfort; but he did not long survive his enforced retirement from public life, although he bore his ups and downs with rare equanimity. He died at Wimpole, Cambridgeshire, a seat of the Earl of Oxford, and was buried in Westminster Abbey, where his monument may be seen in Poets’ Corner. A History of his Own Time was issued by J Bancks in 1740. The book pretended to be derived from Prior’s papers, but it is doubtful how far it should be regarded as authentic. Prior’s poems show considerable variety, a pleasant scholarship and great executive skill. The most ambitious, i.e. Solomon, and the paraphrase of The Nut-Brown Maid, are the least successful. But Alma, an admitted imitation of Samuel Butler, is a delightful piece of wayward easy humour, full of witty turns and well-remembered allusions, and Prior’s mastery of the octo-syllabic couplet is greater than that of Jonathan Swift or Pope. His tales in rhyme, though often objectionable in their themes, are excellent specimens of narrative skill; and as an epigrammatist he is unrivalled in English. The majority of his love songs are frigid and academic, mere wax-flowers of Parnassus; but in familiar or playful efforts, of which the type are the admirable lines To a Child of Quality, he has still no rival. “Prior’s”—says Thackeray, himself no mean proficient in this kind—"seem to me amongst the easiest, the richest, the most charmingly humorous of English lyrical poems. Horace is always in his mind, and his song and his philosophy, his good sense, his happy easy turns and melody, his loves and his Epicureanism, bear a great resemblance to that most delightful and accomplished master.” Wittenham Clumps in Oxfordshire is said to be where Prior wrote Henry and Emma, and this is now commemorated by a plaque. Prior has been commemorated by other poets as well; Everett James Ellis named Prior as a significant influence and source of inspiration. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matthew_Prior


Philip Edward Thomas (3 March 1878– 9 April 1917) was a British poet, essayist, and novelist. He is commonly considered a war poet, although few of his poems deal directly with his war experiences, and his career in poetry only came after he had already been a successful writer and literary critic. In 1915, he enlisted in the British Army to fight in the First World War and was killed in action during the Battle of Arras in 1917, soon after he arrived in France. Life and career Early life Thomas was born in Lambeth, London. He was educated at Battersea Grammar School, St Paul’s School in London and Lincoln College, Oxford. His family were mostly Welsh. In June 1899 he married Helen Berenice Noble (1878-1967), in Fulham, while still an undergraduate, and determined to live his life by the pen. He then worked as a book reviewer, reviewing up to 15 books every week. He was already a seasoned writer by the outbreak of war, having published widely as a literary critic and biographer as well writing on the countryside. He also wrote a novel, The Happy-Go-Lucky Morgans (1913), a “book of delightful disorder”. Thomas worked as literary critic for the Daily Chronicle in London and became a close friend of Welsh tramp poet W. H. Davies, whose career he almost single-handedly developed. From 1905, Thomas lived with his wife Helen and their family at Elses Farm near Sevenoaks, Kent. He rented to Davies a tiny cottage nearby, and nurtured his writing as best he could. On one occasion, Thomas even had to arrange for the manufacture, by a local wheelwright, of a makeshift wooden leg for Davies. Even though Thomas thought that poetry was the highest form of literature and regularly reviewed it, he only became a poet himself at the end of 1914 when living at Steep, East Hampshire, and initially published his poetry under the name Edward Eastaway. Frost in particular encouraged Thomas (then more famous as a critic) to write poetry, and their friendship was so close that the two planned to reside side by side in the United States. By August 1914, the village of Dymock in Gloucestershire had become the residence of a number of literary figures, including Lascelles Abercrombie, Wilfrid Gibson and American poet Robert Frost. Edward Thomas was a visitor at this time. Thomas immortalised the (now-abandoned) railway station at Adlestrop in a poem of that name after his train made a stop at the Cotswolds station on 24 June 1914, shortly before the outbreak of the First World War. War service Thomas enlisted in the Artists Rifles in July 1915, despite being a mature married man who could have avoided enlisting. He was unintentionally influenced in this decision by his friend Frost, who had returned to the U.S. but sent Thomas an advance copy of “The Road Not Taken”. The poem was intended by Frost as a gentle mocking of indecision, particularly the indecision that Thomas had shown on their many walks together; however, most audiences took the poem more seriously than Frost intended, and Thomas similarly took it seriously and personally, and it provided the last straw in Thomas’ decision to enlist. Thomas was promoted corporal, and in November 1916 was commissioned into the Royal Garrison Artillery as a second lieutenant. He was killed in action soon after he arrived in France at Arras on Easter Monday, 9 April 1917. To spare the feelings of his widow Helen, she was told the fiction of a “bloodless death” i.e. that Thomas was killed by the concussive blast wave of one of the last shells fired as he stood to light his pipe and that there was no mark on his body. However, a letter from his commanding officer Franklin Lushington written in 1936 (and discovered many years later in an American archive) states that in reality the cause of Thomas’ death was due to being “shot clean through the chest”. W. H. Davies was devastated by the death and his commemorative poem “Killed In Action (Edward Thomas)” was included in Davies’s 1918 collection “Raptures”. Thomas is buried in the Commonwealth War Graves Cemetery at Agny in France (Row C, Grave 43). Personal life Thomas was survived by his wife, Helen, their son Merfyn and their two daughters Bronwen and Myfanwy. After the war, Thomas’s widow, Helen, wrote about her courtship and early married life with Edward in the autobiography As it Was (1926); later she added a second volume, World Without End (1931). Myfanwy later said that the books had been written by her mother as a form of therapy to help lift herself from the deep depression into which she had fallen following Thomas’s death. Helen’s short memoir My Memory of W. H. Davies was published in 1973, after her own death. In 1988, Helen’s writings were gathered into a book published under the title Under Storm’s Wing, which included As It Was and World Without End as well as a selection of other short works by Helen and her daughter Myfanwy and six letters sent by Robert Frost to her husband. Commemorations Thomas is commemorated in Poets’ Corner, Westminster Abbey, London, by memorial windows in the churches at Steep and at Eastbury in Berkshire and with a blue plaque at 14 Lansdowne Gardens in Stockwell, south London, where he was born. There is also a plaque dedicated to him at 113 Cowley Road, Oxford, where he lodged before entering Lincoln College. East Hampshire District Council have created a “literary walk” at Shoulder of Mutton Hill in Steep dedicated to Thomas, which includes a memorial stone erected in 1935. The inscription includes the final line from one of his essays: “And I rose up and knew I was tired and I continued my journey.” As “Philip Edward Thomas poet-soldier” he is commemorated, alongside "Reginald Townsend Thomas actor-soldier died 1918", who is buried at the spot, and other family members, at the North East Surrey (Old Battersea) Cemetery. He is the subject of the biographical play The Dark Earth and the Light Sky by Nick Dear, which premiered at the Almeida Theatre, London in November 2012, with Pip Carter as Thomas and Hattie Morahan as his wife Helen. In February 2013 his poem “Words” was chosen as the poem of the week by Carol Rumens in The Guardian Poetry Thomas’s poems are noted for their attention to the English countryside and a certain colloquial style. The short poem In Memoriam exemplifies how his poetry blends the themes of war and the countryside. On 11 November 1985, Thomas was among 16 Great War poets commemorated on a slate stone unveiled in Westminster Abbey’s Poet’s Corner. The inscription, written by fellow poet Wilfred Owen, reads: “My subject is War, and the pity of War. The Poetry is in the pity.” Thomas was described by British Poet Laureate Ted Hughes as “the father of us all.” At least nineteen of his poems were set to music by the Gloucester composer Ivor Gurney. Selected works Poetry collections * Six Poems (under pseudonym Edward Eastaway) Pear Tree Press, 1916. * Poems, Holt, 1917, which included “The Sign-Post” * Last Poems, Selwyn & Blount, 1918. * Collected Poems, Selwyn & Blount, 1920. * Two Poems, Ingpen & Grant, 1927. * The Poems of Edward Thomas, ed. R. George Thomas, Oxford University Press, 1978. * Edward Thomas: A Mirror of England, ed. Elaine Wilson, Paul & Co., 1985. * Edward Thomas: Selected Poems, ed. Ian Hamilton, Bloomsbury, 1995. * The Poems of Edward Thomas, ed. Peter Sacks, Handsel Books, 2003. * The Annotated Collected Poems, ed. Edna Longley, Bloodaxe Books, 2008. Prose fiction * The Happy-Go-Lucky Morgans (novel), Duckworth, 1913. Prose * In Pursuit of Spring (travel) Thomas Nelson and Sons, April 1914 Essays and collections * Horae Solitariae, Dutton, 1902. * Oxford, A & C Black, 1903. * Beautiful Wales, Black, 1905. * The Heart of England, Dutton, 1906. * The South Country, Dutton, 1906 (reissued by Tuttle, 1993). * Rest and Unrest, Dutton, 1910. * Light and Twilight, Duckworth, 1911. * The Icknield Way, Constable, 1913. * The Last Sheaf, Jonathan Cape, 1928. References to Thomas by other writers * In 1918 W. H. Davies published his poem Killed In Action (Edward Thomas) to mark the personal loss of his close friend and mentor. * Many poems about Thomas by other poets can be found in the books Elected Friends: Poems For and About Edward Thomas, (1997, Enitharmon Press) edited by Anne Harvey, and Branch-Lines: Edward Thomas and Contemporary Poetry, (2007, Enitharmon Press) edited by Guy Cuthbertson and Lucy Newlyn. * Norman Douglas considered Thomas handicapped in life through lacking “a little touch of bestiality, a little je-m’en-fous-t-ism. He was too scrupulous”. * In his 1980 autobiography, Ways of Escape, Graham Greene references Thomas’s poem “The Other” (about a man who seems to be following his own double from hotel to hotel) in describing his own experience of being bedeviled by an imposter. * Edward Thomas’s Collected Poems was one of Andrew Motion’s ten picks for the poetry section of the “Guardian Essential Library” in October 2002. * In his 2002 novel Youth, J.M. Coetzee has his main character, intrigued by the survival of pre-modernist forms in British poetry, ask himself: “What happened to the ambitions of poets here in Britain? Have they not digested the news that Edward Thomas and his world are gone for ever?” In contrast, Irish critic Edna Longley writes that Thomas’s Lob, a 150-line poem, “strangely preempts The Waste Land through verses like: ”This is tall Tom that bore / The logs in, and with Shakespeare in the hall / Once talked". * In his 1995 novel, Borrowed Time, the author Robert Goddard bases the home of the main character at Greenhayes in the village of Steep, where Thomas lived from 1913. Goddard weaves some of the feeling from Thomas’s poems into the mood of the story and also uses some quotes from Thomas’s works. * Will Self’s 2006 novel, The Book of Dave, has a quote from The South Country as the book’s epigraph: “I like to think how easily Nature will absorb London as she absorbed the mastodon, setting her spiders to spin the winding sheet and her worms to fill in the graves, and her grass to cover it pitifully up, adding flowers—as an unknown hand added them to the grave of Nero.” * The children’s author Linda Newbery has published a novel, “Lob” (David Fickling Books, 2010, illustrated by Pam Smy) inspired by the Edward Thomas’ poem of the same name and containing oblique references to other work by him. * Woolly Wolstenholme, formerly of UK rock band Barclay James Harvest, has used a humorous variation of Thomas’ poem Adlestrop on the first song of his 2004 live album, Fiddling Meanly, where he imagines himself in a retirement home and remembers “the name” of the location where the album was recorded. The poem was read at Wolstenholme’s funeral on 19 January 2011. * Stuart Maconie in his book Adventures On The High Teas mentions Thomas and his poem “Adlestrop”. Maconie visits the now abandoned and overgrown station which was closed by Beeching in 1966. * Robert MacFarlane, in his 2012 book The Old Ways, critiques Thomas and his poetry in the context of his own explorations of paths and walking as an analogue of human consciousness. * In his 2012 novel Sweet Tooth, Ian McEwan has a character invoke Thomas’s poem “Adlestrop,” as a “sweet, old-fashioned thing” and an example of “the sense of pure existence, of being suspended in space and time, a time before a cataclysmic war.” * The last years of Thomas’s life are explored in A Conscious Englishman, a 2013 biographical novel by Margaret Keeping, published by StreetBooks. * Pat Barker’s 1995 WW1 novel, The Ghost Road, Booker Prize winner and the third novel of her Regeneration Trilogy, has as its opening epigraph 4 lines from 'Roads’. * 'Now all roads lead to France/ And heavy is the tread/ Of the living; but the dead/ Returning lightly dance:’ References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Thomas_(poet)

Mary Robinson (27 November 1757 – 26 December 1800) was an English actress, poet, dramatist, novelist, and celebrity figure born in Bristol. During her lifetime she was known as "the English Sappho". She earned her nickname "Perdita" for her role as Perdita (heroine of Shakespeare's The Winter's Tale) in 1779. She was the first public mistress of King George IV while he was still Prince of Wales.


Charlotte Turner Smith (4 May 1749– 28 October 1806) was an English Romantic poet and novelist. She initiated a revival of the English sonnet, helped establish the conventions of Gothic fiction, and wrote political novels of sensibility. Smith was born into a wealthy family and received a typical education for a woman during the late 18th century. However, her father’s reckless spending forced her to marry early. In a marriage that she later described as prostitution, she was given by her father to the violent and profligate Benjamin Smith. Their marriage was deeply unhappy, although they had twelve children together. Charlotte joined Benjamin in debtor’s prison, where she wrote her first book of poetry, Elegiac Sonnets. Its success allowed her to help pay for Benjamin’s release. Benjamin’s father attempted to leave money to Charlotte and her children upon his death, but legal technicalities prevented her from ever acquiring it. Charlotte Smith eventually left Benjamin and began writing to support their children. Smith’s struggle to provide for her children and her frustrated attempts to gain legal protection as a woman provided themes for her poetry and novels; she included portraits of herself and her family in her novels as well as details about her life in her prefaces. Her early novels are exercises in aesthetic development, particularly of the Gothic and sentimentality. “The theme of her many sentimental and didactic novels was that of a badly married wife helped by a thoughtful sensible lover” (Smith’s entry in British Authors Before 1800: A Biographical Dictionary Ed. Stanley Kunitz and Howard Haycraft. New York: H.W. Wilson, 1952. pg. 478.) Her later novels, including The Old Manor House, often considered her best, support the ideals of the French Revolution. Smith was a successful writer, publishing ten novels, three books of poetry, four children’s books, and other assorted works, over the course of her career. She always saw herself as a poet first and foremost, however, as poetry was considered the most exalted form of literature at the time. Scholars credit Smith with transforming the sonnet into an expression of woeful sentiment that would pave the way for poets such as Coleridge, Wordsworth, Shelly and Keats. Smith’s poetry and prose was praised by contemporaries such as Romantic poets William Wordsworth and Samuel Taylor Coleridge as well as novelist Walter Scott. Coleridge, in 1796, even remarked that “those sonnets appear to me the most exquisite, in which moral Sentiments, Affections, or Feelings, are deduced from, and associated with the scenery of Nature”. After 1798, Smith’s popularity waned and by 1803 she was destitute and ill—she could barely hold a pen. She had to sell her books to pay off her debts. In 1806, Smith died. Largely forgotten by the middle of the 19th century, her works have now been republished and she is recognized as an important Romantic writer. Early life Smith was born on 4 May 1749 in London and baptized on 12 June; she was the oldest child of well-to-do Nicholas Turner and Anna Towers. Her two younger siblings, Nicholas and Catherine Ann, were born within the next five years. Smith’s childhood was shaped by her mother’s early death (probably in giving birth to Catherine) and her father’s reckless spending. After losing his wife, Nicholas Turner travelled and the children were raised by Lucy Towers, their maternal aunt (when exactly their father returned is unknown). At the age of six, Charlotte went to school in Chichester and took drawing lessons from the painter George Smith. Two years later, she, her aunt, and her sister moved to London and she attended a girls school in Kensington where she learned dancing, drawing, music, and acting. She loved to read and wrote poems, which her father encouraged. She even submitted a few to the Lady’s Magazine for publication, but they were not accepted. Marriage and first publication Smith’s father encountered financial difficulties upon his return to England and he was forced to sell some of the family’s holdings and to marry the wealthy Henrietta Meriton in 1765. Smith entered society at the age of twelve, leaving school and being tutored at home. On 23 February 1765, at the age of fifteen, she married Benjamin Smith, the son of Richard Smith, a wealthy West Indian merchant and a director of the East India Company. The proposal was accepted for her by her father; forty years later, Smith condemned her father’s action, which she wrote had turned her into a “legal prostitute”. Smith’s marriage was unhappy. She detested living in commercial Cheapside (the family later moved to Southgate and Tottenham) and argued with her in-laws, who she believed were unrefined and uneducated. They, in turn, mocked her for spending time reading, writing, and drawing. Even worse, Benjamin proved to be violent, unfaithful, and profligate. Only her father-in-law, Richard, appreciated her writing abilities, although he wanted her to use them to further his business interests. Richard Smith owned plantations in Barbados and he and his second wife brought five slaves to England, who, along with their descendants, were included as part of the family property in his will. Although Charlotte Smith later argued against slavery in works such as The Old Manor House (1793) and “Beachy Head”, she herself benefited from the income and slave labor of Richard Smith’s plantations. In 1766, Charlotte and Benjamin had their first child, who died the next year just days after the birth of their second, Benjamin Berney (1767–77). Between 1767 and 1785, the couple had ten more children: William Towers (born 1768), Charlotte Mary (born c. 1769), Braithwaite (born 1770), Nicholas Hankey (1771–1837), Married Anni Petroose (1779–1843), Charles Dyer (born 1773), Anna Augusta (1774–94), Lucy Eleanor (born 1776), Lionel (1778–1842), Harriet (born c. 1782), and George (born c. 1785). Only six of Smith’s children survived her. Smith assisted in the family business that her husband had abandoned by helping Richard Smith with his correspondence. She persuaded Richard to set Benjamin up as a gentleman farmer in Hampshire and lived with him at Lys Farm from 1774 until 1783. Worried about Charlotte’s future and that of his grandchildren and concerned that his son would continue his irresponsible ways, Richard Smith willed the majority of his property to Charlotte’s children. However, because he had drawn up the will himself, the documents contained legal problems. The inheritance, originally worth nearly £36,000, was tied up in chancery after his death in 1776 for almost forty years. Smith and her children saw little of it. (It has been proposed that this real case may have inspired the famous fictional case of Jarndyce and Jarndyce, in Dickens’s Bleak House.) In fact, Benjamin illegally spent at least a third of the legacy and ended up in King’s Bench Prison in December 1783. Smith moved in with him and it was in this environment that she wrote and published her first work, Elegiac Sonnets (1784). Elegiac Sonnets achieved instant success, allowing Charlotte to pay for their release from prison. Smith’s sonnets helped initiate a revival of the form and granted an aura of respectability to her later novels (poetry was considered the highest art form at the time). Smith revised Elegiac Poems several times over the years, eventually creating a two-volume work. Novelist After Benjamin Smith was released from prison, the entire family moved to Dieppe, France to avoid further creditors. Charlotte returned to negotiate with them, but failed to come to an agreement. She went back to France and in 1784 began translating works from French into English. In 1787 she published The Romance of Real Life, consisting of translated selections from François Gayot de Pitaval’s trials. She was forced to withdraw her other translation, Manon Lescaut, after it was argued that the work was immoral and plagiarized. In 1786, she published it anonymously. In 1785, the family returned to England and moved to Woolbeding House near Midhurst, Sussex. Smith’s relationship with her husband did not improve and on 15 April 1787, after twenty-two years of marriage, she left him. She wrote that she might “have been contented to reside in the same house with him”, had not “his temper been so capricious and often so cruel” that her “life was not safe”. When Charlotte left Benjamin, she did not secure a legal agreement that would protect her profits—he would have access to them under English primogeniture laws. Smith knew that her children’s future rested on a successful settlement of the lawsuit over her father-in-law’s will, therefore she made every effort to earn enough money to fund the suit and retain the family’s genteel status. Smith claimed the position of gentlewoman, signing herself “Charlotte Smith of Bignor Park” on the title page of Elegiac Sonnets. All of her works were published under her own name, “a daring decision” for a woman at the time. Her success as a poet allowed her to make this choice. Throughout her career, Smith identified herself as a poet. Although she published far more prose than poetry and her novels brought her more money and fame, she believed poetry would bring her respectability. As Sarah Zimmerman claimed in the Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, “She prized her verse for the role it gave her as a private woman whose sorrows were submitted only reluctantly to the public.” After separating from her husband, Smith moved to a town near Chichester and decided to write novels, as they would make her more money than poetry. Her first novel, Emmeline (1788), was a success, selling 1500 copies within months. She wrote nine more novels in the next ten years: Ethelinde (1789), Celestina (1791), Desmond (1792), The Old Manor House (1793), The Wanderings of Warwick (1794), The Banished Man (1794), Montalbert (1795), Marchmont (1796), and The Young Philosopher (1798). Smith began her career as a novelist during the 1780s at a time when women’s fiction was expected to focus on romance and to foreground “a chaste and flawless heroine subjected to repeated melodramatic distresses until reinstated in society by the virtuous hero”. Although Smith’s novels employed this structure, they also incorporated political commentary, particularly support of the French Revolution, through the voices of male characters. At times, she challenged the typical romance plot by including “narratives of female desire” or “tales of females suffering despotism”. Smith’s novels contributed to the development of Gothic fiction and the novel of sensibility. Smith’s novels are autobiographical. While a common device at the time, Antje Blank writes in The Literary Encyclopedia, “few exploited fiction’s potential of self-representation with such determination as Smith”. For example, Mr. and Mrs. Stafford in Emmeline are portraits of Charlotte and Benjamin. The prefaces to Smith’s novels told the story of her own struggles, including the deaths of several of her children. According to Zimmerman, "Smith mourned most publicly for her daughter Anna Augusta, who married an émigré... and died aged twenty in 1795." Smith’s prefaces positioned her as both a suffering sentimental heroine as well as a vocal critic of the laws that kept her and her children in poverty. Smith’s experiences prompted her to argue for legal reforms that would grant women more rights, making the case for these reforms through her novels. Smith’s stories showed the “legal, economic, and sexual exploitation” of women by marriage and property laws. Initially readers were swayed by her arguments and writers such as William Cowper patronized her. However, as the years passed, readers became exhausted by Smith’s stories of struggle and inequality. Public opinion shifted towards the view of poet Anna Seward, who argued that Smith was “vain” and “indelicate” for exposing her husband to “public contempt”. Smith moved frequently due to financial concerns and declining health. During the last twenty years of her life, she lived in: Chichester, Brighton, Storrington, Bath, Exmouth, Weymouth, Oxford, London, Frant, and Elstead. She eventually settled at Tilford, Surrey. Smith became involved with English radicals while she was living in Brighton from 1791 to 1793. Like them, she supported the French Revolution and its republican principles. Her epistolary novel Desmond tells the story of a man who journeys to revolutionary France and is convinced of the rightness of the revolution and contends that England should be reformed as well. The novel was published in June 1792, a year before France and England went to war and before the Reign of Terror began, which shocked the British public, turning them against the revolutionaries. Like many radicals, Smith criticized the French, but she still endorsed the original ideals of the revolution. In order to support her family, Smith had to sell her works, thus she was eventually forced to, as Blank claims, “tone down the radicalism that had characterised the authorial voice in Desmond and adopt more oblique techniques to express her libertarian ideals”. She therefore set her next novel, The Old Manor House (1793), during the American Revolutionary War, which allowed her to discuss democratic reform without directly addressing the French situation. However, in her last novel, The Young Philosopher (1798), Smith wrote a final piece of “outspoken radical fiction”. Smith’s protagonist leaves Britain for America, as there is no hope for a reform in Britain. The Old Manor House is "frequently deemed [Smith’s] best" novel for its sentimental themes and development of minor characters. Novelist Walter Scott labeled it as such and poet and critic Anna Laetitia Barbauld chose it for her anthology of The British Novelists (1810). As a successful novelist and poet, Smith communicated with famous artists and thinkers of the day, including musician Charles Burney (father of Frances Burney), poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge, scientist and poet Erasmus Darwin, lawyer and radical Thomas Erskine, novelist Mary Hays, playwright Richard Brinsley Sheridan, and poet Robert Southey. A wide array of periodicals reviewed her works, including the Anti-Jacobin Review, the Analytical Review, the British Critic, The Critical Review, the European Magazine, the Gentleman’s Magazine, the Monthly Magazine, and the Universal Magazine. Smith earned the most money between 1787 and 1798, after which she was no longer as popular; several reasons have been suggested for the public’s declining interest in Smith, including “a corresponding erosion of the quality of her work after so many years of literary labour, an eventual waning of readerly interest as she published, on average, one work per year for twenty-two years, and a controversy that attached to her public profile” as she wrote about the French revolution. Both radical and conservative periodicals criticized her novels about the revolution. Her insistence on pursuing the lawsuit over Richard Smith’s inheritance lost her several patrons. Also, her increasingly blunt prefaces made her less appealing to the public. In order to continue earning money, Smith began writing in less politically charged genres. She published a collection of tales, Letters of a Solitary Wanderer (1801–02) and the play What Is She? (1799, attributed). Her most successful new foray was into children’s literature: Rural Walks (1795), Rambles Farther (1796), Minor Morals (1798), and Conversations Introducing Poetry (1804). She also wrote two volumes of a history of England (1806) and A Natural History of Birds (1807, posthumous). She also returned to writing poetry and Beachy Head and Other Poems (1807) was published posthumously. Publishers did not pay as much for these works, however, and by 1803, Smith was poverty-stricken. She could barely afford food and had no coal. She even sold her beloved library of 500 books in order to pay off debts, but feared being sent to jail for the remaining £20. Illness and death Smith complained of gout for many years (it was probably rheumatoid arthritis), which made it increasingly difficult and painful for her to write. By the end of her life, it had almost paralyzed her. She wrote to a friend that she was “literally vegetating, for I have very little locomotive powers beyond those that appertain to a cauliflower”. On 23 February 1806, her husband died in a debtors’ prison and Smith finally received some of the money he owed her, but she was too ill to do anything with it. She died a few months later, on 28 October 1806, at Tilford and was buried at Stoke Church, Stoke Park, near Guildford. The lawsuit over her father-in-law’s estate was settled seven years later, on 22 April 1813, more than thirty-six years after Richard Smith’s death. Legacy Stuart Curran, the editor of Smith’s poems, has written that Smith is “the first poet in England whom in retrospect we would call Romantic”. She helped shape the “patterns of thought and conventions of style” for the period. Romantic poet William Wordsworth was the most affected by her works. He said of Smith in the 1830s that she was “a lady to whom English verse is under greater obligations than are likely to be either acknowledged or remembered”. By the second half of the 19th century, Smith was largely forgotten. Smith’s novels were republished again at the end of the 20th century, and “critics interested in the period’s women poets and prose writers, the Gothic novel, the historical novel, the social problem novel, and post-colonial studies” have argued for her significance as a writer. They looked to the contemporary documentation of her importance, discovering that she helped to revitalize the English sonnet, a fact recognized by Coleridge and others. Scott wrote that she “preserves in her landscapes the truth and precision of a painter” and poet and Barbauld claimed that Smith was the first to include sustained natural description in novels. It was not until 2008 however, that Smith’s entire prose collection became available to the general public. The edition contains each novel, the children’s stories and rural walks.


John Newton (24 July 1725– 21 December 1807) was an English sailor, in the Royal Navy for a period, and later a captain of slave ships. He became ordained as an evangelical Anglican cleric, served Olney, Buckinghamshire for two decades, and also wrote hymns, known for “Amazing Grace” and “Glorious Things of Thee Are Spoken”. Newton started his career at sea at a young age, and worked on slave ships in the slave trade for several years. After experiencing a period of Christian conversion Newton eventually renounced his trade and became a prominent supporter of abolitionism, living to see Britain’s abolition of the African slave trade in 1807. Early life John Newton was born in Wapping, London, in 1725, the son of Elizabeth (née Scatliff) and John Newton Sr., a shipmaster in the Mediterranean service. Elizabeth was the only daughter of Simon Scatliff, an instrument maker from London (the marriage register records her maiden name as Seatcliffe). Elizabeth was brought up as a Nonconformist. She died of tuberculosis (then called consumption) in July 1732, about two weeks before John’s seventh birthday. Newton spent two years at boarding school before going to live in Aveley in Essex, the home of his father’s new wife. At age eleven he first went to sea with his father. Newton sailed six voyages before his father retired in 1742. At that time, Newton’s father made plans for him to work at a sugarcane plantation in Jamaica. Instead, Newton signed on with a merchant ship sailing to the Mediterranean Sea. Impressment into naval service In 1743, while going to visit friends, Newton was captured and pressed into the naval service by the Royal Navy. He became a midshipman aboard HMS Harwich. At one point Newton tried to desert and was punished in front of the crew of 350. Stripped to the waist and tied to the grating, he received a flogging of eight dozen lashes and was reduced to the rank of a common seaman. Following that disgrace and humiliation, Newton initially contemplated murdering the captain and committing suicide by throwing himself overboard. He recovered, both physically and mentally. Later, while Harwich was en route to India, he transferred to Pegasus, a slave ship bound for West Africa. The ship carried goods to Africa and traded them for slaves to be shipped to the colonies in the Caribbean and North America. Enslavement and rescue Newton did not get along with the crew of Pegasus. They left him in West Africa with Amos Clowe, a slave dealer. Clowe took Newton to the coast and gave him to his wife, Princess Peye of the Sherbro people. She abused and mistreated Newton equally as much as she did her other slaves. Newton later recounted this period as the time he was “once an infidel and libertine, a servant of slaves in West Africa.” Early in 1748 he was rescued by a sea captain who had been asked by Newton’s father to search for him, and returned to England on the merchant ship Greyhound, which was carrying beeswax and dyer’s wood, now referred to as camwood. Spiritual conversion During his 1748 voyage to England after his rescue, Newton had a spiritual conversion. The ship encountered a severe storm off the coast of County Donegal in Ulster, Ireland, and almost sank. Newton awoke in the middle of the night and, as the ship filled with water, called out to God. The cargo shifted and stopped up the hole, and the ship drifted to safety. Newton marked this experience as the beginning of his conversion to evangelical Christianity. He began to read the Bible and other religious literature. By the time he reached Britain, he had accepted the doctrines of evangelical Christianity. The date was 10 March 1748, an anniversary he marked for the rest of his life. From that point on, he avoided profanity, gambling, and drinking. Although he continued to work in the slave trade, he had gained sympathy for the slaves during his time in Africa. He later said that his true conversion did not happen until some time later: “I cannot consider myself to have been a believer in the full sense of the word, until a considerable time afterwards.” Slave trading Newton returned in 1748 to Liverpool, England, a major port for the Triangle Trade. Partly due to the influence of his father’s friend Joseph Manesty, he obtained a position as first mate aboard the slave ship Brownlow, bound for the West Indies via the coast of Guinea. While in west Africa (1748–49), Newton acknowledged the inadequacy of his spiritual life. He became ill with a fever and professed his full belief in Christ, asking God to take control of his destiny. He later said that this was the first time he felt totally at peace with God. Newton did not however immediately renounce working in the slave trade. After his return to England in 1750, he made three voyages as captain of the slave ships Duke of Argyle (1750) and African (1752–53 and 1753–54). After suffering a severe stroke in 1754, he gave up seafaring and slave-trading activities. But he continued to invest in Manesty’s slaving operations. Marriage and family In 1750 Newton married his childhood sweetheart, Mary Catlett, in St. Margaret’s Church, Rochester. Newton adopted his two orphaned nieces, Elizabeth and Eliza Catlett, children of one of his brothers-in-law and his wife. Newton’s niece Alys Newton later married Mehul, a prince from India. Anglican priest In 1755 Newton was appointed as tide surveyor (a tax collector) of the Port of Liverpool, again through the influence of Manesty. In his spare time, he studied Greek, Hebrew, and Syriac, preparing for serious religious study. He became well known as an evangelical lay minister. In 1757, he applied to be ordained as a priest in the Church of England, but it was more than seven years before he was eventually accepted. During this period, he also applied to the Methodists, Independents and Presbyterians. He mailed applications directly to the Bishops of Chester and Lincoln and the Archbishops of Canterbury and York. Eventually, in 1764, he was introduced by Thomas Haweis to William Legge, 2nd Earl of Dartmouth, who was influential in recommending Newton to William Markham, Bishop of Chester. Haweis suggested Newton for the living of Olney, Buckinghamshire. On 29 April 1764 Newton received deacon’s orders, and finally was ordained as a priest on 17 June. As curate of Olney, Newton was partly sponsored by John Thornton, a wealthy merchant and evangelical philanthropist. He supplemented Newton’s stipend of £60 a year with £200 a year “for hospitality and to help the poor”. Newton soon became well known for his pastoral care, as much as for his beliefs. His friendship with Dissenters and evangelical clergy led to his being respected by Anglicans and Nonconformists alike. He spent sixteen years at Olney. His preaching was so popular that the congregation added a gallery to the church to accommodate the many persons who flocked to hear him. Some five years later, in 1772, Thomas Scott took up the curacy of the neighbouring parishes of Stoke Goldington and Weston Underwood. Newton was instrumental in converting Scott from a cynical ‘career priest’ to a true believer, a conversion which Scott related in his spiritual autobiography The Force Of Truth (1779). Later Scott became a biblical commentator and co-founder of the Church Missionary Society, In 1779 Newton was invited by John Thornton to become Rector of St Mary Woolnoth, Lombard Street, London, where he officiated until his death. The church had been built by Nicholas Hawksmoor in 1727 in the fashionable Baroque style. Newton was one of only two evangelical Anglican priests in the capital, and he soon found himself gaining in popularity amongst the growing evangelical party. He was a strong supporter of evangelicalism in the Church of England. He remained a friend of Dissenters (such as Methodists and Baptists) as well as Anglicans. Young churchmen and people struggling with faith sought his advice, including such well-known social figures as the writer and philanthropist Hannah More, and the young William Wilberforce, a Member of Parliament who had recently suffered a crisis of conscience and religious conversion while contemplating leaving politics. The younger man consulted with Newton, who encouraged Wilberforce to stay in Parliament and “serve God where he was”. In 1792, Newton was presented with the degree of Doctor of Divinity by the College of New Jersey (now Princeton University). Abolitionist In 1788, 34 years after he had retired from the slave trade, Newton broke a long silence on the subject with the publication of a forceful pamphlet Thoughts Upon the Slave Trade, in which he described the horrific conditions of the slave ships during the Middle Passage. He apologized for “a confession, which... comes too late... It will always be a subject of humiliating reflection to me, that I was once an active instrument in a business at which my heart now shudders.” He had copies sent to every MP, and the pamphlet sold so well that it swiftly required reprinting. Newton became an ally of William Wilberforce, leader of the Parliamentary campaign to abolish the African slave trade. He lived to see the British passage of the Slave Trade Act 1807, which enacted this event. Some modern writers have criticised Newton for continuing to participate in the slave trade after his religious conversion, but Christianity did not deter thousands of slaveholders in the colonies from owning other men, nor many others from profiting by the slave trade. Newton came to believe that during the first five of his nine years as a slave trader he had not been a Christian in the full sense of the term. In 1763 he wrote: “I was greatly deficient in many respects... I cannot consider myself to have been a believer in the full sense of the word, until a considerable time afterwards.” Writer and hymnist In 1767 William Cowper, the poet, moved to Olney. He worshipped in Newton’s church, and collaborated with the priest on a volume of hymns; it was published as Olney Hymns in 1779. This work had a great influence on English hymnology. The volume included Newton’s well-known hymns: “Glorious Things of Thee Are Spoken,” “How Sweet the Name of Jesus Sounds!,” “Let Us Love, and Sing, and Wonder,” “Come, My Soul, Thy Suit Prepare,” “Approach, My Soul, the Mercy-seat”, and “Faith’s Review and Expectation,” which has come to be known by its opening phrase, “Amazing Grace”. Many of Newton’s (as well as Cowper’s) hymns are preserved in the Sacred Harp, a hymnal used in the American South during the Second Great Awakening. Hymns were scored according to the tonal scale for shape note singing. Easily learned and incorporating singers into four-part harmony, shape note music was widely used by evangelical preachers to reach new congregants. Newton also contributed to the Cheap Repository Tracts. He wrote an autobiography entitled An Authentic Narrative of Some Remarkable And Interesting Particulars in the Life of———Communicated, in a Series of Letters, to the Reverend T. Haweiss, which he published anonymously. It was later described as 'written in an easy style, distinguished by great natural shrewdness, and sanctified by the Lord God and prayer’. Final years Newton’s wife Mary Catlett died in 1790, after which he published Letters to a Wife (1793), in which he expressed his grief. Plagued by ill health and failing eyesight, Newton died on 21 December 1807 in London. He was buried beside his wife in St. Mary Woolnoth in London. Both were reinterred at the Church of St. Peter and Paul in Olney in 1893. Commemoration Newton is memorialized with his self-penned epitaph on his gravestone at Olney. When he was initially interred in London, a memorial plaque to Newton, containing his self-penned epitaph, was installed on the wall of St Mary Woolnoth. At the bottom of the plaque are the words: "The above Epitaph was written by the Deceased who directed it to be inscribed on a plain Marble Tablet. He died on December the 21st December 1807. Aged 82 Years, and his Mortal Remains are deposited in the Vault beneath the Church.” The town of Newton, Sierra Leone is named after him. To this day his former town of Olney provides philanthropy for the African town. In 1982, Newton was recognized for his influential hymns by the Gospel Music Association when he was inducted into the Gospel Music Hall of Fame. Portrayals in media Film The film Amazing Grace (2006) highlights Newton’s influence on William Wilberforce. Albert Finney portrays Newton, Ioan Gruffudd is Wilberforce, and the film was directed by Michael Apted. The film portrays Newton as a penitent haunted by the ghosts of 20,000 slaves. The Nigerian film The Amazing Grace (2006), the creation of Nigerian director/writer/producer Jeta Amata, provides an African perspective on the slave trade. Nigerian actors Joke Silva, Mbong Odungide, and Fred Amata (brother of the director) portray Africans who are captured and taken away from their homeland by slave traders. Newton is played by Nick Moran. The 2014 film Freedom tells the story of an American slave (Samuel Woodward, played by Cuba Gooding, Jr.) escaping to freedom via the Underground Railroad. A parallel earlier story depicts John Newton (played by Bernhard Forcher) as the captain of a slave ship bound for America carrying Samuel’s grandfather. Newton’s conversion is explored as well. Stage productions African Snow (2007), a play by Murray Watts, takes place in the mind of John Newton. It was first produced at the York Theatre Royal as a co-production with Riding Lights Theatre Company, transferring to the Trafalgar Studios in London’s West End and a National Tour. Newton was played by Roger Alborough and Olaudah Equiano by Israel Oyelumade. The musical Amazing Grace is a dramatisation of Newton’s life. The 2014 pre-Broadway and 2015 Broadway productions starred Josh Young as Newton. Television Newton is portrayed by actor John Castle in the British television miniseries, The Fight Against Slavery (1975). Novels Caryl Phillips’ novel, Crossing the River (1993), includes nearly verbatim excerpts of Newton’s logs from his Journal of a Slave Trader. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Newton


William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was an English textile designer, poet, novelist, translator, and socialist activist. Associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement, he was a major contributor to the revival of traditional British textile arts and methods of production. His literary contributions helped to establish the modern fantasy genre, while he played a significant role in propagating the early socialist movement in Britain.

Edith Nesbit (married name Edith Bland; 15 August 1858 – 4 May 1924) was an English author and poetess; she published her books for children under the name of E. Nesbit. She wrote or collaborated on more than 60 books of fiction for children. She was also a political activist and co-founded the Fabian Society, a socialist organisation later affiliated to the Labour Party.
#English #Women #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Richard Lovelace (1618–1657) was an English poet in the seventeenth century. He was a cavalier poet who fought on behalf of the king during the Civil war. His best known works are To Althea, from Prison, and To Lucasta, Going to the Warres. Richard Lovelace attended Oxford University and he was praised by one of his contemporaries, Anthony Wood. for being “the most amiable and beautiful person that ever eye beheld; a person also of innate modesty, virtue and courtly deportment, which made him then, but especially after, when he retired to the great city, much admired and adored by the female sex"


Algernon Charles Swinburne (5 April 1837– 10 April 1909) was an English poet, playwright, novelist, and critic. He wrote several novels and collections of poetry such as Poems and Ballads, and contributed to the famous Eleventh Edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica. A controversial figure at the time, Swinburne was a sado-masochist and alcoholic and was obsessed with the Middle Ages and lesbianism. Swinburne wrote about many taboo topics, such as lesbianism, cannibalism, sado-masochism, and anti-theism. His poems have many common motifs, such as the Ocean, Time, and Death. Several historical people are featured in his poems, such as Sappho ("Sapphics"), Anactoria ("Anactoria"), Jesus ("Hymn to Proserpine": Galilaee, La. “Galilean”) and Catullus ("To Catullus").
#Decadents #English #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Sir Philip Sidney (30 November 1554– 17 October 1586) was an English poet, courtier, scholar, and soldier, who is remembered as one of the most prominent figures of the Elizabethan age. His works include Astrophel and Stella, The Defence of Poesy (also known as The Defence of Poetry or An Apology for Poetry), and The Countess of Pembroke’s Arcadia. Early life Born at Penshurst Place, Kent, he was the eldest son of Sir Henry Sidney and Lady Mary Dudley. His mother was the eldest daughter of John Dudley, 1st Duke of Northumberland, and the sister of Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester. His younger brother, Robert was a statesman and patron of the arts, and was created Earl of Leicester in 1618. His younger sister, Mary, married Henry Herbert, 2nd Earl of Pembroke and was a writer, translator and literary patron. Sidney dedicated his longest work, the Arcadia, to her. After her brother’s death, Mary reworked the Arcadia, which became known as The Countess of Pembroke’s Arcadia. Philip was educated at Shrewsbury School and Christ Church, Oxford. Politics and marriage In 1572, in which year he turned 18, he was elected to Parliament as Member of Parliament for Shrewsbury and in the same year travelled to France as part of the embassy to negotiate a marriage between Elizabeth I and the Duc D’Alençon. He spent the next several years in mainland Europe, moving through Germany, Italy, Poland, the Kingdom of Hungary and Austria. On these travels, he met a number of prominent European intellectuals and politicians. Returning to England in 1575, Sidney met Penelope Devereux, the future Lady Rich; though much younger, she would inspire his famous sonnet sequence of the 1580s, Astrophel and Stella. Her father, Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex, is said to have planned to marry his daughter to Sidney, but he died in 1576. In England, Sidney occupied himself with politics and art. He defended his father’s administration of Ireland in a lengthy document. More seriously, he quarrelled with Edward de Vere, 17th Earl of Oxford, probably because of Sidney’s opposition to the French marriage, which de Vere championed. In the aftermath of this episode, Sidney challenged de Vere to a duel, which Elizabeth forbade. He then wrote a lengthy letter to the Queen detailing the foolishness of the French marriage. Characteristically, Elizabeth bristled at his presumption, and Sidney prudently retired from court. During a 1577 diplomatic visit to Prague, Sidney secretly visited the exiled Jesuit priest Edmund Campion. Sidney had returned to court by the middle of 1581 and in 1584 was MP for Kent. That same year Penelope Devereux was married, apparently against her will, to Lord Rich. Sidney was knighted in 1583. An early arrangement to marry Anne Cecil, daughter of Sir William Cecil and eventual wife of de Vere, had fallen through in 1571. In 1583, he married Frances, teenage daughter of Sir Francis Walsingham. In the same year, he made a visit to Oxford University with Giordano Bruno, who subsequently dedicated two books to Sidney. Literary writings His artistic contacts were more peaceful and more significant for his lasting fame. During his absence from court, he wrote Astrophel and Stella and the first draft of The Arcadia and The Defence of Poesy. Somewhat earlier, he had met Edmund Spenser, who dedicated The Shepheardes Calender to him. Other literary contacts included membership, along with his friends and fellow poets Fulke Greville, Edward Dyer, Edmund Spenser and Gabriel Harvey, of the (possibly fictitious) 'Areopagus’, a humanist endeavour to classicise English verse. Military activity Both through his family heritage and his personal experience (he was in Walsingham’s house in Paris during the St. Bartholomew’s Day Massacre), Sidney was a keenly militant Protestant. In the 1570s, he had persuaded John Casimir to consider proposals for a united Protestant effort against the Roman Catholic Church and Spain. In the early 1580s, he argued unsuccessfully for an assault on Spain itself. Promoted General of Horse in 1583, his enthusiasm for the Protestant struggle was given a free rein when he was appointed governor of Flushing in the Netherlands in 1585. In the Netherlands, he consistently urged boldness on his superior, his uncle the Earl of Leicester. He conducted a successful raid on Spanish forces near Axel in July, 1586. Injury and death Later that year, he joined Sir John Norris in the Battle of Zutphen, fighting for the Protestant cause against the Spanish. During the battle, he was shot in the thigh and died of gangrene 26 days later, at the age of 31. As he lay dying, Sidney composed a song to be sung by his deathbed. According to the story, while lying wounded he gave his water to another wounded soldier, saying, “Thy necessity is yet greater than mine”. This became possibly the most famous story about Sir Phillip, intended to illustrate his noble and gallant character. It also inspired evolutionary biologist John Maynard Smith to formulate a problem in signalling theory which is known as the Sir Philip Sidney game. Sidney’s body was returned to London and interred in the Old St. Paul’s Cathedral on 16 February 1587. The grave and monument were destroyed in the Great Fire of London in 1666. A modern monument in the crypt lists him among the important graves lost. Already during his own lifetime, but even more after his death, he had become for many English people the very epitome of a Castiglione courtier: learned and politic, but at the same time generous, brave, and impulsive. The funeral procession was one of the most elaborate ever staged, so much so that his father-in-law, Francis Walsingham, almost went bankrupt. Never more than a marginal figure in the politics of his time, he was memorialised as the flower of English manhood in Edmund Spenser’s Astrophel, one of the greatest English Renaissance elegies. An early biography of Sidney was written by his friend and schoolfellow, Fulke Greville. While Sidney was traditionally depicted as a staunch and unwavering Protestant, recent biographers such as Katherine Duncan-Jones have suggested that his religious loyalties were more ambiguous. Works * The Lady of May– This is one of Sidney’s lesser-known works, a masque written and performed for Queen Elizabeth in 1578 or 1579. * Astrophel and Stella– The first of the famous English sonnet sequences, Astrophel and Stella was probably composed in the early 1580s. The sonnets were well-circulated in manuscript before the first (apparently pirated) edition was printed in 1591; only in 1598 did an authorised edition reach the press. The sequence was a watershed in English Renaissance poetry. In it, Sidney partially nativised the key features of his Italian model, Petrarch: variation of emotion from poem to poem, with the attendant sense of an ongoing, but partly obscure, narrative; the philosophical trappings; the musings on the act of poetic creation itself. His experiments with rhyme scheme were no less notable; they served to free the English sonnet from the strict rhyming requirements of the Italian form. * The Countess of Pembroke’s Arcadia– The Arcadia, by far Sidney’s most ambitious work, was as significant in its own way as his sonnets. The work is a romance that combines pastoral elements with a mood derived from the Hellenistic model of Heliodorus. In the work, that is, a highly idealised version of the shepherd’s life adjoins (not always naturally) with stories of jousts, political treachery, kidnappings, battles, and rapes. As published in the sixteenth century, the narrative follows the Greek model: stories are nested within each other, and different storylines are intertwined. The work enjoyed great popularity for more than a century after its publication. William Shakespeare borrowed from it for the Gloucester subplot of King Lear; parts of it were also dramatised by John Day and James Shirley. According to a widely-told story, King Charles I quoted lines from the book as he mounted the scaffold to be executed; Samuel Richardson named the heroine of his first novel after Sidney’s Pamela. Arcadia exists in two significantly different versions. Sidney wrote an early version (the Old Arcadia) during a stay at Mary Herbert’s house; this version is narrated in a straightforward, sequential manner. Later, Sidney began to revise the work on a more ambitious plan, with much more backstory about the princes, and a much more complicated story line, with many more characters. He completed most of the first three books, but the project was unfinished at the time of his death—the third book breaks off in the middle of a sword fight. There were several early editions of the book. Fulke Greville published the revised version alone, in 1590. The Countess of Pembroke, Sidney’s sister, published a version in 1593, which pasted the last two books of the first version onto the first three books of the revision. In the 1621 version, Sir William Alexander provided a bridge to bring the two stories back into agreement. It was known in this cobbled-together fashion until the discovery, in the early twentieth century, of the earlier version. * An Apology for Poetry (also known as A Defence of Poesie and The Defence of Poetry)– Sidney wrote the Defence before 1583. It is generally believed that he was at least partly motivated by Stephen Gosson, a former playwright who dedicated his attack on the English stage, The School of Abuse, to Sidney in 1579, but Sidney primarily addresses more general objections to poetry, such as those of Plato. In his essay, Sidney integrates a number of classical and Italian precepts on fiction. The essence of his defence is that poetry, by combining the liveliness of history with the ethical focus of philosophy, is more effective than either history or philosophy in rousing its readers to virtue. The work also offers important comments on Edmund Spenser and the Elizabethan stage. * The Sidney Psalms– These English translations of the Psalms were completed in 1599 by Philip Sidney’s sister Mary. In popular culture * A memorial, erected in 1986 at the location where he was mortally wounded by the Spanish, can be found at the entrance of a footpath (" 't Gallee") located in front of the petrol station at the Warnsveldseweg 170. * In Arnhem, in front of the house in the Bakkerstraat 68, an inscription on the ground reads: "IN THIS HOUSE DIED ON THE 17 OCTOBER 1586 * SIR PHILIP SIDNEY * ENGLISH POET, DIPLOMAT AND SOLDIER, FROM HIS WOUNDS SUFFERED AT THE BATTLE OF ZUTPHEN. HE GAVE HIS LIFE FOR OUR FREEDOM". The inscription was unveiled on 17 October 2011, exactly 425 years after his death, in the presence of Philip Sidney, Viscount De L’Isle, a descendant of the brother of Philip Sidney. * The city of Sidney, Ohio, in the United States and a street in Zutphen, Netherlands, have been named after Sir Philip. A statue of him can be found in the park at the Coehoornsingel where, in the harsh winter of 1795, English and Hanoverian soldiers were buried who had died while retreating from advancing French troops. * Another statue of Sidney, by Arthur George Walker, forms the centrepiece of Shrewsbury School’s war memorial to alumni who died serving in World War I (unveiled 1924). * Sidney features as a friend of Giordano Bruno and an agent for Sir Francis Walsingham in the historical crime novels of S J Parris. * W. B. Yeats appears to allude to Sidney as a model of the ideal man in his poem “In Memory of Major Robert Gregory” when he calls Robert Gregory “Our Sidney and our perfect man”. * Sidney is referenced in the T.S. Eliot’s poem “A Cooking Egg”, published in his 1920 poetry collection Aras Vos Prec, where Eliot expresses a desire to speak with Sir Philip in heaven. * An extended sketch from Monty Python’s Flying Circus (Series 3, Episode 10 “E. Henry Thripshaw’s Disease”) featured a police officer, disguised as Sir Philip Sidney, finding himself transported to the Tudor era after raiding a pornography shop. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philip_Sidney


Edward Lear (12 or 13 May 1812 – 29 January 1888) was an English artist, illustrator, author and poet, and is known now mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised. His principal areas of work as an artist were threefold: as a draughtsman employed to illustrate birds and animals; making coloured drawings during his journeys, which he reworked later, sometimes as plates for his travel books; as a (minor) illustrator of Alfred Tennyson's poems. As an author, he is known principally for his popular nonsense works, which use real and invented English words. Early years Lear was born into a middle-class family in the village of Holloway near London, the penultimate of twenty-one children (and youngest to survive) of Ann Clark Skerrett and Jeremiah Lear. He was raised by his eldest sister, also named Ann, 21 years his senior. Owing to the family's limited finances, Lear and his sister were required to leave the family home and live together when he was aged four. Ann doted on Edward and continued to act as a mother for him until her death, when he was almost 50 years of age. Lear suffered from lifelong health afflictions. From the age of six he suffered frequent grand mal epileptic seizures, and bronchitis, asthma, and during later life, partial blindness. Lear experienced his first seizure at a fair near Highgate with his father. The event scared and embarrassed him. Lear felt lifelong guilt and shame for his epileptic condition. His adult diaries indicate that he always sensed the onset of a seizure in time to remove himself from public view. When Lear was about seven years old he began to show signs of depression, possibly due to the instability of his childhood. He suffered from periods of severe melancholia which he referred to as "the Morbids.” Artist Lear was already drawing "for bread and cheese" by the time he was aged 16 and soon developed into a serious "ornithological draughtsman" employed by the Zoological Society and then from 1832 to 1836 by the Earl of Derby, who kept a private menagerie at his estate Knowsley Hall. Lear's first publication, published when he was 19 years old, was Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae, or Parrots in 1830. His paintings were well received and he was compared favourably with the naturalist John James Audubon. Among other travels, he visited Greece and Egypt during 1848–49, and toured India and Ceylon (Sri Lanka) during 1873–75. While travelling he produced large quantities of coloured wash drawings in a distinctive style, which he converted later in his studio into oil and watercolour paintings, as well as prints for his books. His landscape style often shows views with strong sunlight, with intense contrasts of colour. Throughout his life he continued to paint seriously. He had a lifelong ambition to illustrate Tennyson's poems; near the end of his life a volume with a small number of illustrations was published. Relationships Lear's most fervent and painful friendship involved Franklin Lushington. He met the young barrister in Malta in 1849 and then toured southern Greece with him. Lear developed an undoubtedly homosexual passion for him that Lushington did not reciprocate. Although they remained friends for almost forty years, until Lear's death, the disparity of their feelings for one another constantly tormented Lear. Indeed, none of Lear's attempts at male companionship were successful; the very intensity of Lear's affections seemingly doomed the relationships. The closest he came to marriage with a woman was two proposals, both to the same person 46 years his junior, which were not accepted. For companions he relied instead on friends and correspondents, and especially, during later life, on his Albanian Souliote chef, Giorgis, a faithful friend and, as Lear complained, a thoroughly unsatisfactory chef. Another trusted companion in Sanremo was his cat, Foss, which died in 1886 and was buried with some ceremony in a garden at Villa Tennyson. San Remo and death Lear travelled widely throughout his life and eventually settled in Sanremo, on his beloved Mediterranean coast, in the 1870s, at a villa he named "Villa Tennyson". Lear was known to introduce himself with a long pseudonym: "Mr Abebika kratoponoko Prizzikalo Kattefello Ablegorabalus Ableborinto phashyph" or "Chakonoton the Cozovex Dossi Fossi Sini Tomentilla Coronilla Polentilla Battledore & Shuttlecock Derry down Derry Dumps" which he based on Aldiborontiphoskyphorniostikos. After a long decline in his health, Lear died at his villa in 1888, of the heart disease from which he had suffered since at least 1870. Lear's funeral was said to be a sad, lonely affair by the wife of Dr. Hassall, Lear's physician, none of Lear's many lifelong friends being able to attend. Lear is buried in the Cemetery Foce in San Remo. On his headstone are inscribed these lines about Mount Tomohrit (in Albania) from Tennyson's poem To E.L. [Edward Lear], On His Travels in Greece: all things fair. With such a pencil, such a pen. You shadow forth to distant men, I read and felt that I was there. The centenary of his death was marked in Britain with a set of Royal Mail stamps in 1988 and an exhibition at the Royal Academy. Lear's birthplace area is now marked with a plaque at Bowman's Mews, Islington, in London, and his bicentenary during 2012 was celebrated with a variety of events, exhibitions and lectures in venues across the world including an International Owl and Pussycat Day on his birthday. References Wikipedia – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Lear


William Arthur Dunkerley (12 November 1852 – 23 January 1941) was an English journalist, novelist and poet. He was born in Manchester, spent a short time after his marriage in the US before moving to Ealing, West London, where he served as deacon and teacher at the Ealing Congregational Church from the 1880s. In 1922 he moved to Worthing in Sussex, where he became the town’s mayor.Dunkerley wrote under his own name, and also as John Oxenham for his poetry, hymn-writing, and novels. His poetry includes Bees in Amber: A Little Book of Thoughtful Verse (1913), which became a bestseller. He also wrote the poem “Greatheart”. He used the pseudonym Julian Ross for journalism. In February 1892 Robert Barr and Dunkerley founded The Idler, a monthly “general interest magazine, one of the first to appear following the enthusiastic reception of The Strand, but not a slavish imitation”. Barr and Dunkerley/Oxenham both contributed as writers. The editors were Barr and Jerome K. Jerome initially.Dunkerley had two sons and four daughters, of whom the eldest, and eldest child, Elsie Jeanette, became well known as a children’s writer, particularly through her Abbey Series of girls’ school stories. Another daughter, Erica, also used the Oxenham pen-name. The elder son, Roderic Dunkerley, had several titles published under his own name.


William Lisle Bowles (24 September 1762– 7 April 1850) was an English priest, poet and critic. Life and career Bowles was born at King’s Sutton, Northamptonshire, where his father was vicar. At the age of 14 he entered Winchester College, where the headmaster at the time was Dr Joseph Warton. In 1781 Bowles left as captain of the school, and went on to Trinity College, Oxford, where he had won a scholarship. Two years later he won the Chancellor’s prize for Latin verse. Bowles came from a line of Church of England clergymen. His great-grandfather Matthew Bowles (1652–1742), grandfather Dr Thomas Bowles (1696–1773) and father William Thomas Bowles (1728–86) had all been parish priests. After taking his degree at Oxford, Bowles followed his forebears into the Church of England, and in 1792, after serving as curate in Donhead St Andrew, was appointed vicar of Chicklade in Wiltshire. In 1797 he received the vicarage of Dumbleton in Gloucestershire, and in 1804 became vicar of Bremhill in Wiltshire, where he wrote the poem seen on Maud Heath’s statue. In the same year his bishop, John Douglas, collated him to a prebendal stall in Salisbury Cathedral. In 1818 he was made chaplain to the Prince Regent, and in 1828 he was elected residentiary canon of Salisbury. Works * In 1789 he published, in a very small quarto volume, Fourteen Sonnets, which were received with extraordinary favour, not only by the general public, but by such men as Samuel Taylor Coleridge and Wordsworth. * The Sonnets even in form were a revival, a return to an older and purer poetic style, and by their grace of expression, melodious versification, tender tone of feeling and vivid appreciation of the life and beauty of nature, stood out in strong contrast to the elaborated commonplaces which at that time formed the bulk of English poetry. Bowles said thereof Poetic trifles from solitary rambles whilst chewing the cud of sweet and bitter fancy, written from memory, confined to fourteen lines, this seemed best adapted to the unity of sentiment, the verse flowed in unpremeditated harmony as my ear directed but are far from being mere elegiac couplets. * The longer poems published by Bowles are not of a very high standard, though all are distinguished by purity of imagination, cultured and graceful diction, and great tenderness of feeling. The most extensive were The Spirit of Discovery (1804), which was mercilessly ridiculed by Lord Byron; The Missionary (1813); The Grave of the Last Saxon (1822); and St John in Patmos (1833). Bowles is perhaps more celebrated as a critic than as a poet.In 1806 he published an edition of Alexander Pope’s works with notes and an essay, in which he laid down certain canons as to poetic imagery which, subject to some modification, were later accepted, but which were received at the time with strong opposition by admirers of Pope and his style. The controversy brought into sharp contrast the opposing views of poetry, which may be roughly described as the natural and the artificial. * Bowles was an amiable, absent-minded, and rather eccentric man. His poems are characterised by refinement of feeling, tenderness, and pensive thought, but are deficient in power and passion. Bowles maintained that images drawn from nature are poetically finer than those drawn from art; and that in the highest kinds of poetry the themes or passions handled should be of the general or elemental kind, and not the transient manners of any society. These positions were attacked by Byron, Thomas Campbell, William Roscoe and others, while for a time Bowles was almost solitary. William Hazlitt and the Blackwood critics came to his assistance, and on the whole Bowles had reason to congratulate himself on having established certain principles which might serve as the basis of a true method of poetical criticism, and of having inaugurated, both by precept and by example, a new era in English poetry. Among other prose works from his prolific pen was a Life of Bishop Ken (two volumes, 1830–1831). Other works include Coombe Ellen and St. Michael’s Mount (1798), The Battle of the Nile (1799), and The Sorrows of Switzerland (1801). * Bowles also enjoyed considerable reputation as an antiquary, his principal work in that department being Hermes Britannicus (1828). His Poetical Works were collected in 1855 as part of the Library Edition of the British Poets, with a memoir by George Gilfillan. Reception * Bowles’ work was important to the young Samuel Taylor Coleridge: * Bowles was the cause in the 1820s of the Alexander Pope controversy into which George Gordon, Lord Byron was drawn. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Lisle_Bowles


Alan Alexander “A. A.” Milne (/ˈmɪln/; 18 January 1882– 31 January 1956) was an English author, best known for his books about the teddy bear Winnie-the-Pooh and for various poems. Milne was a noted writer, primarily as a playwright, before the huge success of Pooh overshadowed all his previous work. Milne served in both World Wars, joining the British Army in World War I, and was a captain of the British Home Guard in World War II. Biography Alan Alexander Milne was born in Kilburn, London to parents John Vince Milne, who was Scottish, and Sarah Marie Milne (née Heginbotham) and grew up at Henley House School, 6/7 Mortimer Road (now Crescent), Kilburn, a small public school run by his father. One of his teachers was H. G. Wells, who taught there in 1889–90. Milne attended Westminster School and Trinity College, Cambridge where he studied on a mathematics scholarship, graduating with a B.A. in Mathematics in 1903. While there, he edited and wrote for Granta, a student magazine. He collaborated with his brother Kenneth and their articles appeared over the initials AKM. Milne’s work came to the attention of the leading British humour magazine Punch, where Milne was to become a contributor and later an assistant editor. Milne played for the amateur English cricket team the Allahakbarries alongside authors J. M. Barrie and Arthur Conan Doyle. Milne joined the British Army in World War I and served as an officer in the Royal Warwickshire Regiment and later, after a debilitating illness, the Royal Corps of Signals. He was commissioned into the 4th Battalion, Royal Warwickshire Regiment on 17 February 1915 as a second lieutenant (on probation). His commission was confirmed on 20 December 1915. On 7 July 1916, he was injured while serving in the Battle of the Somme and invalided back to England. Having recuperated, he was recruited into Military Intelligence to write propaganda articles for MI 7b between 1916 and 1918. He was discharged on 14 February 1919, and settled in Mallord Street, Chelsea. He relinquished his commission on 19 February 1920, retaining the rank of lieutenant. After the war, he wrote a denunciation of war titled Peace with Honour (1934), which he retracted somewhat with 1940's War with Honour. During World War II, Milne was one of the most prominent critics of fellow English writer P. G. Wodehouse, who was captured at his country home in France by the Nazis and imprisoned for a year. Wodehouse made radio broadcasts about his internment, which were broadcast from Berlin. Although the light-hearted broadcasts made fun of the Germans, Milne accused Wodehouse of committing an act of near treason by cooperating with his country’s enemy. Wodehouse got some revenge on his former friend (e.g., in The Mating Season) by creating fatuous parodies of the Christopher Robin poems in some of his later stories, and claiming that Milne “was probably jealous of all other writers.... But I loved his stuff.” Milne married Dorothy “Daphne” de Sélincourt in 1913 and their son Christopher Robin Milne was born in 1920. In 1925, A. A. Milne bought a country home, Cotchford Farm, in Hartfield, East Sussex. During World War II, A. A. Milne was Captain of the British Home Guard in Hartfield & Forest Row, insisting on being plain “Mr. Milne” to the members of his platoon. He retired to the farm after a stroke and brain surgery in 1952 left him an invalid, and by August 1953 “he seemed very old and disenchanted”. Milne died in January 1956, aged 74. Literary career 1903 to 1925 After graduating from Cambridge in 1903, A. A. Milne contributed humorous verse and whimsical essays to Punch, joining the staff in 1906 and becoming an assistant editor. During this period he published 18 plays and 3 novels, including the murder mystery The Red House Mystery (1922). His son was born in August 1920 and in 1924 Milne produced a collection of children’s poems When We Were Very Young, which were illustrated by Punch staff cartoonist E. H. Shepard. A collection of short stories for children Gallery of Children, and other stories that became part of the Winnie-the-Pooh books, were first published in 1925. Milne was an early screenwriter for the nascent British film industry, writing four stories filmed in 1920 for the company Minerva Films (founded in 1920 by the actor Leslie Howard and his friend and story editor Adrian Brunel). These were The Bump, starring Aubrey Smith; Twice Two; Five Pound Reward; and Bookworms. Some of these films survive in the archives of the British Film Institute. Milne had met Howard when the actor starred in Milne’s play Mr Pim Passes By in London. Looking back on this period (in 1926), Milne observed that when he told his agent that he was going to write a detective story, he was told that what the country wanted from a “Punch humorist” was a humorous story; when two years later he said he was writing nursery rhymes, his agent and publisher were convinced he should write another detective story; and after another two years, he was being told that writing a detective story would be in the worst of taste given the demand for children’s books. He concluded that “the only excuse which I have yet discovered for writing anything is that I want to write it; and I should be as proud to be delivered of a Telephone Directory con amore as I should be ashamed to create a Blank Verse Tragedy at the bidding of others.” 1926 to 1928 Milne is most famous for his two Pooh books about a boy named Christopher Robin after his son, Christopher Robin Milne, and various characters inspired by his son’s stuffed animals, most notably the bear named Winnie-the-Pooh. Christopher Robin Milne’s stuffed bear, originally named “Edward”, was renamed “Winnie-the-Pooh” after a Canadian black bear named Winnie (after Winnipeg), which was used as a military mascot in World War I, and left to London Zoo during the war. “The pooh” comes from a swan called “Pooh”. E. H. Shepard illustrated the original Pooh books, using his own son’s teddy, Growler ("a magnificent bear"), as the model. The rest of Christopher Robin Milne’s toys, Piglet, Eeyore, Kanga, Roo and Tigger, were incorporated into A. A. Milne’s stories, and two more characters– Rabbit and Owl– were created by Milne’s imagination. Christopher Robin Milne’s own toys are now under glass in New York where 750,000 people visit them every year. The fictional Hundred Acre Wood of the Pooh stories derives from Five Hundred Acre Wood in Ashdown Forest in East Sussex, South East England, where the Pooh stories were set. Milne lived on the northern edge of the forest at Cotchford Farm, 51.090°N 0.107°E / 51.090; 0.107, and took his son walking there. E. H. Shepard drew on the landscapes of Ashdown Forest as inspiration for many of the illustrations he provided for the Pooh books. The adult Christopher Robin commented: “Pooh’s Forest and Ashdown Forest are identical”. Popular tourist locations at Ashdown Forest include: Galleon’s Lap, The Enchanted Place, the Heffalump Trap and Lone Pine, Eeyore’s Sad and Gloomy Place, and the wooden Pooh Bridge where Pooh and Piglet invented Poohsticks. Not yet known as Pooh, he made his first appearance in a poem, “Teddy Bear”, published in Punch magazine in February 1924. Pooh first appeared in the London Evening News on Christmas Eve, 1925, in a story called “The Wrong Sort Of Bees”. Winnie-the-Pooh was published in 1926, followed by The House at Pooh Corner in 1928. A second collection of nursery rhymes, Now We Are Six, was published in 1927. All three books were illustrated by E. H. Shepard. Milne also published four plays in this period. He also “gallantly stepped forward” to contribute a quarter of the costs of dramatising P. G. Wodehouse’s A Damsel in Distress. The World of Pooh won the Lewis Carroll Shelf Award in 1958. 1929 onwards The success of his children’s books was to become a source of considerable annoyance to Milne, whose self-avowed aim was to write whatever he pleased and who had, until then, found a ready audience for each change of direction: he had freed pre-war Punch from its ponderous facetiousness; he had made a considerable reputation as a playwright (like his idol J. M. Barrie) on both sides of the Atlantic; he had produced a witty piece of detective writing in The Red House Mystery (although this was severely criticised by Raymond Chandler for the implausibility of its plot). But once Milne had, in his own words, "said goodbye to all that in 70,000 words" (the approximate length of his four principal children’s books), he had no intention of producing any reworkings lacking in originality, given that one of the sources of inspiration, his son, was growing older. In his literary home, Punch, where the When We Were Very Young verses had first appeared, Methuen continued to publish whatever Milne wrote, including the long poem “The Norman Church” and an assembly of articles entitled Year In, Year Out (which Milne likened to a benefit night for the author). In 1930, Milne adapted Kenneth Grahame’s novel The Wind in the Willows for the stage as Toad of Toad Hall. The title was an implicit admission that such chapters as Chapter 7, “The Piper at the Gates of Dawn”, could not survive translation to the theatre. A special introduction written by Milne is included in some editions of Grahame’s novel. Legacy and commemoration The rights to A. A. Milne’s Pooh books were left to four beneficiaries: his family, the Royal Literary Fund, Westminster School and the Garrick Club. After Milne’s death in 1956, one week and six days after his 74th birthday, his widow sold her rights to the Pooh characters to Stephen Slesinger, whose widow sold the rights after Slesinger’s death to the Walt Disney Company, which has made many Pooh cartoon movies, a Disney Channel television show, as well as Pooh-related merchandise. In 2001, the other beneficiaries sold their interest in the estate to the Disney Corporation for $350m. Previously Disney had been paying twice-yearly royalties to these beneficiaries. The estate of E. H. Shepard also received a sum in the deal. The copyright on Pooh expires in 2026. In 2008, a collection of original illustrations featuring Winnie-the-Pooh and his animal friends sold for more than £1.2 million at auction in Sotheby’s, London. Forbes magazine ranked Winnie the Pooh the most valuable fictional character in 2002; Winnie the Pooh merchandising products alone had annual sales of more than $5.9 billion. In 2005, Winnie the Pooh generated $6 billion, a figure surpassed by only Mickey Mouse. A memorial plaque in Ashdown Forest, unveiled by Christopher Robin in 1979, commemorates the work of A. A. Milne and Shepard in creating the world of Pooh. Milne once wrote of Ashdown Forest: “In that enchanted place on the top of the forest a little boy and his bear will always be playing”. In 2003, Winnie the Pooh was listed at number 7 on the BBC’s survey The Big Read. In 2006, Winnie the Pooh received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame, marking the 80th birthday of Milne’s creation. That same year a UK poll saw Winnie the Pooh voted onto the list of icons of England. Several of Milne’s children’s poems were set to music by the composer Harold Fraser-Simson. His poems have been parodied many times, including with the books When We Were Rather Older and Now We Are Sixty. The 1963 film The King’s Breakfast was based on Milne’s poem of the same name. Religious views Milne did not speak out much on the subject of religion, although he used religious terms to explain his decision, while remaining a pacifist, to join the British Home Guard: “In fighting Hitler”, he wrote, “we are truly fighting the Devil, the Anti-Christ... Hitler was a crusader against God.” His best known comment on the subject was recalled on his death: The Old Testament is responsible for more atheism, agnosticism, disbelief—call it what you will—than any book ever written; it has emptied more churches than all the counter-attractions of cinema, motor bicycle and golf course. He also wrote the poem “Explained”: Works Novels * Lovers in London (1905. Some consider this more of a short story collection; Milne did not like it and considered The Day’s Play as his first book.) * Once on a Time (1917) * Mr. Pim (1921) (A novelisation of his play Mr. Pim Passes By (1919)) * The Red House Mystery (1922) * Two People (1931) (Inside jacket claims this is Milne’s first attempt at a novel.) * Four Days’ Wonder (1933) * Chloe Marr (1946) Non-fiction * Peace With Honour (1934) * It’s Too Late Now: The Autobiography of a Writer (1939) * War With Honour (1940) * War Aims Unlimited (1941) * Year In, Year Out (1952) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) Punch articles * The Day’s Play (1910) * Once A Week (1914) * The Holiday Round (1912) * The Sunny Side (1921) * Those Were the Days (1929) [The four volumes above, compiled] Newspaper articles and book introductions * The Chronicles of Clovis by “Saki” (1911) [Introduction to] * Not That It Matters (1920) * By Way of Introduction (1929) Story collections for children * A Gallery of Children (1925) * Winnie-the-Pooh (1926) (illustrated by Ernest H. Shepard) * The House at Pooh Corner (1928) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Short Stories Poetry collections for children * When We Were Very Young (1924) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Now We Are Six (1927) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) Story collections * The Secret and other stories (1929) * The Birthday Party (1948) * A Table Near the Band (1950) Poetry * For the Luncheon Interval [poems from Punch] * When We Were Very Young (1924) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Now We Are Six (1927) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Behind the Lines (1940) * The Norman Church (1948) * “The Knight Whose Armor Didn’t Squeak” Screenplays and plays * Wurzel-Flummery (1917) * Belinda (1918) * The Boy Comes Home (1918) * Make-Believe (1918) (children’s play) * The Camberley Triangle (1919) * Mr. Pim Passes By (1919) * The Red Feathers (1920) * The Bump (1920, Minerva Films), starring Aubrey Smith * Twice Two (1920, Minerva Films) * Five Pound Reward (1920, Minerva Films) * Bookworms (1920, Minerva Films) * The Great Broxopp (1921) * The Dover Road (1921) * The Lucky One (1922) * The Truth About Blayds (1922) * The Artist: A Duologue (1923) * Give Me Yesterday (1923) (a.k.a. Success in the UK) * Ariadne (1924) * The Man in the Bowler Hat: A Terribly Exciting Affair (1924) * To Have the Honour (1924) * Portrait of a Gentleman in Slippers (1926) * Success (1926) * Miss Marlow at Play (1927) * The Fourth Wall or The Perfect Alibi (1928) (later adapted for the film Birds of Prey (1930), directed by Basil Dean) * The Ivory Door (1929) * Toad of Toad Hall (1929) (adaptation of The Wind in the Willows) * Michael and Mary (1930) * Other People’s Lives (1933) (a.k.a. They Don’t Mean Any Harm) * Miss Elizabeth Bennet (1936) [based on Pride and Prejudice] * Sarah Simple (1937) * Gentleman Unknown (1938) * The General Takes Off His Helmet (1939) in The Queen’s Book of the Red Cross * The Ugly Duckling (1941) * Before the Flood (1951). References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A._A._Milne


John Keble (25 April 1792– 29 March 1866) was an English churchman and poet, one of the leaders of the Oxford Movement. Keble College, Oxford was named after him. Life and writings Early life Keble was born in Fairford, Gloucestershire where his father, the Rev. John Keble, was Vicar of Coln St. Aldwyns. He attended Corpus Christi College, Oxford, and, after a brilliant academic performance there, became a Fellow of Oriel College, Oxford, and was for some years a tutor and examiner in the University. While still at Oxford he took Holy Orders in 1815, and became first a curate to his father, and later curate of St Michael and St Martin’s Church, Eastleach Martin in Gloucestershire. The Christian Year Meantime, he had been writing 'The Christian Year’, which appeared in 1827, and met with an almost unparalleled acceptance. Though at first anonymous, its authorship soon became known, with the result that Keble was in 1831 appointed to the Chair of Poetry at Oxford, which he held until 1841. Victorian scholar Michael Wheeler calls The Christian Year simply “the most popular volume of verse in the nineteenth century”. In his essay on Tractarian Aesthetics and the Romantic Tradition, Gregory Goodwin claims that The Christian Year is “Keble’s greatest contribution to the Oxford Movement and to English literature.” As evidence of that Goodwin cites E. B. Pusey’s report that ninety-five editions of this devotional text were printed during Keble’s lifetime, and “at the end of the year following his death, the number had arisen to a hundred-and-nine”. By the time the copyright expired in 1873, over 375,000 copies had been sold in Britain and 158 editions had been published. Notwithstanding its widespread appeal among the Victorian readers, the popularity of Keble’s The Christian Year faded in the twentieth century despite the familiarity of certain well-known hymns, e.g. “New every morning is the love.” Tractarianism and Vicar of Hursley In 1833 his famous Assize Sermon on “National Apostasy” gave the first impulse to the Oxford Movement, also known as the Tractarian movement. Along with his colleagues, including John Henry Newman and Edward Pusey, he became a leading light in the movement, but did not follow Newman into the Roman Catholic Church. In 1835 he was appointed Vicar of Hursley, Hampshire, where he settled down to family life and remained for the rest of his life as a parish priest at All Saints Church. He was a profound influence on a near neighbour, the author Charlotte Mary Yonge. Other writings In 1846 he published another book of poems, Lyra Innocentium. Other works were a Life of Wilson, Bishop of Sodor and Man, and an edition of the Works of Hooker. After his death appeared Letters of Spiritual Counsel, and 12 volumes of Parish Sermons. He also wrote hymns, such as “The Voice that Breathed o’er Eden” and Sun of our soul, Thou Saviour dear Biographies Two lives of Keble have been written, one by John Taylor Coleridge (1869), and the other by Rev. Walter Lock (1895). In 1963 Georgina Battiscombe wrote a biography titled John Keble: a Study in Limitations. Death Keble died in Bournemouth at the Hermitage Hotel, after visiting the area to try and recover from a long term illness as he believed the sea air had therapeutic qualities. He is buried in All Saints’ churchyard, Hursley. Legacy Keble’s feast day is kept on 14 July (the anniversary of his Assize Sermon) in the Church of England, and a commemoration observed on 29 March (the anniversary of his death) elsewhere in the Anglican Communion. Keble College, Oxford was founded in his memory. The view from Bulverton Hill, Sidmouth, is thought to have inspired 19th century poet and hymn writer John Keble to compose some of his best loved work, Keble’s Seat at Bulverton Hill is named after the English churchman and commands a panoramic view of the Lower Otter Valley and Dartmoor in the distance. He was a frequent visitor to Sidmouth and folklore suggests that Keble’s favourite spot was at Bulverton Hill where a wooden bench known as Keble’s Seat remains to this day. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Keble


Walter John de la Mare (25 April 1873 – 22 June 1956) was an English poet, short story writer and novelist. He is probably best remembered for his works for children, for his poem “The Listeners”, and for subtle psychological horror stories, amongst them “Seaton’s Aunt” and “Out of the Deep”. His 1921 novel Memoirs of a Midget won the James Tait Black Memorial Prize for fiction, and his post-war Collected Stories for Children won the 1947 Carnegie Medal for British children’s books.
#English #XIXCentury #XXCentury

.jpg?locale=es)
Sir William Schwenck Gilbert (18 November 1836– 29 May 1911) was an English dramatist, librettist, poet and illustrator best known for the fourteen comic operas (known as the Savoy operas) produced in collaboration with the composer Sir Arthur Sullivan. The most famous of these include H.M.S. Pinafore, The Pirates of Penzance and one of the most frequently performed works in the history of musical theatre, The Mikado. These, as well as several of the other Savoy operas, continue to be frequently performed in the English-speaking world and beyond by opera companies, repertory companies, schools and community theatre groups. Lines from these works have become part of the English language, such as “short, sharp shock”, “What, never? Well, hardly ever!”, and “Let the punishment fit the crime”. Gilbert also wrote the Bab Ballads, an extensive collection of light verse accompanied by his own comical drawings. His creative output included over 75 plays and libretti, numerous stories, poems, lyrics and various other comic and serious pieces. His plays and realistic style of stage direction inspired other dramatists, including Oscar Wilde and George Bernard Shaw. According to The Cambridge History of English and American Literature, Gilbert’s “lyrical facility and his mastery of metre raised the poetical quality of comic opera to a position that it had never reached before and has not reached since”. Early life and career Beginnings Gilbert was born at 17 Southampton Street, Strand, London. His father, also named William, was briefly a naval surgeon, who later became a writer of novels and short stories, some of which were illustrated by his son. Gilbert’s mother was the former Anne Mary Bye Morris (1812–1888), the daughter of Thomas Morris, an apothecary. Gilbert’s parents were distant and stern, and he did not have a particularly close relationship with either of them. They quarrelled increasingly, and following the break-up of their marriage in 1876, his relationships with them, especially his mother, became even more strained. Gilbert had three younger sisters, two of whom were born outside England because of the family’s travels during these years: Jane Morris (b. 1838 in Milan, Italy– 1906), who married Alfred Weigall, a miniatures painter; Anne Maude (1845–1932) and Mary Florence (b. 1843 in Boulogne, France– 1911), neither of whom married. Gilbert was nicknamed “Bab” as a baby, and then “Schwenck”, after his father’s godparents. As a child, Gilbert travelled to Italy in 1838 and then France for two years with his parents, who finally returned to settle in London in 1847. He was educated at Boulogne, France from the age of seven (he later kept his diary in French so that the servants could not read it), then at Western Grammar School, Brompton, London, and then at the Great Ealing School, where he became head boy and wrote plays for school performances and painted scenery. He then attended King’s College London, graduating in 1856. He intended to take the examinations for a commission in the Royal Artillery, but with the end of the Crimean War, fewer recruits were needed, and the only commission available to Gilbert would have been in a line regiment. Instead he joined the Civil Service: he was an assistant clerk in the Privy Council Office for four years and hated it. In 1859 he joined the Militia, a part-time volunteer force formed for the defence of Britain, with which he served until 1878 (in between writing and other work), reaching the rank of Captain. In 1863 he received a bequest of £300 that he used to leave the civil service and take up a brief career as a barrister (he had already entered the Inner Temple as a student), but his legal practice was not successful, averaging just five clients a year. To supplement his income from 1861 on, Gilbert wrote a variety of stories, comic rants, grotesque illustrations, theatre reviews (many in the form of a parody of the play being reviewed), and, under the pseudonym “Bab” (his childhood nickname), illustrated poems for several comic magazines, primarily Fun, started in 1861 by H. J. Byron. He published stories, articles, and reviews in papers such as the Cornhill Magazine, London Society, Tinsley’s Magazine and Temple Bar. In addition, Gilbert was the London correspondent for L’Invalide Russe and a drama critic for the Illustrated London Times. In the 1860s he also contributed to Tom Hood’s Christmas annuals, to Saturday Night, the Comic News and the Savage Club Papers. The Observer newspaper in 1870 sent him to France as a war correspondent reporting on the Franco-Prussian War. The poems, illustrated humorously by Gilbert, proved immensely popular and were reprinted in book form as the Bab Ballads. He would later return to many of these as source material for his plays and comic operas. Gilbert and his colleagues from Fun, including Tom Robertson, Tom Hood, Clement Scott and F. C. Burnand (who defected to Punch in 1862) frequented the Arundel Club, the Savage Club, and especially Evans’s café, where they had a table in competition with the Punch 'Round table’. After a relationship in the mid-1860s with novelist Annie Thomas, Gilbert married Lucy Agnes Turner, whom he called “Kitty”, in 1867; she was 11 years his junior. He wrote many affectionate letters to her over the years. Gilbert and Lucy were socially active both in London and later at Grim’s Dyke, often holding dinner parties and being invited to others’ homes for dinner, in contrast to the picture painted by fictionalisations such as the film Topsy-Turvy. The Gilberts had no children, but they had many pets, including some exotic ones. First plays Gilbert wrote and directed a number of plays at school, but his first professionally produced play was Uncle Baby, which ran for seven weeks in the autumn of 1863. In 1865–66, Gilbert collaborated with Charles Millward on several pantomimes, including one called Hush-a-Bye, Baby, On the Tree Top, or, Harlequin Fortunia, King Frog of Frog Island, and the Magic Toys of Lowther Arcade (1866). Gilbert’s first solo success, however, came a few days after Hush-a-Bye Baby premiered. His friend and mentor, Tom Robertson, was asked to write a pantomime but did not think he could do it in the two weeks available, and so he recommended Gilbert instead. Written and rushed to the stage in 10 days, Dulcamara, or the Little Duck and the Great Quack, a burlesque of Gaetano Donizetti’s L’elisir d’amore, proved extremely popular. This led to a long series of further Gilbert opera burlesques, pantomimes and farces, full of awful puns (traditional in burlesques of the period), though showing, at times, signs of the satire that would later be a defining part of Gilbert’s work. For instance: This was followed by Gilbert’s penultimate operatic parody, Robert the Devil, a burlesque of Giacomo Meyerbeer’s opera, Robert le diable, which was part of a triple bill that opened the Gaiety Theatre, London in 1868. The piece was Gilbert’s biggest success to date, running for over 100 nights and being frequently revived and played continuously in the provinces for three years thereafter. In Victorian theatre, "[to degrade] high and beautiful themes... had been the regular proceeding in burlesque, and the age almost expected it" However, Gilbert’s burlesques were considered unusually tasteful compared to the others on the London stage. Isaac Goldberg wrote that these pieces “reveal how a playwright may begin by making burlesque of opera and end by making opera of burlesque.” Gilbert would depart even further from the burlesque style from about 1869 with plays containing original plots and fewer puns. His first full-length prose comedy was An Old Score (1869). German Reed entertainments and other plays of the early 1870s Theatre, at the time Gilbert began writing, had fallen into disrepute. Badly translated and adapted French operettas and poorly written, prurient Victorian burlesques dominated the London stage. As Jessie Bond vividly described it, “stilted tragedy and vulgar farce were all the would-be playgoer had to choose from, and the theatre had become a place of evil repute to the righteous British householder.” From 1869 to 1875, Gilbert joined with one of the leading figures in theatrical reform, Thomas German Reed (and his wife Priscilla), whose Gallery of Illustration sought to regain some of theatre’s lost respectability by offering family entertainments in London. So successful were they that by 1885 Gilbert stated that original British plays were appropriate for an innocent 15-year-old girl in the audience. Three months before the opening of Gilbert’s last burlesque (The Pretty Druidess), the first of his pieces for the Gallery of Illustration, No Cards, was produced. Gilbert created six musical entertainments for the German Reeds, some with music composed by Thomas German Reed himself. The environment of the German Reeds’ intimate theatre allowed Gilbert quickly to develop a personal style and freedom to control all aspects of production, including set, costumes, direction and stage management. These works were a success, with Gilbert’s first big hit at the Gallery of Illustration, Ages Ago, opening in 1869. Ages Ago was also the beginning of a collaboration with the composer Frederic Clay that would last seven years and produce four works. It was at a rehearsal for Ages Ago that Clay formally introduced Gilbert to his friend, Arthur Sullivan. The Bab Ballads and Gilbert’s many early musical works gave him much practice as a lyricist even before his collaboration with Sullivan. Many of the plot elements of the German Reed Entertainments (as well as some from his earlier plays and Bab Ballads) would be reused by Gilbert later in the Gilbert and Sullivan operas. These elements include paintings coming to life (Ages Ago, used again in Ruddigore), a deaf nursemaid binding a respectable man’s son to a “pirate” instead of to a “pilot” by mistake (Our Island Home, 1870, reused in The Pirates of Penzance), and the forceful mature lady who is “an acquired taste” (Eyes and No Eyes, 1875, reused in The Mikado). During this time, Gilbert perfected the 'topsy-turvy’ style that he had been developing in his Bab Ballads, where the humour was derived by setting up a ridiculous premise and working out its logical consequences, however absurd. Mike Leigh describes the “Gilbertian” style as follows: "With great fluidity and freedom, [Gilbert] continually challenges our natural expectations. First, within the framework of the story, he makes bizarre things happen, and turns the world on its head. Thus the Learned Judge marries the Plaintiff, the soldiers metamorphose into aesthetes, and so on, and nearly every opera is resolved by a deft moving of the goalposts... His genius is to fuse opposites with an imperceptible sleight of hand, to blend the surreal with the real, and the caricature with the natural. In other words, to tell a perfectly outrageous story in a completely deadpan way.” At the same time, Gilbert created several 'fairy comedies’ at the Haymarket Theatre. This series of plays was founded upon the idea of self-revelation by characters under the influence of some magic or some supernatural interference. The first was The Palace of Truth (1870), based partly on a story by Madame de Genlis. In 1871, with Pygmalion and Galatea, one of seven plays that he produced that year, Gilbert scored his greatest hit to date. Together, these plays and their successors such as The Wicked World (1873), Sweethearts (1874), and Broken Hearts (1875), did for Gilbert on the dramatic stage what the German Reed entertainments had done for him on the musical stage: they established that his capabilities extended far beyond burlesque, won him artistic credentials, and demonstrated that he was a writer of wide range, as comfortable with human drama as with farcical humour. The success of these plays, especially Pygmalion and Galatea, gave Gilbert a prestige that would be crucial to his later collaboration with as respected a musician as Sullivan. Though dated, these works demonstrate Gilbert’s desire to give respectable and well-educated theatre audiences comedies that were more refined and tasteful than the usual farces and burlesques playing in London. On the other hand, during the same period, Gilbert pushed the boundaries of how far satire could go in the theatre. He collaborated with Gilbert Arthur à Beckett on The Happy Land (1873), a political satire (in part, a parody of his own The Wicked World), which was briefly banned because of its unflattering caricatures of Gladstone and his ministers. Similarly, The Realm of Joy (1873) was set in the lobby of a theatre performing a scandalous play (implied to be the Happy Land), with many jokes at the expense of the Lord Chamberlain (the “Lord High Disinfectant”, as he’s referred to in the play). In Charity (1874), however, Gilbert uses the freedom of the stage in a different way: to provide a tightly-written critique of the contrasting ways in which Victorian society treated men and women who had sex outside of marriage, which anticipated the 'problem plays’ of Shaw and Ibsen. As a director Once he became established, Gilbert was the stage director for his plays and operas and had strong opinions on how they should best be performed. He was strongly influenced by the innovations in 'stagecraft’, now called stage direction, by the playwrights James Planché and especially Tom Robertson. Gilbert attended rehearsals directed by Robertson to learn this art firsthand from the older director, and he began to apply it in some of his earliest plays. He sought realism in acting, settings, costumes and movement, if not in content of his plays (although he did write a romantic comedy in the “naturalist” style, as a tribute to Robertson, Sweethearts), shunned self-conscious interaction with the audience, and insisted on a style of portrayal in which the characters were never aware of their own absurdity, but were coherent internal wholes. In Gilbert’s 1874 burlesque, Rosencrantz and Guildenstern, the character Hamlet, in his speech to the players, sums up Gilbert’s theory of comic acting: “I hold that there is no such antick fellow as your bombastical hero who doth so earnestly spout forth his folly as to make his hearers believe that he is unconscious of all incongruity”. With his work along these lines, Gilbert set the ground for later playwrights such as George Bernard Shaw and Oscar Wilde to be able to flourish on the English stage. Robertson "introduced Gilbert both to the revolutionary notion of disciplined rehearsals and to mise-en-scène or unity of style in the whole presentation– direction, design, music, acting." Like Robertson, Gilbert demanded discipline in his actors. He required that his actors know their words perfectly, enunciate them clearly and obey his stage directions, which was something quite new to many actors of the day. A major innovation was the replacement of the star actor with the disciplined ensemble, “raising the director to a new position of dominance” in the theatre. “That Gilbert was a good director is not in doubt. He was able to extract from his actors natural, clear performances, which served the Gilbertian requirements of outrageousness delivered straight.” Gilbert prepared meticulously for each new work, making models of the stage, actors and set pieces, and designing every action and bit of business in advance. Gilbert would not work with actors who challenged his authority. Even during long runs and revivals, Gilbert closely supervised the performances of his plays, making sure that the actors did not make unauthorised additions, deletions or paraphrases. Gilbert was famous for demonstrating the action himself, even as he grew older. Gilbert himself went on stage in a number of productions throughout his lifetime, including several performances as the Associate in Trial by Jury, as substitute for an ailing actor in his play Broken Hearts, and in charity matinees of his one-act plays, such as King Claudius in Rosencrantz and Guildenstern. Collaboration with Sullivan First collaborations amidst other works In 1871, John Hollingshead commissioned Gilbert to work with Sullivan on a holiday piece for Christmas, Thespis, or The Gods Grown Old, at the Gaiety Theatre. Thespis outran five of its nine competitors for the 1871 holiday season, and its run was extended beyond the length of a normal run at the Gaiety, However, nothing more came of it at that point, and Gilbert and Sullivan went their separate ways. Gilbert worked again with Clay on Happy Arcadia (1872), and with Alfred Cellier on Topsyturveydom (1874), as well as writing several farces, operetta libretti, extravaganzas, fairy comedies, adaptations from novels, translations from the French, and the dramas described above. Also in 1874, he published his last contribution for Fun magazine ("Rosencrantz and Guildenstern"), after a gap of three years, then resigned due to disapproval of the new owner’s other publishing interests. It would be nearly four years after Thespis was produced before the two men worked together again. In 1868, Gilbert had published a short comedic sketch libretto in Fun magazine entitled “Trial by Jury: An Operetta”. In 1873, Gilbert arranged with the theatrical manager and composer, Carl Rosa, to expand the piece into a one-act libretto. Rosa’s wife was to sing the role of the plaintiff. However, Rosa’s wife died in childbirth in 1874. Later in 1874 Gilbert offered the libretto to Richard D’Oyly Carte, but Carte could not use the piece at that time. By early 1875, Carte was managing the Royalty Theatre, and he needed a short opera to be played as an afterpiece to Offenbach’s La Périchole. He contacted Gilbert, asked about the piece, and suggested Sullivan to set the work. Sullivan was enthusiastic, and Trial by Jury was composed in a matter of weeks. The little piece was a runaway hit, outlasting the run of La Périchole and being revived at another theatre. Gilbert continued his quest to gain respect in and respectability for his profession. One thing that may have been holding dramatists back from respectability was that plays were not published in a form suitable for a “gentleman’s library”, as, at the time, they were generally cheaply and unattractively published for the use of actors rather than the home reader. To help rectify this, at least for himself, Gilbert arranged in late 1875 for publishers Chatto and Windus to print a volume of his plays in a format designed to appeal to the general reader, with an attractive binding and clear type, containing Gilbert’s most respectable plays, including his most serious works, but mischievously capped off with Trial by Jury. After the success of Trial by Jury, there were discussions towards reviving Thespis, but Gilbert and Sullivan were not able to agree on terms with Carte and his backers. The score to Thespis was never published, and most of the music is now lost. It took some time for Carte to gather funds for another Gilbert and Sullivan opera, and in this gap Gilbert produced several works including Tom Cobb (1875), Eyes and No Eyes (1875, his last German Reed Entertainment), and Princess Toto (1876), his last and most ambitious work with Clay, a three-act comic opera with full orchestra, as opposed to the shorter works for much reduced accompaniment that came before. Gilbert also wrote two serious works during this time, Broken Hearts (1875) and Dan’l Druce, Blacksmith (1876). Also during this period, Gilbert wrote his most successful comic play, Engaged (1877), which inspired Oscar Wilde’s The Importance of Being Earnest. Engaged is a parody of romantic drama written in the “topsy-turvy” satiric style of many of Gilbert’s Bab Ballads and the Savoy Operas, with one character pledging his love, in the most poetic and romantic language possible, to every single woman in the play; the “innocent” Scottish rustics being revealed to be making a living through throwing trains off the lines and then charging the passengers for services, and, in general, romance being gladly thrown over in favour of monetary gain. Engaged continues to be performed today by both professional and amateur companies. Peak collaborative years Carte finally assembled a syndicate in 1877 and formed the Comedy Opera Company to launch a series of original English comic operas, beginning with a third collaboration between Gilbert and Sullivan, The Sorcerer, in November 1877. This work was a modest success, and H.M.S. Pinafore followed in May 1878. Despite a slow start, mainly due to a scorching summer, Pinafore became a red-hot favourite by autumn. After a dispute with Carte over the division of profits, the other Comedy Opera Company partners hired thugs to storm the theatre one night to steal the sets and costumes, intending to mount a rival production. The attempt was repelled by stagehands and others at the theatre loyal to Carte, and Carte continued as sole impresario of the newly renamed D’Oyly Carte Opera Company. Indeed, Pinafore was so successful that over a hundred unauthorised productions sprang up in America alone. Gilbert, Sullivan and Carte tried for many years to control the American performance copyrights over their operas, without success. For the next decade, the Savoy Operas (as the series came to be known, after the theatre Carte later built to house them) were Gilbert’s principal activity. The successful comic operas with Sullivan continued to appear every year or two, several of them being among the longest-running productions up to that point in the history of the musical stage. After Pinafore came The Pirates of Penzance (1879), Patience (1881), Iolanthe (1882), Princess Ida (1884, based on Gilbert’s earlier farce, The Princess), The Mikado (1885), Ruddigore (1887), The Yeomen of the Guard (1888), and The Gondoliers (1889). Gilbert not only directed and oversaw all aspects of production for these works, but he actually designed the costumes himself for Patience, Iolanthe, Princess Ida, and Ruddigore. He insisted on precise and authentic sets and costumes, which provided a foundation to ground and focus his absurd characters and situations. During this time, Gilbert and Sullivan also collaborated on one other major work, the oratorio The Martyr of Antioch, premiered at the Leeds music festival in October 1880. Gilbert arranged the original epic poem by Henry Hart Milman into a libretto suitable for the music, and it contains some original work. During this period, also, Gilbert occasionally wrote plays to be performed elsewhere–both serious dramas (for example The Ne’er-Do-Weel, 1878; and Gretchen, 1879) and humorous works (for example Foggerty’s Fairy, 1881). However, he no longer needed to turn out multiple plays each year, as he had done before. Indeed, during the more than nine years that separated The Pirates of Penzance and The Gondoliers, he wrote just three plays outside of the partnership with Sullivan. Only one of these works, Comedy and Tragedy, proved successful. In 1878, Gilbert realised a lifelong dream to play Harlequin, which he did at the Gaiety Theatre as part of an amateur charity production of The Forty Thieves, partly written by himself. Gilbert trained for Harlequin’s stylised dancing with his friend John D’Auban, who had arranged the dances for some of his plays and would choreograph most of the Gilbert and Sullivan operas. Producer John Hollingshead later remembered, “the gem of the performance was the grimly earnest and determined Harlequin of W. S. Gilbert. It gave me an idea of what Oliver Cromwell would have made of the character.” Another member of the cast recalled that Gilbert was tirelessly enthusiastic about the piece and often invited the cast to his home for dinner extra rehearsals. “A pleasanter, more genial, or agreeable companion than he was it would have been difficult, if not impossible, to find.” In 1882, Gilbert had a telephone installed in his home and at the prompt desk at the Savoy Theatre, so that he could monitor performances and rehearsals from his home study. Gilbert had referred to the new technology in Pinafore in 1878, only two years after the device was invented and before London even had telephone service. Carpet quarrel and end of the collaboration Gilbert sometimes had a strained working relationship with Sullivan, partly because each man saw himself allowing his work to be subjugated to the other’s, and partly due to their opposing personalities. Gilbert was often confrontational and notoriously thin-skinned, though prone to acts of extraordinary kindness, while Sullivan eschewed conflict. In addition, Gilbert imbued his libretti with “topsy-turvy” situations in which the social order was turned upside down. After a time, these subjects were often at odds with Sullivan’s desire for realism and emotional content. In addition, Gilbert’s political satire often poked fun at those in the circles of privilege, while Sullivan was eager to socialise among the wealthy and titled people who would become his friends and patrons. Throughout their collaboration, Gilbert and Sullivan disagreed several times over the choice of a subject. After both Princess Ida and Ruddigore, which were less successful than the seven other operas from H.M.S. Pinafore to The Gondoliers, Sullivan asked to leave the partnership, saying that he found Gilbert’s plots repetitive and that the operas were not artistically satisfying to him. While the two artists worked out their differences, Carte kept the Savoy open with revivals of their earlier works. On each occasion, after a few months’ pause, Gilbert responded with a libretto that met Sullivan’s objections, and the partnership continued successfully. In April 1890, during the run of The Gondoliers, however, Gilbert challenged Carte over the expenses of the production. Among other items to which Gilbert objected, Carte had charged the cost of a new carpet for the Savoy Theatre lobby to the partnership. Gilbert believed that this was a maintenance expense that should be charged to Carte alone. Gilbert confronted Carte, who refused to reconsider the accounts. Gilbert stormed out and wrote to Sullivan that “I left him with the remark that it was a mistake to kick down the ladder by which he had risen”. Helen Carte wrote that Gilbert had addressed Carte “in a way that I should not have thought you would have used to an offending menial.” As scholar Andrew Crowther has explained: After all, the carpet was only one of a number of disputed items, and the real issue lay not in the mere money value of these things, but in whether Carte could be trusted with the financial affairs of Gilbert and Sullivan. Gilbert contended that Carte had at best made a series of serious blunders in the accounts, and at worst deliberately attempted to swindle the others. It is not easy to settle the rights and wrongs of the issue at this distance, but it does seem fairly clear that there was something very wrong with the accounts at this time. Gilbert wrote to Sullivan on 28 May 1891, a year after the end of the “Quarrel”, that Carte had admitted "an unintentional overcharge of nearly £1,000 in the electric lighting accounts alone.” Gilbert brought suit, and after The Gondoliers closed in 1891, he withdrew the performance rights to his libretti, vowing to write no more operas for the Savoy. Gilbert next wrote The Mountebanks with Alfred Cellier and the flop Haste to the Wedding with George Grossmith, and Sullivan wrote Haddon Hall with Sydney Grundy. Gilbert eventually won the lawsuit and felt vindicated, but his actions and statements had been hurtful to his partners. Nevertheless, the partnership had been so profitable that, after the financial failure of the Royal English Opera House, Carte and his wife sought to reunite the author and composer. In 1891, after many failed attempts at reconciliation by the pair, Tom Chappell, the music publisher responsible for printing the Gilbert and Sullivan operas, stepped in to mediate between two of his most profitable artists, and within two weeks had succeeded. Two more operas resulted: Utopia, Limited (1893) and The Grand Duke (1896). Gilbert also offered a third libretto to Sullivan (His Excellency, 1894), but Gilbert’s insistence on casting Nancy McIntosh, his protegée from Utopia, led to Sullivan’s refusal. Utopia, concerning an attempt to “anglicise” a south Pacific island kingdom, was only a modest success, and The Grand Duke, in which a theatrical troupe, by means of a “statutory duel” and a conspiracy, takes political control of a grand duchy, was an outright failure. After that, the partnership ended for good. Sullivan continued to compose comic opera with other librettists but died four years later. In 1904, Gilbert would write, “... Savoy opera was snuffed out by the deplorable death of my distinguished collaborator, Sir Arthur Sullivan. When that event occurred, I saw no one with whom I felt that I could work with satisfaction and success, and so I discontinued to write libretti.” Later years Gilbert built the Garrick Theatre in 1889. The Gilberts moved to Grim’s Dyke in Harrow in 1890, which he purchased from Robert Heriot, to whom the artist Frederick Goodall had sold the property in 1880. In 1891, Gilbert was appointed Justice of the Peace for Middlesex. After casting Nancy McIntosh in Utopia, Limited, he and Lady Gilbert developed an affection for her, and she eventually gained the status of an unofficially adopted daughter, moving to Grim’s Dyke to live with them. She continued living there, even after Gilbert’s death, until Lady Gilbert’s death in 1936. A statue of Charles II, carved by Danish sculptor Caius Gabriel Cibber in 1681, was moved in 1875 from Soho Square to an island in the lake at Grim’s Dyke, where it remained when Gilbert purchased the property. On Lady Gilbert’s direction, it was restored to Soho Square in 1938. Although Gilbert announced a retirement from the theatre after the poor initial run of his last work with Sullivan, The Grand Duke (1896) and the poor reception of his 1897 play The Fortune Hunter, he produced at least three more plays over the last dozen years of his life, including an unsuccessful opera, Fallen Fairies (1909), with Edward German. Gilbert also continued to supervise the various revivals of his works by the D’Oyly Carte Opera Company, including its London Repertory seasons in 1906–09. His last play, The Hooligan, produced just four months before his death, is a study of a young condemned thug in a prison cell. Gilbert shows sympathy for his protagonist, the son of a thief who, brought up among thieves, kills his girlfriend. As in some earlier work, the playwright displays “his conviction that nurture rather than nature often accounted for criminal behaviour”. The grim and powerful piece became one of Gilbert’s most successful serious dramas, and experts conclude that, in those last months of Gilbert’s life, he was developing a new style, a “mixture of irony, of social theme, and of grubby realism,” to replace the old “Gilbertianism” of which he had grown weary. In these last years, Gilbert also wrote children’s book versions of H.M.S. Pinafore and The Mikado giving, in some cases, backstory that is not found in the librettos. Gilbert was knighted on 15 July 1907 in recognition of his contributions to drama. Sullivan had been knighted for his contributions to music almost a quarter of a century earlier, in 1883. Gilbert was, however, the first British writer ever to receive a knighthood for his plays alone—earlier dramatist knights, such as Sir William Davenant and Sir John Vanbrugh, were knighted for political and other services. On 29 May 1911, Gilbert was about to give a swimming lesson to two young women, Winifred Isabel Emery (1890–1972), and 17-year-old Ruby Preece in the lake of his home, Grim’s Dyke, when Preece lost her footing and called for help. Gilbert dived in to save her but suffered a heart attack in the middle of the lake and died. He was cremated at Golders Green and his ashes buried at the Church of St. John the Evangelist, Stanmore. The inscription on Gilbert’s memorial on the south wall of the Thames Embankment in London reads: “His Foe was Folly, and his Weapon Wit”. There is also a memorial plaque at All Saints’ Church, Harrow Weald. Personality Gilbert was known for being prickly. Aware of this general impression, he claimed that “If you give me your attention”, the misanthrope’s song from Princess Ida, was a satiric self-reference, saying: “I thought it my duty to live up to my reputation.” However, many people have defended him, often citing his generosity. Actress May Fortescue recalled, “His kindness was extraordinary. On wet nights and when rehearsals were late and the last buses were gone, he would pay the cab-fares of the girls whether they were pretty or not, instead of letting them trudge home on foot... He was just as large-hearted when he was poor as when he was rich and successful. For money as money he cared less than nothing. Gilbert was no plaster saint, but he was an ideal friend.” Journalist Frank M. Boyd wrote: I fancy that seldom was a man more generally given credit for a personality quite other than his own, than was the case with Sir W. S. Gilbert... Till one actually came to know the man, one shared the opinion held by so many, that he was a gruff, disagreeable person; but nothing could be less true of the really great humorist. He had rather a severe appearance... and like many other clever people, he had precious little use for fools of either sex, but he was at heart as kindly and lovable a man as you could wish to meet. Jessie Bond wrote that Gilbert “was quick-tempered, often unreasonable, and he could not bear to be thwarted, but how anyone could call him unamiable I cannot understand.” George Grossmith wrote to The Daily Telegraph that, although Gilbert had been described as an autocrat at rehearsals, “That was really only his manner when he was playing the part of stage director at rehearsals. As a matter of fact, he was a generous, kind true gentleman, and I use the word in the purest and original sense.” Aside from his occasional creative disagreements with, and eventual rift from, Sullivan, Gilbert’s temper led to the loss of friendships with a number of people. For instance, he quarrelled with his old associate C. H. Workman, over the firing of Nancy McIntosh from the production of Fallen Fairies, and with actress Henrietta Hodson. He also saw his friendship with theatre critic Clement Scott turn bitter. However, Gilbert could be extraordinarily kind. During Scott’s final illness in 1904, for instance, Gilbert donated to a fund for him, visited nearly every day, and assisted Scott’s wife, despite having not been on friendly terms with him for the previous sixteen years. Similarly, Gilbert had written several plays at the behest of comic actor Ned Sothern. However, Sothern died before he could perform the last of these, Foggerty’s Fairy. Gilbert purchased the play back from his grateful widow. According to one London society lady: [Gilbert]'s wit was innate, and his rapier-like retorts slipped out with instantaneous ease. His mind was naturally fastidious and clean; he never asserted himself, never tried to make an effect. He was great-hearted and most understanding, with an underlying poetry of fancy that made him the most delicious companion. They spoke of his quick temper, but that was entirely free from malice or guile. He was soft-hearted as a babe, but there was nothing of the hypocrite about him. What he thought he said on the instant, and though by people of sensitive vanity this might on occasion be resented, to a sensitiveness of a finer kind it was an added link, binding one to a faithful, valued friend. As the writings about Gilbert by husband and wife Seymour Hicks and Ellaline Terriss (frequent guests at his home) vividly illustrate, Gilbert’s relationships with women were generally more successful than his relationships with men. According to George Grossmith, Gilbert “was to those who knew him a courteous and amiable gentleman– a gentleman without veneer.” Grossmith and many others wrote of how Gilbert loved to amuse children: During my dangerous illness, Mr. Gilbert never failed a day to come up and enquire after me... and kept me in roars of laughter the whole time... But to see Gilbert at his best, is to see him at one of his juvenile parties. Though he has no children of his own, he loves them, and there is nothing he would not do to please them. I was never so astonished as when on one occasion he put off some of his own friends to come with Mrs. Gilbert to a juvenile party at my own house. Gilbert’s niece Mary Carter confirmed, "... he loved children very much and lost no opportunity of making them happy... [He was] the kindest and most human of uncles." Grossmith quoted Gilbert as saying, “Deer-stalking would be a very fine sport if only the deer had guns.” Legacy In 1957, a review in The Times explained “the continued vitality of the Savoy operas” as follows: [T]hey were never really contemporary in their idiom... Gilbert and Sullivan’s [world], from the first moment was obviously not the audience’s world, [it was] an artificial world, with a neatly controlled and shapely precision which has not gone out of fashion– because it was never in fashion in the sense of using the fleeting conventions and ways of thought of contemporary human society... The neat articulation of incredibilities in Gilbert’s plots is perfectly matched by his language... His dialogue, with its primly mocking formality, satisfies both the ear and the intelligence. His verses show an unequalled and very delicate gift for creating a comic effect by the contrast between poetic form and prosaic thought and wording... How deliciously [his lines] prick the bubble of sentiment. Gilbert had many imitators, but no equals, at this sort of thing... [Of] equal importance... Gilbert’s lyrics almost invariably take on extra point and sparkle when set to Sullivan’s music... The two men together remain endlessly and incomparably delightful... Light, and even trifling, though [the operas] may seem upon grave consideration, they yet have the shapeliness and elegance that can make a trifle into a work of art. Gilbert’s legacy, aside from building the Garrick Theatre and writing the Savoy Operas and other works that are still being performed or in print over a hundred and twenty-five years after their creation, is felt perhaps most strongly today through his influence on the American and British musical theatre. The innovations in content and form of the works that he and Sullivan developed, and in Gilbert’s theories of acting and stage direction, directly influenced the development of the modern musical throughout the 20th century. Gilbert’s lyrics employ punning, as well as complex internal and two and three-syllable rhyme schemes, and served as a model for such 20th century Broadway lyricists as P.G. Wodehouse, Cole Porter, Ira Gershwin, and Lorenz Hart. Gilbert’s influence on the English language has also been marked, with well-known phrases such as “A policeman’s lot is not a happy one”, “short, sharp shock”, “What never? Well, hardly ever!”, and “let the punishment fit the crime” arising from his pen. In addition, biographies continue to be written about Gilbert’s life and career, and his work is not only performed, but frequently parodied, pastiched, quoted and imitated in comedy routines, film, television and other popular media. Ian Bradley, in connection with the 100th anniversary of Gilbert’s death in 2011 wrote: There has been much discussion about Gilbert’s proper place in British literary and dramatic history. Was he essentially a writer of burlesque, a satirist, or, as some have argued, the forerunner of the theatre of the absurd?... Perhaps he stands most clearly in that distinctively English satirical tradition which stretches back to Jonathan Swift.... Its leading exponents lampoon and send up the major institutions and public figures of the day, wielding the weapon of grave and temperate irony with devastating effect, while themselves remaining firmly within the Establishment and displaying a deep underlying affection for the objects of their often merciless attacks. It is a combination that remains a continuing enigma. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/W._S._Gilbert


Charles Lamb (London, 10 February 1775 – Edmonton, 27 December 1834) was an English essayist, best known for his Essays of Elia and for the children's book Tales from Shakespeare, which he produced with his sister, Mary Lamb (1764–1847). Lamb has been referred to by E.V. Lucas, his principal biographer, as "the most lovable figure in English literature”. Youth and schooling Lamb was the son of Elizabeth Field and John Lamb. Lamb was the youngest child, with an 11 year older sister Mary, an even older brother John, and 4 other siblings who did not survive their infancy. John Lamb (father), who was a lawyer's clerk, spent most of his professional life as the assistant and servant to a barrister by the name of Samuel Salt who lived in the Inner Temple in London. It was there in the Inner Temple in Crown Office Row, that Charles Lamb was born and spent his youth. Lamb created a portrait of his father in his "Elia on the Old Benchers" under the name Lovel. Lamb's older brother was too much his senior to be a youthful companion to the boy but his sister Mary, being born eleven years before him, was probably his closest playmate. Lamb was also cared for by his paternal aunt Hetty, who seems to have had a particular fondness for him. A number of writings by both Charles and Mary suggest that the conflict between Aunt Hetty and her sister-in-law created a certain degree of tension in the Lamb household. However, Charles speaks fondly of her and her presence in the house seems to have brought a great deal of comfort to him. Some of Lamb's fondest childhood memories were of time spent with Mrs. Field, his maternal grandmother, who was for many years a servant to the Plummer family, who owned a large country house called Blakesware, near Widford, Hertfordshire. After the death of Mrs. Plummer, Lamb's grandmother was in sole charge of the large home and, as Mr. Plummer was often absent, Charles had free rein of the place during his visits. A picture of these visits can be glimpsed in the Elia essay Blakesmoor in H—shire. "Why, every plank and panel of that house for me had magic in it. The tapestried [sic] bed-rooms – tapestry so much better than painting – not adorning merely, but peopling the wainscots – at which childhood ever and anon would steal a look, shifting its coverlid (replaced as quickly) to exercise its tender courage in a momentary eye-encounter with those stern bright visages, staring reciprocally – all Ovid on the walls, in colours vivider than his descriptions.” Little is known about Charles's life before the age of seven. We know that Mary taught him to read at a very early age and he read voraciously. It is believed that he suffered from smallpox during his early years which forced him into a long period of convalescence. After this period of recovery Lamb began to take lessons from Mrs. Reynolds, a woman who lived in the Temple and is believed to have been the former wife of a lawyer. Mrs. Reynolds must have been a sympathetic schoolmistress because Lamb maintained a relationship with her throughout his life and she is known to have attended dinner parties held by Mary and Charles in the 1820s. E.V. Lucas suggests that sometime in 1781 Charles left Mrs. Reynolds and began to study at the Academy of William Bird. His time with William Bird did not last long, however, because by October 1782 Lamb was enrolled in Christ's Hospital, a charity boarding school chartered by King Edward VI in 1552. Christ's Hospital was a traditional English boarding school; bleak and full of violence. The headmaster, Mr. Boyer, has become famous for his teaching in Latin and Greek, but also for his brutality. A thorough record of Christ's Hospital in Several essays by Lamb as well as the Autobiography of Leigh Hunt and the Biographia Literaria of Samuel Taylor Coleridge, with whom Charles developed a friendship that would last for their entire lives. Despite the brutality Lamb got along well at Christ's Hospital, due in part, perhaps, to the fact that his home was not far distant thus enabling him, unlike many other boys, to return often to the safety of home. Years later, in his essay "Christ’s Hospital Five and Thirty Years Ago," Lamb described these events, speaking of himself in the third person as "L.” “I remember L. at school; and can well recollect that he had some peculiar advantages, which I and other of his schoolfellows had not. His friends lived in town, and were near at hand; and he had the privilege of going to see them, almost as often as he wished, through some invidious distinction, which was denied to us.” Christ's Hospital was a typical English boarding school and many students later wrote of the terrible violence they suffered there. The upper master of the school from 1778 to 1799 was Reverend James Boyer, a man renowned for his unpredictable and capricious temper. In one famous story Boyer was said to have knocked one of Leigh Hunt's teeth out by throwing a copy of Homer at him from across the room. Lamb seemed to have escaped much of this brutality, in part because of his amiable personality and in part because Samuel Salt, his father's employer and Lamb's sponsor at the school was one of the institute's Governors. Charles Lamb suffered from a stutter and this "an inconquerable impediment" in his speech deprived him of Grecian status at Christ's Hospital and thus disqualifying him for a clerical career. While Coleridge and other scholarly boys were able to go on to Cambridge, Lamb left school at fourteen and was forced to find a more prosaic career. For a short time he worked in the office of Joseph Paice, a London merchant and then, for 23 weeks, until 8 February 1792, held a small post in the Examiner's Office of the South Sea House. Its subsequent downfall in a pyramid scheme after Lamb left would be contrasted to the company's prosperity in the first Elia essay. On 5 April 1792 he went to work in the Accountant's Office for British East India Company, the death of his father's employer having ruined the family's fortunes.Charles would continue to work there for 25 years, until his retirement with pension. In 1792 while tending to his grandmother, Mary Field, in Hertfordshire, Charles Lamb fell in love with a young woman named Ann Simmons. Although no epistolary record exists of the relationship between the two, Lamb seems to have spent years wooing Miss Simmons. The record of the love exists in several accounts of Lamb's writing. Rosamund Gray is a story of a young man named Allen Clare who loves Rosamund Gray but their relationship comes to nothing because of the sudden death of Miss Gray. Miss Simmons also appears in several Elia essays under the name "Alice M." The essays "Dream Children," "New Year's Eve," and several others, speak of the many years that Lamb spent pursuing his love that ultimately failed. Miss Simmons eventually went on to marry a silversmith by the name of Bartram and Lamb called the failure of the affair his 'great disappointment. Family tragedy Charles and his sister Mary both suffered periods of mental illness. Charles spent six weeks in a psychiatric hospital during 1795. He was, however, already making his name as a poet. On 22 September 1796, a terrible event occurred: Mary, "worn down to a state of extreme nervous misery by attention to needlework by day and to her mother at night," was seized with acute mania and stabbed her mother to the heart with a table knife. Although there was no legal status of 'insanity' at the time, a jury returned a verdict of 'Lunacy' and therefore freed her from guilt of willful murder. With the help of friends Lamb succeeded in obtaining his sister's release from what would otherwise have been lifelong imprisonment, on the condition that he take personal responsibility for her safekeeping. Lamb used a large part of his relatively meagre income to keep his beloved sister in a private 'madhouse' in Islington called Fisher House. The 1799 death of John Lamb was something of a relief to Charles because his father had been mentally incapacitated for a number of years since suffering a stroke. The death of his father also meant that Mary could come to live again with him in Pentonville, and in 1800 they set up a shared home at Mitre Court Buildings in the Temple, where they lived until 1809. Despite Lamb's bouts of melancholia and alcoholism, both he and his sister enjoyed an active and rich social life. Their London quarters became a kind of weekly salon for many of the most outstanding theatrical and literary figures of the day. Charles Lamb, having been to school with Samuel Coleridge, counted Coleridge as perhaps his closest, and certainly his oldest, friend. On his deathbed, Coleridge had a mourning ring sent to Lamb and his sister. Fortuitously, Lamb's first publication was in 1796, when four sonnets by "Mr. Charles Lamb of the India House" appeared in Coleridge's Poems on Various Subjects. In 1797 he contributed additional blank verse to the second edition, and met the Wordsworths, William and Dorothy, on his short summer holiday with Coleridge at Nether Stowey, thereby also striking up a lifelong friendship with William. In London, Lamb became familiar with a group of young writers who favoured political reform, including Percy Bysshe Shelley, William Hazlitt, and Leigh Hunt. Lamb continued to clerk for the East India Company and doubled as a writer in various genres, his tragedy, John Woodvil, being published in 1802. His farce, Mr H, was performed at Drury Lane in 1807, where it was roundly booed. In the same year, Tales from Shakespeare (Charles handled the tragedies; his sister Mary, the comedies) was published, and became a best seller for William Godwin's "Children's Library." In 1819, at age 44, Lamb, who, because of family commitments, had never married, fell in love with an actress, Fanny Kelly, of Covent Garden, and proposed marriage. She refused him, and he died a bachelor. His collected essays, under the title Essays of Elia, were published in 1823 ("Elia" being the pen name Lamb used as a contributor to the London Magazine). A further collection was published ten years or so later, shortly before Lamb's death. He died of a streptococcal infection, erysipelas, contracted from a minor graze on his face sustained after slipping in the street, on 27 December 1834, just a few months after Coleridge. He was 59. From 1833 till their deaths Charles and Mary lived at Bay Cottage, Church Street, Edmonton north of London (now part of the London Borough of Enfield. Lamb is buried in All Saints' Churchyard, Edmonton. His sister, who was ten years his senior, survived him for more than a dozen years. She is buried beside him. Work Lamb's first publication was the inclusion of four sonnets in the Coleridge's Poems on Various Subjects published in 1796 by Joseph Cottle. The sonnets were significantly influenced by the poems of Burns and the sonnets of William Bowles, a largely forgotten poet of the late 18th century. His poems garnered little attention and are seldom read today. Lamb's contributions to the second edition of the Poems showed significant growth as a poet. These poems included The Tomb of Douglas and A Vision of Repentance. Because of a temporary fall-out with Coleridge, Lamb's poems were to be excluded in the third edition of the Poems. As it turned out, a third edition never emerged and instead Coleridge's next publication was the monumentally influential Lyrical Ballads co-published with Wordsworth. Lamb, on the other hand, published a book entitled Blank Verse with Charles Lloyd, the mentally unstable son of the founder of Lloyd's Bank. Lamb's most famous poem was written at this time entitled The Old Familiar Faces. Like most of Lamb's poems it is particularly sentimental but it is still remembered and widely read, often included in Poetic Collections. Of particular interest to Lambarians is the opening verse of the original version of The Old Familiar Faces which is concerned with Lamb's mother. It was a verse that Lamb chose to remove from the edition of his Collected Work published in 1818. I had a mother, but she died, and left me, Died prematurely in a day of horrors - All, all are gone, the old familiar faces. From a fairly young age Lamb desired to be a poet but never gained the success that he had hoped. Lamb lived under the poetic shadow of his friend Coleridge. In the final years of the 18th century Lamb began to work on prose with the novella entitled Rosamund Gray, a story of a young girl who was thought to be inspired by Ann Simmonds, with whom Charles Lamb was thought to be in love. Although the story is not particularly successful as a narrative because of Lamb's poor sense of plot, it was well thought of by Lamb's contemporaries and led Shelley to observe “what a lovely thing is Rosamund Gray! How much knowledge of the sweetest part of our nature in it!" (Quoted in Barnett, page 50) n the first years of the 19th century Lamb began his fruitful literary cooperation with his sister Mary. Together they wrote at least three books for William Godwin’s Juvenile Library. The most successful of these was of course Tales From Shakespeare which ran through two editions for Godwin and has now been published dozens of times in countless editions, many of them illustrated. Lamb also contributed a footnote to Shakespearean studies at this time with his essay "On the Tragedies of Shakespeare," in which he argues that Shakespeare should be read rather than performed in order to gain the proper effect of his dramatic genius. Beside contributing to Shakespeare studies with his book Tales From Shakespeare, Lamb also contributed to the popularization of Shakespeare's contemporaries with his book Specimens of the English Dramatic Poets Who Lived About the Time of Shakespeare. Although he did not write his first Elia essay until 1820, Lamb’s gradual perfection of the essay form for which he eventually became famous began as early 1802 in a series of open letters to Leigh Hunt’s Reflector. The most famous of these is called "The Londoner" in which Lamb famously derides the contemporary fascination with nature and the countryside. Legacy Anne Fadiman notes regretfully that Lamb is not widely read in modern times: "I do not understand why so few other readers are clamoring for his company... [he] is kept alive largely through the tenuous resuscitations of university English departments." Lamb was honoured by The Latymer School, a grammar school in Edmonton, a suburb of London where he lived for a time; it has six houses, one of which, "Lamb", is named after Charles. Selected works * Blank Verse, poetry, 1798 * A Tale of Rosamund Gray, and old blind Margaret, 1798 * John Woodvil, poetic drama, 1802 * Tales from Shakespeare, 1807 * The Adventures of Ulysses, 1808 * Specimens of English Dramatic poets who lived about the time of Shakespeare, 1808 * On the Tragedies of Shakespeare, 1811 * Witches and Other Night Fears, 1821 * The Pawnbroker's Daughter, 1825 * Eliana, 1867 * Essays of Elia, 1823 * The Last Essays of Elia, 1833 References Wikipedia – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Lamb


William Cosmo Monkhouse (18 March 1840– 20 July 1901) was an English poet and critic. He was born in London. His father, Cyril John Monkhouse, was a solicitor; his mother’s maiden name was Delafosse. He was educated at St Paul’s School, quitting it at seventeen to enter the board of trade as a junior supplementary clerk, from which grade he rose eventually to be the assistant-secretary to the finance department of the office. In 1870–71 he visited South America in connection with the hospital accommodation for seamen at Valparaíso, Chile, and other ports; and he served on different departmental committees, notably that of 1894–96 on the Mercantile Marine Fund. He was twice married: first, to Laura, daughter of James Keymer of Dartford; and, secondly, to Leonora Eliza, daughter of Commander Blount, R.N.



