
Ursula Kroeber Le Guin (October 21, 1929 – January 22, 2018) was an American novelist. She worked mainly in the genres of fantasy and science fiction. She also authored children’s books, short stories, poetry, and essays. Her writing was first published in the 1960s and often depicted futuristic or imaginary alternative worlds in politics, the natural environment, gender, religion, sexuality, and ethnography. In 2016, The New York Times described her as “America’s greatest living science fiction writer”, although she said that she would prefer to be known as an “American novelist”. She influenced Booker Prize winners and other writers, such as Salman Rushdie and David Mitchell, and science fiction and fantasy writers including Neil Gaiman and Iain Banks. She won the Hugo Award, Nebula Award, Locus Award, and World Fantasy Award, each more than once. In 2014, she was awarded the National Book Foundation Medal for Distinguished Contribution to American Letters. In 2003, she was made a Grandmaster of Science Fiction, one of a few women writers to take the top honor in the genre. Life Birth and family Ursula Kroeber was the daughter of anthropologist Alfred Louis Kroeber of the University of California, Berkeley, and writer Theodora Kracaw. Childhood and education Ursula and her three older brothers, Clifton, Theodore, and Karl Kroeber, were encouraged to read and were exposed to their parents’ dynamic friend group, which included Native Americans and Robert Oppenheimer, who was later to become in part a model for her hero in The Dispossessed. Le Guin stated that, in retrospect, she was grateful for the ease and happiness of her upbringing. The encouraging environment fostered Le Guin’s interest in literature; her first fantasy story was written at age 9, her first science fiction story submitted for publication in the magazine Astounding Science Fiction at age 11. The family spent the academic year in Berkeley, retreating in the summers to “Kishamish” in Napa Valley, "an old, tumble-down ranch... [and] a gathering place for scientists, writers, students, and California Indians. Even though I didn’t pay much attention, I heard a lot of interesting, grown-up conversation." She was interested in biology and poetry, but found math difficult. Le Guin attended Berkeley High School. She received her B.A. (Phi Beta Kappa) in Renaissance French and Italian literature from Radcliffe College in 1951, and M.A. in French and Italian literature from Columbia University in 1952. Soon after, Le Guin began her Ph.D. work and won a Fulbright grant to continue her studies in France from 1953 to 1954. Marriage and family In 1953, while traveling to France aboard the Queen Mary, Le Guin met her future husband, historian Charles Le Guin. They married later that year in Paris. After marrying, Le Guin chose not to continue her doctoral studies of the poet Jean Lemaire de Belges. The couple returned to the United States so that he could pursue his Ph.D. at Emory University. During this time, she worked as a secretary and taught French at the university level. Their first child, Elisabeth (1957), was born in Moscow, Idaho, where Charles taught. In 1958 the Le Guins moved to Portland, Oregon, where their daughter Caroline (1959) was born, and where they lived thereafter. Charles is Emeritus Professor of History at Portland State University. During this time, she continued to make time for writing in addition to maintaining her family life. In 1964, her third child, Theodore, was born. Death Le Guin died on January 22, 2018, at her home in Portland, Oregon; her son stated that she had been in poor health for several months. Her New York Times obituary called her “the immensely popular author who brought literary depth and a tough-minded feminist sensibility to science fiction and fantasy with books like The Left Hand of Darkness and the Earthsea series”. Writing career Le Guin became interested in literature quite early. At age 11, she submitted her first story to the magazine Astounding Science Fiction. Despite being rejected, she continued writing but did not attempt to publish for the next ten years. From 1951 to 1961 she wrote five novels, which publishers rejected, because they seemed inaccessible. She also wrote poetry during this time, including Wild Angels (1975). Her earliest writings, some of which she adapted in Orsinian Tales and Malafrena, were non-fantastic stories set in the imaginary country of Orsinia. Searching for a way to express her interests, she returned to her early interest in science fiction; in the early 1960s her work began to be published regularly. One Orsinian Tale was published in the Summer 1961 issue of The Western Humanities Review and three of her stories appeared in 1962 and 1963 numbers of Fantastic Stories of Imagination, a monthly edited by Cele Goldsmith. Goldsmith also edited Amazing Stories, which ran two of Le Guin’s stories in 1964, including the first “Hainish” story. In 1964 the short story “The Word of Unbinding” was published. This was the first of the Earthsea fantasy series, which includes six books and eight short stories. The three linked young adult novels beginning with A Wizard of Earthsea (1968), The Tombs of Atuan (1970), and The Farthest Shore (1972), sometimes referred to as The Earthsea Trilogy, in later years would be joined by the books Tehanu, Tales from Earthsea and The Other Wind. Le Guin received wide recognition for her novel The Left Hand of Darkness, which won the Hugo and Nebula awards in 1970. Her subsequent novel The Dispossessed made her the first person to win both the Hugo and Nebula Awards for Best Novel twice for the same two books. In later years, Le Guin worked in film and audio. She contributed to The Lathe of Heaven, a 1979 PBS film based on her novel of the same name. In 1985 she collaborated with avant-garde composer David Bedford on the libretto of Rigel 9, a space opera. In May 1983 she delivered a well-received commencement address entitled “A Left-Handed Commencement Address” at Mills College, Oakland, California. “A Left-Handed Commencement Address” is included in her nonfiction collection Dancing at the Edge of the World. In 1984, Le Guin was part of a group along with Ken Kesey, Brian Booth, and William Stafford that founded the Oregon Institute of Literary Arts, which is now known as Literary Arts in Portland. In December 2009, Le Guin resigned from the Authors Guild in protest over its endorsement of Google Books, Google’s book digitization project. “You decided to deal with the devil”, she wrote in her resignation letter. “There are principles involved, above all the whole concept of copyright; and these you have seen fit to abandon to a corporation, on their terms, without a struggle.” (See Authors Guild, Inc. v. Google, Inc..) Influences Le Guin was influenced by fantasy writers, including J. R. R. Tolkien, by science fiction writers, including Philip K. Dick (who was in her high school class, though they did not know each other), by central figures of Western literature such as Leo Tolstoy, Virgil and the Brontë sisters, by feminist writers such as Virginia Woolf, by children’s literature such as Alice in Wonderland, The Wind in the Willows, The Jungle Book, by Norse mythology, and by books from the Eastern tradition such as the Tao Te Ching. When asked about her influences, she replied: Once I learned to read, I read everything. I read all the famous fantasies – Alice in Wonderland, and Wind in the Willows, and Kipling. I adored Kipling’s Jungle Book. And then when I got older I found Lord Dunsany. He opened up a whole new world – the world of pure fantasy. And... Worm Ouroboros. Again, pure fantasy. Very, very fattening. And then my brother and I blundered into science fiction when I was 11 or 12. Early Asimov, things like that. But that didn’t have too much effect on me. It wasn’t until I came back to science fiction and discovered Sturgeon – but particularly Cordwainer Smith.... I read the story “Alpha Ralpha Boulevard”, and it just made me go, “Wow! This stuff is so beautiful, and so strange, and I want to do something like that.” In the mid-1950s, she read J. R. R. Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings, which had an enormous impact on her. But rather than making her want to follow in Tolkien’s footsteps, it simply showed her what was possible with the fantasy genre. Themes Le Guin exploits the creative flexibility of the science fiction and fantasy genres to undertake thorough explorations of dimensions of both social and psychological identity and of broader cultural and social structures. In doing so, she draws on sociology, anthropology, and psychology, leading some critics to categorize her work as soft science fiction. She objected to this classification of her writing, arguing the term is divisive and implies a narrow view of what constitutes valid science fiction. Underlying ideas of anarchism and environmentalism also make repeated appearances throughout Le Guin’s work. In 2014 Le Guin said about the appeal of contemplating possible futures in science fiction: anything at all can be said to happen [in the future] without fear of contradiction from a native. The future is a safe, sterile laboratory for trying out ideas in, a means of thinking about reality, a method. Sociology, anthropology and psychology Being so thoroughly informed by social science perspectives on identity and society, Le Guin treats race and gender quite deliberately. The majority of her main characters are people of color, a choice made to reflect the non-white majority of humans, and one to which she attributes the frequent lack of character illustrations on her book covers. Her writing often makes use of alien (i.e., human but non-Terran) cultures to examine structural characteristics of human culture and society and their impact on the individual. This prominent theme of cultural interaction is most likely rooted in the fact that Le Guin grew up in a household of anthropologists where she was surrounded by the remarkable case of Ishi – a Native American acclaimed in his time as the “last wild Indian” – and his interaction with the white man’s world. Le Guin’s father was director of the University of California Museum of Anthropology, where Ishi was studied and worked as a research assistant. Her mother wrote the bestseller Ishi in Two Worlds. Similar elements are echoed through many of Le Guin’s stories – from Planet of Exile and City of Illusions to The Word for World Is Forest and The Dispossessed. Le Guin’s writing notably employs the ordinary actions and transactions of everyday life, clarifying how these daily activities embed individuals in a context of relation to the physical world and to one another. For example, the engagement of the main characters with the everyday business of looking after animals, tending gardens and doing domestic chores is central to the novel Tehanu. Themes of Jungian psychology also are prominent in her writing. For example Le Guin’s Hainish Cycle, a series of novels encompassing a loose collection of societies, of various related human species, that exist largely in isolation from one another, providing the setting for her explorations of intercultural encounter. The Left Hand of Darkness, The Dispossessed and The Telling all consider the consequences of contact between different worlds and cultures. Unlike those in much mainstream science fiction, Hainish Cycle civilization does not possess reliable human faster-than-light travel, but does have technology for instantaneous communication. The social and cultural impact of the arrival of Ekumen envoys (known as “mobiles”) on remote planets, and the culture shock that the envoys experience, constitute major themes of The Left Hand of Darkness. Le Guin’s concept has been borrowed explicitly by several other well-known authors, to the extent of using the name of the communication device (the “ansible”). The Left Hand of Darkness is particularly noted for the way she explores social, cultural, and personal consequences of sexual identity through a novel involving a human’s encounter with an intermittently androgynous race. In addition to androgyny, Le Guin’s focus on sexuality breaks down normative gender roles. “Solitude”, one of the stories in The Birthday of the World: and Other Stories follows a young girl, more adventurous and daring than her older brother, into a world dominated by strong, territorial women. In Paradises Lost, the people of a spaceship several generations into the voyage to a new colony-world are saved by a female interstellar navigator, an archetypal role typically reserved for men. Environmentalism Elizabeth McDowell states in her 1992 master’s thesis that Le Guin "identif[ies] the present dominant socio-political American system as problematic and destructive to the health and life of the natural world, humanity, and their interrelations". This idea recurs in several of Le Guin’s works, most notably The Left Hand of Darkness (1969), The Word for World Is Forest (1972), The Dispossessed (1974), The Eye of the Heron (1978), Always Coming Home (1985), and “Buffalo Gals, Won’t You Come Out Tonight” (1987). All of these works center on ideas regarding socio-political organization and value-system experiments in both utopias and dystopias. As McDowell explains, “Although many of Le Guin’s works are exercises in the fantastic imagination, they are equally exercises of the political imagination.” In addition to her fiction, Le Guin’s book Out Here: Poems and Images from Steens Mountain Country, a collaboration with artist Roger Dorband, is a clear environmental testament to the natural beauty of that area of Eastern Oregon. Le Guin also wrote several works of poetry and nonfiction on Mount St. Helens following the 1980 eruption. These works explore local stories and discussions surrounding the eruption event in conjunction with Le Guin’s own perspective as it relates to viewing the eruption and mountain from her home in Portland, as well as her various visits into the blast zone. Anarchism and Taoism Le Guin’s feelings towards anarchism were closely tied to her Taoist beliefs and both ideas appear in her work. “Taoism and Anarchism fit together in some very interesting ways and I’ve been a Taoist ever since I learned what it was.” She participated in numerous peace marches and although she did not call herself an anarchist, since she did not live the lifestyle, she did feel that “Democracy is good but it isn’t the only way to achieve justice and a fair share.” Le Guin said: “The Dispossessed is an Anarchist utopian novel. Its ideas come from the Pacifist Anarchist tradition – Kropotkin etc. So did some of the ideas of the so-called counterculture of the sixties and seventies.” She also said that anarchism “is a necessary ideal at the very least. It is an ideal without which we couldn’t go on. If you are asking me is anarchism at this point a practical movement, well, then you get in the question of where you try to do it and who’s living on your boundary?” Le Guin has been credited with helping to popularize anarchism as her work "rescues anarchism from the cultural ghetto to which it has been consigned [and] introduces the anarchist vision... into the mainstream of intellectual discourse". Indeed her works were influential in developing a new anarchist way of thinking; a postmodern way that is more adaptable and looks at/addresses a broader range of concerns. Adaptations of her work Few of Le Guin’s major works have been adapted for film or television. Her 1971 novel The Lathe of Heaven has been adapted twice: The first adaptation was made in 1979 by WNET Channel 13 in New York, with her own participation, and the second adaptation was made in 2002 by the A&E Network. In a 2008 interview, she said she considers the 1979 adaptation as “the only good adaptation to film” of her work to date. In the early 1980s animator and director Hayao Miyazaki asked permission to create an animated adaptation of Earthsea. However, Le Guin, who was unfamiliar with his work and anime in general, turned down the offer. Years later, after seeing My Neighbor Totoro, she reconsidered her refusal, believing that if anyone should be allowed to direct an Earthsea film, it should be Hayao Miyazaki. The third and fourth Earthsea books were used as the basis of the 2006 animated film Tales from Earthsea (ゲド戦記, Gedo Senki). The film, however, was directed by Miyazaki’s son, Gorō, rather than Hayao Miyazaki himself, which disappointed Le Guin. While she was positive about the aesthetic of the film, writing that “much of it was beautiful”, she took great issue with its re-imagining of the moral sense of the books and greater focus on physical violence. "[E]vil has been comfortably externalized in a villain", Le Guin writes, "the wizard Kumo/Cob, who can simply be killed, thus solving all problems. In modern fantasy (literary or governmental), killing people is the usual solution to the so-called war between good and evil. My books are not conceived in terms of such a war, and offer no simple answers to simplistic questions.” In 1987, the CBC Radio anthology program Vanishing Point adapted The Dispossessed into a series of six 30-minute episodes, and at an unspecified date The Word for World Is Forest as a series of three 30-minute episodes. In 1995, Chicago’s Lifeline Theatre presented its adaptation of The Left Hand of Darkness. Reviewer Jack Helbig at the Chicago Reader wrote that the “adaptation is intelligent and well crafted but ultimately unsatisfying”, in large measure because it is extremely difficult to compress a complex 300-page novel into a two-hour stage presentation. In 2004 the Sci Fi Channel adapted the first two books of the Earthsea trilogy as the miniseries Legend of Earthsea. Le Guin was highly critical of the adaptation, calling it a “far cry from the Earthsea I envisioned”, objecting both to the use of white actors for her red, brown, or black-skinned characters, and to the way she was “cut out of the process”. Her novella, Paradises Lost, published in The Birthday of the World: and Other Stories, was adapted into an opera by the American composer Stephen Andrew Taylor and Canadian librettist Marcia Johnson. The opera premiered April 26, 2012 at the Krannert Center for the Performing Arts on the campus of the University of Illinois. In 2013, the Portland Playhouse and Hand2Mouth Theatre produced a stage adaptation of The Left Hand of Darkness, directed and adapted by Jonathan Walters, with text adapted by John Schmor. The play opened May 2, 2013, and ran until June 16, 2013, in Portland, Oregon. In 2015, the BBC commissioned radio adaptations of The Left Hand of Darkness and the first three Earthsea novels. The Left Hand of Darkness was aired as two hour-long episodes, and Earthsea as six half-hour episodes. In early 2017 Le Guin’s award winning novel The Left Hand of Darkness was picked up by Critical Content, a production company formerly known as Relativity Television, to be produced as a television limited series. Le Guin was to serve as a consulting producer on the project.

Helen Joy Davidman (18 April 1915 – 13 July 1960) was an American poet and writer. Often referred to as a child prodigy, she earned a master's degree from Columbia University in English literature at age twenty in 1935. For her book of poems, Letter to a Comrade, she won the Yale Series of Younger Poets Competition in 1938 and the Russell Loines Award for Poetry in 1939. She was the author of several books, including two novels.


Nicholas Breton (also Britton or Brittaine) (1545–1626), English poet and novelist, belonged to an old family settled at Layer Breton, Essex. Life His father, William Breton, a London merchant who had made a considerable fortune, died in 1559, and the widow (née Elizabeth Bacon) married the poet George Gascoigne before her sons had attained their majority. Nicholas Breton was probably born at the “capitall mansion house” in Red Cross Street, in the parish of St Giles without Cripplegate, mentioned in his father’s will. There is no official record of his residence at the university, but the diary of the Rev. Richard Madox tells us that he was at Antwerp in 1583 and was “once of Oriel College.” He married Ann Sutton in 1593, and had a family. He is supposed to have died shortly after the publication of his last work, Fantastickes (1626). Breton found a patron in Mary, countess of Pembroke, and wrote much in her honour until 1601, when she seems to have withdrawn her favour. It is probably safe to supplement the meagre record of his life by accepting as autobiographical some of the letters signed N.B. in A Poste with a Packet of Mad Letters (1603, enlarged 1637); the 19th letter of the second part contains a general complaint of many griefs, and proceeds as follows: “Hath another been wounded in the warres, fared hard, lain in a cold bed many a bitter storme, and beene at many a hard banquet? all these have I; another imprisoned? so have I; another long been sicke? so have I; another plagued with an unquiet life? so have I; another indebted to his hearts griefe, and fame would pay and cannot? so am I.” Works * Breton was a prolific author of considerable versatility and gift, popular with his contemporaries, and forgotten by the next generation. His work consists of religious and pastoral poems, satires, and a number of miscellaneous prose tracts. His religious poems are sometimes wearisome by their excess of fluency and sweetness, but they are evidently the expression of a devout and earnest mind. His lyrics are pure and fresh, and his romances, though full of conceits, are pleasant reading, remarkably free from grossness. His praise of the Virgin and his references to Mary Magdalene have suggested that he was a Roman Catholic, but his prose writings abundantly prove that he was an ardent Anglican. * Breton had little gift for satire, and his best work is to be found in his pastoral poetry. His Passionate Shepheard (1604) is full of sunshine and fresh air, and of unaffected gaiety. The third pastoral in this book—"Who can live in heart so glad As the merrie country lad"—is well known; with some other of Breton’s daintiest poems, among them the lullaby, “Come little babe, come silly soule,” (This poem, however, comes from The Arbor of Amorous Devises, which is only in part Breton’s work.)—it is incorporated in A. H. Bullen’s Lyrics from Elizabethan Romances (1890). His keen observation of country life appears also in his prose idyll, Wits Trenckrnour, “a conference betwixt a scholler and an angler,” and in his Fantastickes, a series of short prose pictures of the months, the Christian festivals and the hours, which throw much light on the customs of the times. Most of Breton’s books are very rare and have great bibliographical value. His works, with the exception of some belonging to private owners, were collected by Dr AB Grosart in the Chertsey Worthies Library in 1879, with an elaborate introduction quoting the documents for the poet’s history. * Breton’s poetical works, the titles of which are here somewhat abbreviated, include: * The Workes of a Young Wit (1577) * A Floorish upon Fancie (1577) * The Pilgrimage to Paradise (1592), with a prefatory letter by John Case * The Countess of Penbrook’s Passion (manuscript), first printed by JO Halliwell-Phillipps in 1853 [1] * Pasquil’s Fooles cappe (entered at Stationers’ Hall in 1600) * Pasquil’s Mistresse (1600) * Pasquil’s Passe and Passeth Not (1600) * Melancholike Humours (1600) - reprinted by Scholartis Press London. 1929. * Marie Magdalen’s Love: a Solemne Passion of the Soules Love (1595), the first part of which, a prose treatise, is probably by another hand; the second part, a poem in six-lined stanza, is certainly by Breton * A Divine Poem, including “The Ravisht Soul” and “The Blessed Weeper” (1601) * An Excellent Poem, upon the Longing of a Blessed heart (1601) * The Soules Heavenly Exercise (1601) * The Soules Harmony (1602) * Olde Madcappe newe Gaily mawfrey (1602) * The Mother’s Blessing (1602) * A True Description of Unthankfulnesse (1602) * The Passionate Shepheard (1604) * The Souies Immortail Crowne (1605) * The Honour of Valour (1605) * An Invective against Treason; I would and I would not (1614) * Bryton’s Bowre of Delights (1591), edited by Dr Grosart in 1893, an unauthorized publication which contained some poems disclaimed by Breton * The Arbor of Amorous Devises (entered at Stationers’ Hall, 1594), only in part Breton’s * contributions to England’s Helicon and other miscellanies of verse. * Of his twenty-two prose tracts may be mentioned Wit’s Trenchmour (1597), The Wil of Wit (1599), A Poste with a Packet of Mad Letters (1602-6). Sir Philip Sidney’s Ourania by N. B. (1606), A Mad World, my Masters, Adventures of Two Excellent Princes, Grimello’s Fortunes (1603), Strange News out of Divers Countries (1622), etc.; Mary Magdalen’s Lamentations (1604), and The Passion of a Discontented Mind (1601), are sometimes, but erroneously, ascribed to Breton. Footnotes References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicholas_Breton


Ralph Nicholas Chubb (8 February 1892– 14 January 1960) was an English poet, printer, and artist. Heavily influenced by Whitman, Blake, and the Romantics, his work was the creation of a highly intricate personal mythology, one that was anti-materialist and sexually revolutionary. Life Ralph Chubb was born in Harpenden, Hertfordshire. His family moved to the historic town of St Albans before his first birthday. Chubb attended St Albans School and Selwyn College, Cambridge before becoming an officer in the First World War. He served with distinction but developed neurasthenia, and he was invalided out in 1918. From 1919 to 1922 Chubb studied at the Slade School of Art in London. It was there that he met Leon Underwood and other influential artists. He went on to contribute several articles and poems for Underwood’s magazine, The Island. Although his work was displayed at such venues as the Goupil Gallery and the Royal Academy of Art, his paintings did not sell. There are several in public collections in Britain. His major painting The Well (1920) is in Wakefield; Southampton has bathers with boys wrestling, and there are nudes at Leamington, all illustrated in the Public Art Foundation catalogues. He moved with his family to the village of Curridge, near Newbury in Berkshire. He began to devote his artistic talents to the printed works which would remain his chief labour in life. His books were created in several chief phases. His typeset books of the twenties were a humble offering, exhibiting Chubb’s talent for woodcutting and his quaint, visually inspired poetry. Even at this early stage, Chubb’s lifelong obsession with adolescent males was beginning to become apparent. He expands upon this theme more explicitly in An Appendix, a pederastic and spiritualist manifesto duplicated from a cursive manuscript. An Appendix was the first of his printed works to be printed in his own hand; he soon followed this with the first of his opulent lithographic books, The Sun Spirit. Throughout the nineteen-thirties, Chubb’s books became more elaborate and appealing. Water Cherubs crystallizes Chubb’s aesthetic of the youthful male form, and The Secret Country unfolds like an illuminated manuscript, recounting stories of Chubb’s family and his journeys among the Romani of the New Forest in Hampshire. Chubb’s printing press was interrupted by the war, but in 1948 he entered into the third period of career with two massive volumes: The Child Of Dawn and Flames of Sunrise. Each page of these two volumes is crowded with obscure digressions on Chubb’s mythology and drawings of symbolic significance. Briefly summarized, Chubb’s vision was a prophecy of the redemption of 'Albion’, or England, by the boy-god Ra-el-phaos, of whom Ralph claimed himself to be the prophet and herald. This echoes an earlier announcement to be found in The Heavenly Cupid: I announce a secret event as tremendous and mysterious as any that has occurred in the spiritual history of the world. I announce the inauguration of a Third Dispensation, the dispensation of the Holy Ghost on earth, and the visible advent thereof on earth in the form of a Young Boy of thirteen years old, naked perfect and unblemished. Other themes run through all of Chubb’s work. He was forever haunted by the memory of a young chorister at St Albans who disappeared from Chubb’s life just as he had summoned up the courage to speak to him. Similarly, a brief sexual relationship with another boy when Ralph was 19 seemed to serve as a template for future visions of paradise. Chubb’s books become progressively more self-involved and paranoid. Seeking to articulate his pederastic desires, he created a personal mythology which explained everything in terms only he could understand. Nonetheless, Chubb’s work is of fascinating psychological significance; each of the various angels, knights, seers, and boy-gods in his dream world represents an aspect of his introspective and persecuted self. Chubb, like many other artists of his generation, resented science for its intrusion into his imagination. He disparaged the scientists, orthodox theologians, and politicians of world, accusing them of squelching his personal thirst for liberty. In 1927 he wrote: Existence, besides being a miracle, is a symbol. Albeit here for inscrutable purposes the spirit is only to be discerned as it were in a distorting-glass. (The Book of God’s Madness) Chubb sought to persuade his readers in An Appendix of the verity of his solipsism by illustrating some examples of serendipitous events from his life. His aim is more on the mark when he excoriates the taboos and frustrations of modern life. The green green hills, the blue blue sky, blue sea, great golden SUN, yellow dandelions, the pink naked beauty of ripe boyhood, deathless free and happy, brimming with health. This I must have. Nothing less than this can ever satisfy me! GIVE ME MY HEAVEN! GIVE ME MY HEAVEN! (Water-Cherubs) Failing in health and facing continuing legal and financial difficulties, Ralph Chubb abandoned his controversial works in the mid-fifties, and began to collect and reprint his early poems and childhood memories. Treasure Trove and The Golden City (published posthumously) are devoid of the usual profusion of naked, lissome youths, but instead offer a glimpse into his youthful imagination, and some of his most charming poetry. In the final years of his life he donated his remaining volumes to the national libraries of Britain. He died peacefully at Fair Oak Cottage in Hampshire and was buried next to his parents at the Kingsclere Woodland Church. Chubb’s own assessment of his work conforms to the general critical reaction: I do not necessarily claim to be a great artist or writer; but I claim to be a true spirit– this is a subtler test. Seek me out; but you may not find me. (An Appendix) Works * None of the editions of Chubb’s books exceed more than 200 copies, and some of his lithographed masterworks exist in only 30 or 40 copies, of which a mere 6 or 7 are meticulously hand-colored by Chubb. * The dates and titles of Chubb’s printed works are given below. Early typeset works * 1924 Manhood * 1924 The Sacrifice of Youth * 1925 A Fable of Love & War * 1927 The Cloud & the Voice * 1928 Woodcuts * 1928 The Book of God’s Madness * 1929 An Appendix (duplicated hand-written text) Lithographed texts * 1930 Songs of Mankind * 1931 The Sun Spirit * 1934 The Heavenly Cupid * 1935 Songs Pastoral and Paradisal (illustrated by Vincent Stuart; script by Helen Hinkley) * 1936 Water Cherubs * 1939 The Secret Country Post-war prophetic texts * 1948 The Child of Dawn * 1953 Flames of Sunrise Juvenalia and early romances * 1957 Treasure Trove * 1960 The Golden City Posthumous works * 1965 The Day of St Alban * 1970 Autumn Leaves References and further reading * Cave, Roderick (1960). In Blake’s Tradition: the Press of Ralph Chubb. The American Book Collector. 11 (2), p8-17 * Cave, Roderick (1960). 'Blake’s Mantle’, a Memoir of Ralph Chubb. Book Design and Production. 3 (2), p24-8 * D’Arch Smith, Timothy (1970). Love in Earnest. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul. * Rahman, Tariq (1991). Ephebophilia and the Creation of a Spiritual Myth in the Works of Ralph Nicholas Chubb. Journal of Homosexuality. 20 (1-2), p103-127 * Reid, Anthony (1970). Ralph Chubb: The Unknown. Reprinted from The Private Library. 3 (3-4). References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ralph_Chubb


Edward Dowden (/ˈdaʊdən/; 3 May 1843– 4 April 1913), was an Irish critic and poet. Biography He was the son of John Wheeler Dowden, a merchant and landowner, and was born at Cork, three years after his brother John, who became Bishop of Edinburgh in 1886. Edward’s literary tastes emerged early, in a series of essays written at the age of twelve. His home education continued at Queen’s College, Cork and at Trinity College, Dublin; at the latter he had a distinguished career, becoming president of the Philosophical Society, and winning the vice-chancellor’s prize for English verse and prose, and the first senior moderatorship in ethics and logic. In 1867 he was elected professor of oratory and English literature in Dublin University. Dowden’s first book, Shakespeare, his Mind and Art (1875), resulted from a revision of a course of lectures, and made him widely known as a critic: translations appeared in German and Russian; his Poems (1876) went into a second edition. His Shakespeare Primer (1877) was translated into Italian and German. In 1878 the Royal Irish Academy awarded him the Cunningham gold medal “for his literary writings, especially in the field of Shakespearian criticism.” Later works by him in this field included an edition of The Sonnets of William Shakespeare (1881), Passionate Pilgrim (1883), Introduction to Shakespeare (1893), Hamlet (1899), Romeo and Juliet (1900), Cymbeline (1903), and an article entitled “Shakespeare as a Man of Science” (in the National Review, July 1902), which criticized T.E. Webb’s Mystery of William Shakespeare. His critical essays “Studies in Literature” (1878), “Transcripts and Studies” (1888), “New Studies in Literature” (1895) showed a profound knowledge of the currents and tendencies of thought in various ages and countries; but his Life of Shelley (1886) made him best known to the public at large. In 1900 he edited an edition of Shelley’s works. Other books by him which indicate his interests in literature include: Robert Southey (in the “English Men of Letters” series, 1880), his edition of Southey’s Correspondence with Caroline Bowles (1881), and Select Poems of Southey (1895), his Correspondence of Sir Henry Taylor (1888), his edition of Wordsworth’s Poetical Works (1892) and of his Lyrical Ballads (1890), his French Revolution and English Literature (1897; lectures given at Princeton University in 1896), History of French Literature (1897), Puritan and Anglican (1900), Robert Browning (1904) and Michel de Montaigne (1905). His devotion to Goethe led to his succeeding Max Müller in 1888 as president of the English Goethe Society. In 1889 he gave the first annual Taylorian Lecture at the University of Oxford, and from 1892 to 1896 served as Clark lecturer at Trinity College, Cambridge. To his research are due, among other matters of literary interest, the first account of Thomas Carlyle’s Lectures on periods of European culture; the identification of Shelley as the author of a review (in The Critical Review of December 1814) of a lost romance by James Hogg; a description of Shelley’s Philosophical View of Reform; a manuscript diary of Fabre d’Églantine; and a record by Dr Wilhelm Weissenborn of Goethe’s last days and death. He also discovered a Narrative of a Prisoner of War under Napoleon (published in Blackwood’s Magazine), an unknown pamphlet by Bishop Berkeley, some unpublished writings of William Hayley relating to Cowper, and a unique copy of the Tales of Terror. His wide interests and scholarly methods made his influence on criticism both sound and stimulating, and his own ideals are well described in his essay on The Interpretation of Literature in his Transcripts and Studies. As commissioner of education in Ireland (1896–1901), trustee of the National Library of Ireland, secretary of the Irish Liberal Union and vice-president of the Irish Unionist Alliance, he enforced his view that literature should not be divorced from practical life. His biographical/critical concepts, particularly in connection with Shakespeare, are played with by Stephen Dedalus in the library chapter of James Joyce’s Ulysses. Leslie Fiedler was to play with them again in The Stranger in Shakespeare. Dowden married twice, first (1866) Mary Clerke, and secondly (1895) Elizabeth Dickinson West, daughter of the dean of St Patrick’s. His daughter by his first wife, Hester Dowden, was a well-known spiritualist medium. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Dowden


Henry VIII (28 June 1491– 28 January 1547) was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was the first English King of Ireland, and continued the nominal claim by English monarchs to the Kingdom of France. Henry was the second Tudor monarch, succeeding his father, Henry VII. Henry is known for his consequential role in the separation of the Church of England from the Roman Catholic Church, besides his six marriages and many extramarital affairs, as well as his effort to obtain an annulment of his marriage to Catherine of Aragon, which led to conflict with the Pope. His disagreements with the Pope led Henry to separate the Church of England from papal authority, with himself as king and as the Supreme Head of the Church of England; the disputes also led to the Dissolution of the Monasteries. His principal dispute was with papal authority rather than with doctrinal matters, and he remained a believer in core Catholic theological teachings despite his excommunication from the Roman Catholic Church. Henry oversaw the legal union of England and Wales with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. He is also well known for a long personal rivalry with both Francis I of France and the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, with whom he frequently warred. Domestically, Henry is known for his radical changes to the English Constitution, ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings to England. Besides asserting the sovereign’s supremacy over the Church of England, thus initiating the English Reformation, he greatly expanded royal power. Charges of treason and heresy were commonly used to quash dissent, and those accused were often executed without a formal trial, by means of bills of attainder. He achieved many of his political aims through the work of his chief ministers, some of whom were banished or executed when they fell out of his favour. People such as Thomas Wolsey, Thomas More, Thomas Cromwell, Richard Rich, and Thomas Cranmer figured prominently in Henry’s administration. He was an extravagant spender and used the proceeds from the Dissolution of the Monasteries and acts of the Reformation Parliament to convert money into royal revenue that was formerly paid to Rome. Despite the influx of money from these sources, Henry was continually on the verge of financial ruin due to his personal extravagance as well as his numerous costly continental wars. His contemporaries considered Henry in his prime to be an attractive, educated, and accomplished king, and he has been described as “one of the most charismatic rulers to sit on the English throne”. Besides ruling with considerable power, he was also an author and composer. His desire to provide England with a male heir stemmed partly from personal vanity and partly from his belief that a daughter would be unable to consolidate Tudor power and maintain the fragile peace that existed following the Wars of the Roses. This led to the two things for which Henry is most remembered: his six marriages and his break with the pope (who would not allow an annulment of Henry’s first marriage). As he aged, Henry became severely obese and his health suffered, contributing to his death in 1547. He is frequently characterised in his later life as a lustful, egotistical, harsh, and insecure king. He was succeeded by his son Edward VI. Early years Born 28 June 1491 at the Palace of Placentia in Greenwich, London, Henry Tudor was the third child and second son of Henry VII and Elizabeth of York. Of the young Henry’s six siblings, only three– Arthur, Prince of Wales; Margaret; and Mary– survived infancy. He was baptised by Richard Fox, the Bishop of Exeter, at a church of the Observant Franciscans close to the palace. In 1493, at the age of two, Henry was appointed Constable of Dover Castle and Lord Warden of the Cinque Ports. He was subsequently appointed Earl Marshal of England and Lord Lieutenant of Ireland at age three, and was inducted into the Order of the Bath soon after. The day after the ceremony he was created Duke of York and a month or so later made Warden of the Scottish Marches. In May 1495, he was appointed to the Order of the Garter. Henry was given a first-rate education from leading tutors, becoming fluent in Latin and French, and learning at least some Italian. Not much is known about his early life– save for his appointments– because he was not expected to become king. In November 1501, Henry also played a considerable part in the ceremonies surrounding the marriage of his brother, Prince Arthur, to Catherine of Aragon, the youngest surviving child of King Ferdinand II of Aragon and Queen Isabella I of Castile. As Duke of York, Henry used the arms of his father as king, differenced by a label of three points ermine. In 1502, Arthur died at the age of 15 of sweating sickness, just 20 weeks after his marriage to Catherine. Arthur’s death thrust all his duties upon his younger brother, the 10-year-old Henry. After a little debate, Henry became the new Duke of Cornwall in October 1502, and the new Prince of Wales and Earl of Chester in February 1503. Henry VII gave the boy few tasks. Young Henry was strictly supervised and did not appear in public. As a result, the young Henry would later ascend the throne “untrained in the exacting art of kingship”. Henry VII renewed his efforts to seal a marital alliance between England and Spain, by offering his second son in marriage to Arthur’s widow Catherine. Both Isabella and Henry VII were keen on the idea, which had arisen very shortly after Arthur’s death. On 23 June 1503, a treaty was signed for their marriage, and they were betrothed two days later. A papal dispensation was only needed for the “impediment of public honesty” if the marriage had not been consummated as Catherine and her duenna claimed, but Henry VII and the Spanish ambassador set out instead to obtain a dispensation for “affinity”, which took account of the possibility of consummation. The young Henry’s age, only eleven, prevented cohabitation. Isabella’s death in 1504, and the ensuing problems of succession in Castile, complicated matters. Her father preferred her to stay in England, but Henry VII’s relations with Ferdinand had deteriorated. Catherine was therefore left in limbo for some time, culminating in Prince Henry’s rejection of the marriage as soon he was able, at the age of 14. Ferdinand’s solution was to make his daughter ambassador, allowing her to stay in England indefinitely. Devout, she began to believe that it was God’s will that she marry the prince despite his opposition. Early reign Henry VII died on 21 April 1509, and the 17-year-old Henry succeeded him as king. Soon after his father’s burial on 10 May, Henry suddenly declared that he would indeed marry Catherine, leaving unresolved several issues concerning the papal dispensation and a missing part of the marriage portion. The new king maintained that it had been his father’s dying wish that he marry Catherine. Whether or not this was true, it was certainly convenient. Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I had been attempting to marry his granddaughter (and Catherine’s niece) Eleanor to Henry; she had now been jilted. Henry’s wedding to Catherine was kept low-key and was held at the friar’s church in Greenwich on 11 June 1509. On 23 June 1509, Henry led the now 23-year-old Catherine from the Tower of London to Westminster Abbey for their coronation, which took place the following day. It was a grand affair: the king’s passage was lined with tapestries and laid with fine cloth. Following the ceremony, there was a grand banquet in Westminster Hall. As Catherine wrote to her father, “our time is spent in continuous festival”. Two days after Henry’s coronation, he arrested his father’s two most unpopular ministers, Sir Richard Empson and Edmund Dudley. They were charged with high treason and were executed in 1510. Historian Ian Crofton has maintained that such executions would become Henry’s primary tactic for dealing with those who stood in his way; the two executions were certainly not the last. Henry also returned to the public some of the money supposedly extorted by the two ministers. By contrast, Henry’s view of the House of York– potential rival claimants for the throne– was more moderate than his father’s had been. Several who had been imprisoned by his father, including the Marquess of Dorset, were pardoned. Others (most notably Edmund de la Pole) went unreconciled; de la Pole was eventually beheaded in 1513, an execution prompted by his brother Richard siding against the king. Soon after, Catherine conceived, but the child, a girl, was stillborn on 31 January 1510. About four months later, Catherine again became pregnant. On New Year’s Day 1511, the child– Henry– was born. After the grief of losing their first child, the couple were pleased to have a boy and there were festivities to celebrate, including a jousting tournament. However, the child died seven weeks later. Catherine had two stillborn sons in 1514 and 1515, but gave birth in February 1516 to a girl, Mary. Relations between Henry and Catherine had been strained, but they eased slightly after Mary’s birth. Although Henry’s marriage to Catherine has since been described as “unusually good”, it is known that Henry took mistresses. It was revealed in 1510 that Henry had been conducting an affair with one of the sisters of Edward Stafford, 3rd Duke of Buckingham, either Elizabeth or Anne Hastings, Countess of Huntingdon. The most significant mistress for about three years, starting in 1516, was Elizabeth Blount. Blount is one of only two completely undisputed mistresses, few for a virile young king. Exactly how many Henry had is disputed: David Loades believes Henry had mistresses “only to a very limited extent”, whilst Alison Weir believes there were numerous other affairs. Catherine did not protest, and in 1518 fell pregnant again with another girl, who was also stillborn. Blount gave birth in June 1519 to Henry’s illegitimate son, Henry FitzRoy. The young boy was made Duke of Richmond in June 1525 in what some thought was one step on the path to his eventual legitimisation. In 1533, FitzRoy married Mary Howard, but died childless three years later. At the time of Richmond’s death in June 1536, Parliament was enacting the Second Succession Act, which could have allowed him to become king. France and the Habsburgs In 1510, France, with a fragile alliance with the Holy Roman Empire in the League of Cambrai, was winning a war against Venice. Henry renewed his father’s friendship with Louis XII of France, an issue that divided his council. Certainly war with the combined might of the two powers would have been exceedingly difficult. Shortly thereafter, however, Henry also signed a pact with Ferdinand. After Pope Julius II created the anti-French Holy League in October 1511, Henry followed Ferdinand’s lead and brought England into the new League. An initial joint Anglo-Spanish attack was planned for the spring to recover Aquitaine for England, the start of making Henry’s dreams of ruling France a reality. The attack, however, following a formal declaration of war in April 1512, was not led by Henry personally and was a considerable failure; Ferdinand used it simply to further his own ends, and it strained the Anglo-Spanish alliance. Nevertheless, the French were pushed out of Italy soon after, and the alliance survived, with both parties keen to win further victories over the French. Henry then pulled off a diplomatic coup by convincing the Emperor to join the Holy League. Remarkably, Henry had also secured the promised title of “Most Christian King of France” from Julius and possibly coronation by the Pope himself in Paris, if only Louis could be defeated. On 30 June 1513, Henry invaded France, and his troops defeated a French army at the Battle of the Spurs– a relatively minor result, but one which was seized on by the English for propaganda purposes. Soon after, the English took Thérouanne and handed it over to Maximillian; Tournai, a more significant settlement, followed. Henry had led the army personally, complete with large entourage. His absence from the country, however, had prompted his brother-in-law, James IV of Scotland, to invade England at the behest of Louis. Nevertheless, the English army, overseen by Queen Catherine, decisively defeated the Scots at the Battle of Flodden on 9 September 1513. Among the dead was the Scottish king, thus ending Scotland’s brief involvement in the war. These campaigns had given Henry a taste of the military success he so desired. However, despite initial indications, he decided not to pursue a 1514 campaign. He had been supporting Ferdinand and Maximilian financially during the campaign but had received little in return; England’s coffers were now empty. With the replacement of Julius by Pope Leo X, who was inclined to negotiate for peace with France, Henry signed his own treaty with Louis: his sister Mary would become Louis’ wife, having previously been pledged to the younger Charles, and peace was secured for eight years, a remarkably long time. Charles V ascended the thrones of both Spain and the Holy Roman Empire following the deaths of his grandfathers, Ferdinand in 1516 and Maximilian in 1519. Francis I likewise became king of France upon the death of Louis in 1515, leaving three relatively young rulers and an opportunity for a clean slate. The careful diplomacy of Cardinal Thomas Wolsey had resulted in the Treaty of London in 1518, aimed at uniting the kingdoms of western Europe in the wake of a new Ottoman threat, and it seemed that peace might be secured. Henry met Francis I on 7 June 1520 at the Field of the Cloth of Gold near Calais for a fortnight of lavish entertainment. Both hoped for friendly relations in place of the wars of the previous decade. The strong air of competition laid to rest any hopes of a renewal of the Treaty of London, however, and conflict was inevitable. Henry had more in common with Charles, whom he met once before and once after Francis. Charles brought the Empire into war with France in 1521; Henry offered to mediate, but little was achieved and by the end of the year Henry had aligned England with Charles. He still clung to his previous aim of restoring English lands in France, but also sought to secure an alliance with Burgundy, then part of Charles’ realm, and the continued support of Charles. A small English attack in the north of France made up little ground. Charles defeated and captured Francis at Pavia and could dictate peace; but he believed he owed Henry nothing. Sensing this, Henry decided to take England out of the war before his ally, signing the Treaty of the More on 30 August 1525. Annulment from Catherine During his first marriage to Catherine of Aragon, Henry conducted an affair with Mary Boleyn, Catherine’s lady-in-waiting. There has been speculation that Mary’s two children, Henry and Catherine Carey, were fathered by Henry, but this has never been proved, and the King never acknowledged them as he did Henry FitzRoy. In 1525, as Henry grew more impatient with Catherine’s inability to produce the male heir he desired, he became enamoured of Mary Boleyn’s sister, Anne, then a charismatic young woman of 25 in the Queen’s entourage. Anne, however, resisted his attempts to seduce her, and refused to become his mistress as her sister Mary Boleyn had. It was in this context that Henry considered his three options for finding a dynastic successor and hence resolving what came to be described at court as the King’s “great matter”. These options were legitimising Henry FitzRoy, which would take the intervention of the pope and would be open to challenge; marrying off Mary as soon as possible and hoping for a grandson to inherit directly, but Mary was considered unlikely to conceive before Henry’s death; or somehow rejecting Catherine and marrying someone else of child-bearing age. Probably seeing the possibility of marrying Anne, the third was ultimately the most attractive possibility to the 34-year-old Henry, and it soon became the King’s absorbing desire to annul his marriage to the now 40-year-old Catherine. It was a decision that would lead Henry to reject papal authority and initiate the English Reformation. Henry’s precise motivations and intentions over the coming years are not widely agreed on. Henry himself, at least in the early part of his reign, was a devout and well-informed Catholic to the extent that his 1521 publication Assertio Septem Sacramentorum ("Defence of the Seven Sacraments") earned him the title of Fidei Defensor (Defender of the Faith) from Pope Leo X. The work represented a staunch defence of papal supremacy, albeit one couched in somewhat contingent terms. It is not clear exactly when Henry changed his mind on the issue as he grew more intent on a second marriage. Certainly, by 1527 he had convinced himself that in marrying Catherine, his brother’s wife, he had acted contrary to Leviticus 20:21, an impediment the Pope had never had (he now believed) the authority to dispense with. It was this argument Henry took to Pope Clement VII in 1527 in the hope of having his marriage to Catherine annulled, forgoing at least one less openly defiant line of attack. In going public, all hope of tempting Catherine to retire to a nunnery or otherwise stay quiet were lost. Henry sent his secretary, William Knight, to appeal directly to the Holy See by way of a deceptively worded draft papal bull. Knight was unsuccessful; the Pope could not be misled so easily. Other missions concentrated on arranging an ecclesiastical court to meet in England, with a representative from Clement VII. Though Clement agreed to the creation of such a court, he never had any intention of empowering his legate, Lorenzo Campeggio, to decide in Henry’s favour. This bias was perhaps the result of pressure from Charles V, Catherine’s nephew, though it is not clear how far this influenced either Campeggio or the Pope. After less than two months of hearing evidence, Clement called the case back to Rome in July 1529, from which it was clear that it would never re-emerge. With the chance for an annulment lost and England’s place in Europe forfeit, Cardinal Wolsey bore the blame. He was charged with praemunire in October 1529 and his fall from grace was “sudden and total”. Briefly reconciled with Henry (and officially pardoned) in the first half of 1530, he was charged once more in November 1530, this time for treason, but died while awaiting trial. After a short period in which Henry took government upon his own shoulders, Sir Thomas More took on the role of Lord Chancellor and chief minister. Intelligent and able, but also a devout Catholic and opponent of the annulment, More initially cooperated with the king’s new policy, denouncing Wolsey in Parliament. A year later, Catherine was banished from court, and her rooms were given to Anne. Anne was an unusually educated and intellectual woman for her time, and was keenly absorbed and engaged with the ideas of the Protestant Reformers, though the extent to which she herself was a committed Protestant is much debated. When Archbishop of Canterbury William Warham died, Anne’s influence and the need to find a trustworthy supporter of the annulment had Thomas Cranmer appointed to the vacant position. This was approved by the Pope, unaware of the King’s nascent plans for the Church. Marriage to Anne Boleyn In the winter of 1532, Henry met with Francis I at Calais and enlisted the support of the French king for his new marriage. Immediately upon returning to Dover in England, Henry, now 41, and Anne, now 32, went through a secret wedding service. She soon became pregnant, and there was a second wedding service in London on 25 January 1533. On 23 May 1533, Cranmer, sitting in judgment at a special court convened at Dunstable Priory to rule on the validity of the king’s marriage to Catherine of Aragon, declared the marriage of Henry and Catherine null and void. Five days later, on 28 May 1533, Cranmer declared the marriage of Henry and Anne to be valid. Catherine was formally stripped of her title as queen, becoming instead “princess dowager” as the widow of Arthur. In her place, Anne was crowned queen consort on 1 June 1533. The queen gave birth to a daughter slightly prematurely on 7 September 1533. The child was christened Elizabeth, in honour of Henry’s mother, Elizabeth of York. Following the marriage, there was a period of consolidation taking the form of a series of statutes of the Reformation Parliament aimed at finding solutions to any remaining issues, whilst protecting the new reforms from challenge, convincing the public of their legitimacy, and exposing and dealing with opponents. Although the canon law was dealt with at length by Cranmer and others, these acts were advanced by Thomas Cromwell, Thomas Audley and the Duke of Norfolk and indeed by Henry himself. With this process complete, in May 1532 More resigned as Lord Chancellor, leaving Cromwell as Henry’s chief minister. With the Act of Succession 1533, Catherine’s daughter, Mary, was declared illegitimate; Henry’s marriage to Anne was declared legitimate; and Anne’s issue was decided to be next in the line of succession. With the Acts of Supremacy in 1534, Parliament also recognised the King’s status as head of the church in England and, with the Act in Restraint of Appeals in 1532, abolished the right of appeal to Rome. It was only then that Pope Clement took the step of excommunicating Henry and Thomas Cranmer, although the excommunication was not made official until some time later. The king and queen were not pleased with married life. The royal couple enjoyed periods of calm and affection, but Anne refused to play the submissive role expected of her. The vivacity and opinionated intellect that had made her so attractive as an illicit lover made her too independent for the largely ceremonial role of a royal wife and it made her many enemies. For his part, Henry disliked Anne’s constant irritability and violent temper. After a false pregnancy or miscarriage in 1534, he saw her failure to give him a son as a betrayal. As early as Christmas 1534, Henry was discussing with Cranmer and Cromwell the chances of leaving Anne without having to return to Catherine. Henry is traditionally believed to have had an affair with Margaret ("Madge") Shelton in 1535, although historian Antonia Fraser argues that Henry in fact had an affair with her sister Mary Shelton. Opposition to Henry’s religious policies was quickly suppressed in England. A number of dissenting monks, including the first Carthusian Martyrs, were executed and many more pilloried. The most prominent resisters included John Fisher, Bishop of Rochester, and Sir Thomas More, both of whom refused to take the oath to the King. Neither Henry nor Cromwell sought to have the men executed; rather, they hoped that the two might change their minds and save themselves. Fisher openly rejected Henry as supreme head of the Church, but More was careful to avoid openly breaking the Treason Act, which (unlike later acts) did not forbid mere silence. Both men were subsequently convicted of high treason, however– More on the evidence of a single conversation with Richard Rich, the Solicitor General. Both were duly executed in the summer of 1535. These suppressions, as well as the Dissolution of the Lesser Monasteries Act of 1536, in turn contributed to more general resistance to Henry’s reforms, most notably in the Pilgrimage of Grace, a large uprising in northern England in October 1536. Some 20,000 to 40,000 rebels were led by Robert Aske, together with parts of the northern nobility. Henry VIII promised the rebels he would pardon them and thanked them for raising the issues. Aske told the rebels they had been successful and they could disperse and go home. Henry saw the rebels as traitors and did not feel obliged to keep his promises with them, so when further violence occurred after Henry’s offer of a pardon he was quick to break his promise of clemency. The leaders, including Aske, were arrested and executed for treason. In total, about 200 rebels were executed, and the disturbances ended. Execution of Anne Boleyn On 8 January 1536 news reached the king and the queen that Catherine of Aragon had died. Henry called for public displays of joy regarding Catherine’s death. The queen was pregnant again, and she was aware of the consequences if she failed to give birth to a son. Later that month, the King was unhorsed in a tournament and was badly injured and it seemed for a time that his life was in danger. When news of this accident reached the queen, she was sent into shock and miscarried a male child that was about 15 weeks old, on the day of Catherine’s funeral, 29 January 1536. For most observers, this personal loss was the beginning of the end of the royal marriage. Given the king’s desperate desire for a son, the sequence of Anne’s pregnancies has attracted much interest. Author Mike Ashley speculated that Anne had two stillborn children after Elizabeth’s birth and before the birth of the male child she miscarried in 1536. Most sources attest only to the birth of Elizabeth in September 1533, a possible miscarriage in the summer of 1534, and the miscarriage of a male child, of almost four months gestation, in January 1536. Although the Boleyn family still held important positions on the Privy Council, Anne had many enemies, including the Duke of Suffolk. Even her own uncle, the Duke of Norfolk, had come to resent her attitude to her power. The Boleyns preferred France over the Emperor as a potential ally, but the King’s favour had swung towards the latter (partly because of Cromwell), damaging the family’s influence. Also opposed to Anne were supporters of reconciliation with Princess Mary (among them the former supporters of Catherine), who had reached maturity. A second annulment was now a real possibility, although it is commonly believed that it was Cromwell’s anti-Boleyn influence that led opponents to look for a way of having her executed. Anne’s downfall came shortly after she had recovered from her final miscarriage. Whether it was primarily the result of allegations of conspiracy, adultery, or witchcraft remains a matter of debate among historians. Early signs of a fall from grace included the King’s new mistress, the 28-year-old Jane Seymour, being moved into new quarters, and Anne’s brother, George Boleyn, being refused the Order of the Garter, which was instead given to Nicholas Carew. Between 30 April and 2 May, five men, including Anne’s brother, were arrested on charges of treasonable adultery and accused of having sexual relationships with the queen. Anne was also arrested, accused of treasonous adultery and incest. Although the evidence against them was unconvincing, the accused were found guilty and condemned to death. George Boleyn and the other accused men were executed on 17 May 1536. At 8 am on 19 May 1536, Anne, age 36, was executed on Tower Green. Marriage to Jane Seymour; domestic and foreign affairs The day after Anne’s execution in 1536 the 45-year-old Henry became engaged to Seymour, who had been one of the Queen’s ladies-in-waiting. They were married ten days later. On 12 October 1537, Jane gave birth to a son, Prince Edward, the future Edward VI. The birth was difficult, and the queen died on 24 October 1537 from an infection and was buried in Windsor. The euphoria that had accompanied Edward’s birth became sorrow, but it was only over time that Henry came to long for his wife. At the time, Henry recovered quickly from the shock. Measures were immediately put in place to find another wife for Henry, which, at the insistence of Cromwell and the court, were focused on the European continent. With Charles V distracted by the internal politics of his many kingdoms and external threats, and Henry and Francis on relatively good terms, domestic and not foreign policy issues had been Henry’s priority in the first half of the 1530s. In 1536, for example, Henry granted his assent to the Laws in Wales Act 1535, which legally annexed Wales, uniting England and Wales into a single nation. This was followed by the Second Succession Act (the Act of Succession 1536), which declared Henry’s children by Jane to be next in the line of succession and declared both Mary and Elizabeth illegitimate, thus excluding them from the throne. The king was also granted the power to further determine the line of succession in his will, should he have no further issue. However, when Charles and Francis made peace in January 1539, Henry became increasingly paranoid, perhaps as a result of receiving a constant list of threats to the kingdom (real or imaginary, minor or serious) supplied by Cromwell in his role as spymaster. Enriched by the dissolution of the monasteries, Henry used some of his financial reserves to build a series of coastal defences and set some aside for use in the event of a Franco-German invasion. Marriage to Anne of Cleves Having considered the matter, Cromwell, now Earl of Essex, suggested Anne, the 25-year-old sister of the Duke of Cleves, who was seen as an important ally in case of a Roman Catholic attack on England, for the duke fell between Lutheranism and Catholicism. Hans Holbein the Younger was dispatched to Cleves to paint a portrait of Anne for the king. Despite speculation that Holbein painted her in an overly flattering light, it is more likely that the portrait was accurate; Holbein remained in favour at court. After seeing Holbein’s portrait, and urged on by the complimentary description of Anne given by his courtiers, the 49-year-old king agreed to wed Anne. However, it was not long before Henry wished to annul the marriage so he could marry another. Anne did not argue, and confirmed that the marriage had never been consummated. Anne’s previous betrothal to the Duke of Lorraine’s son provided further grounds for the annulment. The marriage was subsequently dissolved, and Anne received the title of “The King’s Sister”, two houses and a generous allowance. It was soon clear that Henry had fallen for the 17-year-old Catherine Howard, the Duke of Norfolk’s niece, the politics of which worried Cromwell, for Norfolk was a political opponent. Shortly after, the religious reformers (and protégés of Cromwell) Robert Barnes, William Jerome and Thomas Garret were burned as heretics. Cromwell, meanwhile, fell out of favour although it is unclear exactly why, for there is little evidence of differences of domestic or foreign policy. Despite his role, he was never formally accused of being responsible for Henry’s failed marriage. Cromwell was now surrounded by enemies at court, with Norfolk also able to draw on his niece’s position. Cromwell was charged with treason, selling export licences, granting passports, and drawing up commissions without permission, and may also have been blamed for the failure of the foreign policy that accompanied the attempted marriage to Anne. He was subsequently attainted and beheaded. Marriage to Catherine Howard On 28 July 1540 (the same day Cromwell was executed), Henry married the young Catherine Howard, a first cousin and lady-in-waiting of Anne Boleyn. He was absolutely delighted with his new queen, and awarded her the lands of Cromwell and a vast array of jewellery. Soon after the marriage, however, Queen Catherine had an affair with the courtier Thomas Culpeper. She also employed Francis Dereham, who had previously been informally engaged to her and had an affair with her prior to her marriage, as her secretary. The court was informed of her affair with Dereham whilst Henry was away; they dispatched Thomas Cranmer to investigate, who brought evidence of Queen Catherine’s previous affair with Dereham to the king’s notice. Though Henry originally refused to believe the allegations, Dereham confessed. It took another meeting of the council, however, before Henry believed the accusations against Dereham and went into a rage, blaming the council before consoling himself in hunting. When questioned, the queen could have admitted a prior contract to marry Dereham, which would have made her subsequent marriage to Henry invalid, but she instead claimed that Dereham had forced her to enter into an adulterous relationship. Dereham, meanwhile, exposed Queen Catherine’s relationship with Culpeper. Culpeper and Dereham were both executed, and Catherine too was beheaded on 13 February 1542. Shrines destroyed and monasteries dissolved In 1538, the chief minister T. Cromwell pursued an extensive campaign against what is termed “idolatry” by the followers of the old religion, culminating in September with the dismantling of the shrine of St. Thomas Becket at Canterbury. As a consequence, the king was excommunicated by the Pope Paul III on 17 December of the same year. In 1540, Henry sanctioned the complete destruction of shrines to saints. In 1542, England’s remaining monasteries were all dissolved, and their property transferred to the Crown. Abbots and priors lost their seats in the House of Lords; only archbishops and bishops remained. Consequently, the Lords Spiritual– as members of the clergy with seats in the House of Lords were known– were for the first time outnumbered by the Lords Temporal. Second invasion of France and the “Rough Wooing” of Scotland The 1539 alliance between Francis and Charles had soured, eventually degenerating into renewed war. With Catherine of Aragon and Anne Boleyn dead, relations between Charles and Henry improved considerably, and Henry concluded a secret alliance with the Emperor and decided to enter the Italian War in favour of his new ally. An invasion of France was planned for 1543. In preparation for it, Henry moved to eliminate the potential threat of Scotland under the youthful James V. Victory would continue the Reformation in Scotland, which was still Catholic, and Henry hoped to unite the crowns of England and Scotland by marriage of James’ daughter, the future Mary, Queen of Scots, to his son Edward. Henry made war on Scotland for several years in pursuit of this goal, a campaign dubbed by Victorian chroniclers as “the Rough Wooing”. The Scots were defeated at Battle of Solway Moss on 24 November 1542, and James died on 15 December. The Scottish Regent Arran agreed to the marriage in the Treaty of Greenwich on 1 July 1543. Despite the success with Scotland, Henry hesitated to invade France, annoying Charles. Henry finally went to France in June 1544 with a two-pronged attack. One force under Norfolk ineffectively besieged Montreuil. The other, under Suffolk, laid siege to Boulogne. Henry later took personal command, and Boulogne fell on 18 September 1544. However, Henry had refused Charles’ request to march against Paris. Charles’ own campaign fizzled, and he made peace with France that same day. Henry was left alone against France, unable to make peace. Francis attempted to invade England in the summer of 1545, but reached only the Isle of Wight before being repulsed. Out of money, France and England signed the Treaty of Camp on 7 June 1546. Henry secured Boulogne for eight years. The city was then to be returned to France for 2 million crowns (£750,000). Henry needed the money; the 1544 campaign had cost £650,000, and England was once again bankrupt. Meanwhile, though Henry still clung to the Treaty of Greenwich, the Scots repudiated it in December 1543. Henry launched another war on Scotland, sending an army to burn Edinburgh and lay waste to the country. The Scots would not submit, though. Defeat at Ancrum Moor prompted a second invasion force. This war was nominally ended by the Treaty of Camp, although unrest continued in Scotland, including French and English interventions, up to Henry’s death. Marriage to Catherine Parr Henry married his last wife, the wealthy widow Catherine Parr, in July 1543. A reformer at heart, she argued with Henry over religion. Ultimately, Henry remained committed to an idiosyncratic mixture of Catholicism and Protestantism; the reactionary mood which had gained ground following the fall of Cromwell had neither eliminated his Protestant streak nor been overcome by it. Parr helped reconcile Henry with his daughters Mary and Elizabeth. In 1543, an Act of Parliament put the daughters back in the line of succession after Edward, Prince of Wales. The same act allowed Henry to determine further succession to the throne in his will. Physical decline Late in life, Henry became obese, with a waist measurement of 54 inches (140 cm), and had to be moved about with the help of mechanical inventions. He was covered with painful, pus-filled boils and possibly suffered from gout. His obesity and other medical problems can be traced from the jousting accident in 1536, in which he suffered a leg wound. The accident re-opened and aggravated a previous injury he had sustained years earlier, to the extent that his doctors found it difficult to treat. The wound festered for the remainder of his life and became ulcerated, thus preventing him from maintaining the level of physical activity he had previously enjoyed. The jousting accident is also believed to have caused Henry’s mood swings, which may have had a dramatic effect on his personality and temperament. The theory that Henry suffered from syphilis has been dismissed by most historians. A more recent theory suggests that Henry’s medical symptoms are characteristic of untreated type 2 diabetes. Alternatively, his wives’ pattern of pregnancies and his mental deterioration have led some to suggest that the king may have been Kell positive and suffered from McLeod syndrome. According to another study, Henry VIII’s history and body morphology may have been the result of traumatic brain injury after his 1536 jousting accident, which in turn led to a neuroendocrine cause of his obesity. This analysis identifies growth hormone deficiency (GHD) as the source for his increased adiposity but also significant behavioural changes noted in his later years, including his multiple marriages. Death and burial Henry’s obesity hastened his death at the age of 55, which occurred on 28 January 1547 in the Palace of Whitehall, on what would have been his father’s 90th birthday. He allegedly uttered his last words: “Monks! Monks! Monks!” perhaps in reference to the monks he caused to be evicted during the Dissolution of the Monasteries. On 14 February 1547 Henry’s coffin lay overnight at Syon Monastery, en route for burial in St George’s Chapel, Windsor Castle. Twelve years before in 1535 a Franciscan friar named William Peyto (or Peto, Petow) (died 1558 or 1559), had preached before the King at Greenwich Palace “that God’s judgements were ready to fall upon his head and that dogs would lick his blood, as they had done to Ahab”, whose infamy rests upon 1 Kings 16:33: “And Ahab did more to provoke the Lord God of Israel to anger than all the kings of Israel that were before him”. The prophecy was said to have been fulfilled during this night at Syon, when some “corrupted matter of a bloody colour” fell from the coffin to the floor. Henry VIII was interred in St George’s Chapel in Windsor Castle, next to Jane Seymour. Over a hundred years later, King Charles I (1625–1649) was buried in the same vault. Succession After his death, Henry’s only legitimate son, Edward, inherited the Crown, becoming Edward VI (1547–1553). Since Edward was then only nine years old, he could not exercise actual power. Rather, Henry’s will designated 16 executors to serve on a council of regency until Edward reached the age of 18. The executors chose Edward Seymour, 1st Earl of Hertford, Jane Seymour’s elder brother, to be Lord Protector of the Realm. If Edward went childless, the throne was to pass to Mary, Henry VIII’s daughter by Catherine of Aragon, and her heirs. If Mary’s issue failed, the crown was to go to Elizabeth, Henry’s daughter by Anne Boleyn, and her heirs. Finally, if Elizabeth’s line became extinct, the crown was to be inherited by the descendants of Henry VIII’s deceased younger sister, Queen Mary of France, the Greys. The descendants of Henry’s sister Margaret– the Stuarts, rulers of Scotland– were thereby excluded from the succession. This final provision failed when James VI of Scotland became James I of England upon Elizabeth’s death. Public image Henry cultivated the image of a Renaissance man, and his court was a centre of scholarly and artistic innovation and glamorous excess, epitomised by the Field of the Cloth of Gold. He scouted the country for choirboys, taking some directly from Wolsey’s choir, and introduced Renaissance music into court. Musicians included Benedict de Opitiis, Richard Sampson, Ambrose Lupo, and Venetian organist Dionisio Memo. Henry himself kept a considerable collection of instruments; he was skilled on the lute, could play the organ, and was a talented player of the virginals. He could also sight read music and sing well. He was an accomplished musician, author, and poet; his best known piece of music is “Pastime with Good Company” ("The Kynges Ballade"). He is often reputed to have written “Greensleeves” but probably did not. He was an avid gambler and dice player, and excelled at sports, especially jousting, hunting, and real tennis. He was known for his strong defence of conventional Christian piety. The King was involved in the original construction and improvement of several significant buildings, including Nonsuch Palace, King’s College Chapel, Cambridge and Westminster Abbey in London. Many of the existing buildings Henry improved were properties confiscated from Wolsey, such as Christ Church, Oxford; Hampton Court Palace; the Palace of Whitehall; and Trinity College, Cambridge. Henry was an intellectual. The first English king with a modern humanist education, he read and wrote English, French and Latin, and was thoroughly at home in his well-stocked library. He personally annotated many books and wrote and published one of his own. To promote the public support for the reformation of the church, Henry had numerous pamphlets and lectures prepared. For example, Richard Sampson’s Oratio (1534) was an argument for absolute obedience to the monarchy and claimed that the English church had always been independent from Rome. At the popular level, theatre and minstrel troupes funded by the crown travelled around the land to promote the new religious practices: the pope and Catholic priests and monks were mocked as foreign devils, while the glorious king was hailed as a brave and heroic defender of the true faith. Henry worked hard to present an image of unchallengeable authority and irresistible power. A large well-built athlete (over 6 feet [1.8 m] tall and strong and broad in proportion), Henry excelled at jousting and hunting. More than pastimes, they were political devices that served multiple goals, from enhancing his athletic royal image to impressing foreign emissaries and rulers, to conveying Henry’s ability to suppress any rebellion. Thus he arranged a jousting tournament at Greenwich in 1517, where he wore gilded armour, gilded horse trappings, and outfits of velvet, satin and cloth of gold dripping with pearls and jewels. It suitably impressed foreign ambassadors, one of whom wrote home that, “The wealth and civilisation of the world are here, and those who call the English barbarians appear to me to render themselves such”. Henry finally retired from jousting in 1536 after a heavy fall from his horse left him unconscious for two hours, but he continued to sponsor two lavish tournaments a year. He then started adding weight and lost the trim, athletic figure that had made him so handsome; Henry’s courtiers began dressing in heavily padded clothes to emulate– and flatter– their increasingly stout monarch. Towards the end of his reign his health rapidly declined. Government The power of Tudor monarchs, including Henry, was 'whole’ and 'entire’, ruling, as they claimed, by the grace of God alone. The crown could also rely on the exclusive use of those functions that constituted the royal prerogative. These included acts of diplomacy (including royal marriages), declarations of war, management of the coinage, the issue of royal pardons and the power to summon and dissolve parliament as and when required. Nevertheless, as evident during Henry’s break with Rome, the monarch worked within established limits, whether legal or financial, that forced him to work closely with both the nobility and parliament (representing the gentry). In practice, Tudor monarchs used patronage to maintain a royal court that included formal institutions such as the Privy Council as well as more informal advisers and confidants. Both the rise and fall of court nobles could be swift: although the often-quoted figure of 72,000 executions during his reign is inflated, Henry did undoubtedly execute at will, burning or beheading two of his wives, twenty peers, four leading public servants, six close attendants and friends, one cardinal (John Fisher) and numerous abbots. Among those who were in favour at any given point in Henry’s reign, one could usually be identified as a chief minister, though one of the enduring debates in the historiography of the period has been the extent to which those chief ministers controlled Henry rather than vice versa. In particular, historian G. R. Elton has argued that one such minister, Thomas Cromwell, led a “Tudor revolution in government” quite independent of the king, whom Elton presented as an opportunistic, essentially lazy participant in the nitty-gritty of politics. Where Henry did intervene personally in the running of the country, Elton argued, he mostly did so to its detriment. The prominence and influence of faction in Henry’s court is similarly discussed in the context of at least five episodes of Henry’s reign, including the downfall of Anne Boleyn. From 1514 to 1529, Thomas Wolsey (1473–1530), a cardinal of the established Church, oversaw domestic and foreign policy for the young king from his position as Lord Chancellor. Wolsey centralised the national government and extended the jurisdiction of the conciliar courts, particularly the Star Chamber. The Star Chamber’s overall structure remained unchanged, but Wolsey used it to provide for much-needed reform of the criminal law. The power of the court itself did not outlive Wolsey, however, since no serious administrative reform was undertaken and its role was eventually devolved to the localities. Wolsey helped fill the gap left by Henry’s declining participation in government (particularly in comparison to his father) but did so mostly by imposing himself in the King’s place. His use of these courts to pursue personal grievances, and particularly to treat delinquents as if mere examples of a whole class worthy of punishment, angered the rich, who were annoyed as well by his enormous wealth and ostentatious living. Following Wolsey’s downfall, Henry took full control of his government, although at court numerous complex factions continued to try to ruin and destroy each other. Thomas Cromwell (c. 1485–1540) also came to define Henry’s government. Returning to England from the continent in 1514 or 1515, Cromwell soon entered Wolsey’s service. He turned to law, also picking up a good knowledge of the Bible, and was admitted to Gray’s Inn in 1524. He became Wolsey’s “man of all work”. Cromwell, driven in part by his religious beliefs, attempted to reform the body politic of the English government through discussion and consent, and through the vehicle of continuity and not outward change. He was seen by many people as the man they wanted to bring about their shared aims, including Thomas Audley. By 1531, Cromwell and those associated with him were already responsible for the drafting of much legislation. Cromwell’s first office was that of the master of the King’s jewels in 1532, from which he began to invigorate the government finances. By this point, Cromwell’s power as an efficient administrator in a Council full of politicians exceeded what Wolsey had achieved. Cromwell did much work through his many offices to remove the tasks of government from the Royal Household (and ideologically from the personal body of the King) and into a public state. He did so, however, in a haphazard fashion that left several remnants, not least because he needed to retain Henry’s support, his own power, and the possibility of actually achieving the plan he set out. Cromwell made the various income streams put in place by Henry VII more formal and assigned largely autonomous bodies for their administration. The role of the King’s Council was transferred to a reformed Privy Council, much smaller and more efficient than its predecessor. A difference emerged between the financial health of the king, and that of the country, although Cromwell’s fall undermined much of his bureaucracy, which required his hand to keep order among the many new bodies and prevent profligate spending that strained relations as well as finances. Cromwell’s reforms ground to a halt in 1539, the initiative lost, and he failed to secure the passage of an enabling act, the Proclamation by the Crown Act 1539. He too was executed, on 28 July 1540. Finances Henry inherited a vast fortune and a prosperous economy from his father Henry VII, who had been frugal and careful with money. This fortune was estimated to £1,250,000 (£375 million by today’s standards). By comparison, however, the reign of Henry was a near-disaster in financial terms. Although he further augmented his royal treasury through the seizure of church lands, Henry’s heavy spending and long periods of mismanagement damaged the economy. Much of this wealth was spent by Henry on maintaining his court and household, including many of the building works he undertook on royal palaces. Henry hung 2,000 tapestries in his palaces; by comparison, James V of Scotland hung just 200. Henry took pride in showing off his collection of weapons, which included exotic archery equipment, 2,250 pieces of land ordnance and 6,500 handguns. Tudor monarchs had to fund all the expenses of government out of their own income. This income came from the Crown lands that Henry owned as well as from customs duties like tonnage and poundage, granted by parliament to the king for life. During Henry’s reign the revenues of the Crown remained constant (around £100,000), but were eroded by inflation and rising prices brought about by war. Indeed, war and Henry’s dynastic ambitions in Europe exhausted the surplus he had inherited from his father by the mid-1520s. Whereas Henry VII had not involved Parliament in his affairs very much, Henry VIII had to turn to Parliament during his reign for money, in particular for grants of subsidies to fund his wars. The Dissolution of the Monasteries provided a means to replenish the treasury, and as a result the Crown took possession of monastic lands worth £120,000 (£36 million) a year. The Crown had profited a small amount in 1526 when Wolsey had put England onto a gold, rather than silver, standard, and had debased the currency slightly. Cromwell debased the currency more significantly, starting in Ireland in 1540. The English pound halved in value against the Flemish pound between 1540 and 1551 as a result. The nominal profit made was significant, helping to bring income and expenditure together, but it had a catastrophic effect on the overall economy of the country. In part, it helped to bring about a period of very high inflation from 1544 onwards. Reformation Henry is generally credited with initiating the English Reformation– the process of transforming England from a Catholic country to a Protestant one– though his progress at the elite and mass levels is disputed, and the precise narrative not widely agreed. Certainly, in 1527, Henry, until then an observant and well-informed Catholic, appealed to the Pope for an annulment of his marriage to Catherine. No annulment was immediately forthcoming, the result in part of Charles V’s control of the Papacy. The traditional narrative gives this refusal as the trigger for Henry’s rejection of papal supremacy (which he had previously defended), though as historian A. F. Pollard has argued, even if Henry had not needed an annulment, Henry may have come to reject papal control over the governance of England purely for political reasons. In any case, between 1532 and 1537, Henry instituted a number of statutes that dealt with the relationship between king and pope and hence the structure of the nascent Church of England. These included the Statute in Restraint of Appeals (passed 1533), which extended the charge of praemunire against all who introduced papal bulls into England, potentially exposing them to the death penalty if found guilty. Other acts included the Supplication against the Ordinaries and the Submission of the Clergy, which recognised Royal Supremacy over the church. The Ecclesiastical Appointments Act 1534 required the clergy to elect bishops nominated by the Sovereign. The Act of Supremacy in 1534 declared that the King was “the only Supreme Head in Earth of the Church of England” and the Treasons Act 1534 made it high treason, punishable by death, to refuse the Oath of Supremacy acknowledging the King as such. Similarly, following the passage of the Act of Succession 1533, all adults in the Kingdom were required to acknowledge the Act’s provisions (declaring Henry’s marriage to Anne legitimate and his marriage to Catherine illegitimate) by oath; those who refused were subject to imprisonment for life, and any publisher or printer of any literature alleging that the marriage to Anne was invalid subject to the death penalty. Finally, the Peter’s Pence Act was passed, and it reiterated that England had “no superior under God, but only your Grace” and that Henry’s “imperial crown” had been diminished by “the unreasonable and uncharitable usurpations and exactions” of the Pope. The King had much support from the Church under Cranmer. Henry, to Thomas Cromwell’s annoyance, insisted on parliamentary time to discuss questions of faith, which he achieved through the Duke of Norfolk. This led to the passing of the Act of Six Articles, whereby six major questions were all answered by asserting the religious orthodoxy, thus restraining the reform movement in England. It was followed by the beginnings of a reformed liturgy and of the Book of Common Prayer, which would take until 1549 to complete. The victory won by religious conservatives did not convert into much change in personnel, however, and Cranmer remained in his position. Overall, the rest of Henry’s reign saw a subtle movement away from religious orthodoxy, helped in part by the deaths of prominent figures from before the break with Rome, especially the executions of Thomas More and John Fisher in 1535 for refusing to renounce papal authority. Henry established a new political theology of obedience to the crown that was continued for the next decade. It reflected Martin Luther’s new interpretation of the fourth commandment ("Honour thy father and mother"), brought to England by William Tyndale. The founding of royal authority on the Ten Commandments was another important shift: reformers within the Church utilised the Commandments’ emphasis on faith and the word of God, while conservatives emphasised the need for dedication to God and doing good. The reformers’ efforts lay behind the publication of the Great Bible in 1539 in English. Protestant Reformers still faced persecution, particularly over objections to Henry’s annulment. Many fled abroad, including the influential Tyndale, who was eventually executed and his body burned at Henry’s behest. When taxes once payable to Rome were transferred to the Crown, Cromwell saw the need to assess the taxable value of the Church’s extensive holdings as they stood in 1535. The result was an extensive compendium, the Valor Ecclesiasticus. In September of the same year, Cromwell commissioned a more general visitation of religious institutions, to be undertaken by four appointee visitors. The visitation focussed almost exclusively on the country’s religious houses, with largely negative conclusions. In addition to reporting back to Cromwell, the visitors made the lives of the monks more difficult by enforcing strict behavioural standards. The result was to encourage self-dissolution. In any case, the evidence gathered by Cromwell led swiftly to the beginning of the state-enforced dissolution of the monasteries with all religious houses worth less than £200 vested by statute in the crown in January 1536. After a short pause, surviving religious houses were transferred one by one to the Crown and onto new owners, and the dissolution confirmed by a further statute in 1539. By January 1540 no such houses remained: some 800 had been dissolved. The process had been efficient, with minimal resistance, and brought the crown some £90,000 a year. The extent to which the dissolution of all houses was planned from the start is debated by historians; there is some evidence that major houses were originally intended only to be reformed. Cromwell’s actions transferred a fifth of England’s landed wealth to new hands. The programme was designed primarily to create a landed gentry beholden to the crown, which would use the lands much more efficiently. Although little opposition to the supremacy could be found in England’s religious houses, they had links to the international church and were an obstacle to further religious reform. Response to the reforms was mixed. The religious houses had been the only support of the impoverished, and the reforms alienated much of the population outside London, helping to provoke the great northern rising of 1536–1537, known as the Pilgrimage of Grace. Elsewhere the changes were accepted and welcomed, and those who clung to Catholic rites kept quiet or moved in secrecy. They would re-emerge during the reign of Henry’s daughter Mary (1553–1558). Military Apart from permanent garrisons at Berwick, Calais, and Carlisle, England’s standing army numbered only a few hundred men. This was increased only slightly by Henry. Henry’s invasion force of 1513, some 30,000 men, was composed of billmen and longbowmen, at a time when the other European nations were moving to hand guns and pikemen. The difference in capability was at this stage not significant, however, and Henry’s forces had new armour and weaponry. They were also supported by battlefield artillery, a relatively new invention, and several large and expensive siege guns. The invasion force of 1544 was similarly well-equipped and organised, although command on the battlefield was laid with the dukes of Suffolk and Norfolk, which in the case of the latter produced disastrous results at Montreuil. Henry is traditionally cited as one of the founders of the Royal Navy. Technologically, Henry invested in large cannon for his warships, an idea that had taken hold in other countries, to replace the smaller serpentines in use. He also flirted with designing ships personally– although his contribution to larger vessels, if any, is not known, it is believed that he influenced the design of rowbarges and similar galleys. Henry was also responsible for the creation of a permanent navy, with the supporting anchorages and dockyards. Tactically, Henry’s reign saw the Navy move away from boarding tactics to employ gunnery instead. The Navy was enlarged up to fifty ships (the Mary Rose was one of them), and Henry was responsible for the establishment of the “council for marine causes” to specifically oversee all the maintenance and operation of the Navy, becoming the basis for the later Admiralty. Henry’s break with Rome incurred the threat of a large-scale French or Spanish invasion. To guard against this, in 1538, he began to build a chain of expensive, state-of-the-art defences, along Britain’s southern and eastern coasts from Kent to Cornwall, largely built of material gained from the demolition of the monasteries. These were known as Henry VIII’s Device Forts. He also strengthened existing coastal defence fortresses such as Dover Castle and, at Dover, Moat Bulwark and Archcliffe Fort, which he personally visited for a few months to supervise. Wolsey had many years before conducted the censuses required for an overhaul of the system of militia, but no reform resulted. In 1538–39, Cromwell overhauled the shire musters, but his work mainly served to demonstrate how inadequate they were in organisation. The building works, including that at Berwick, along with the reform of the militias and musters, were eventually finished under Queen Mary. Ireland At the beginning of Henry’s reign, Ireland was effectively divided into three zones: the Pale, where English rule was unchallenged; Leinster and Munster, the so-called “obedient land” of Anglo-Irish peers; and the Gaelic Connaught and Ulster, with merely nominal English rule. Until 1513, Henry continued the policy of his father, to allow Irish lords to rule in the king’s name and accept steep divisions between the communities. However, upon the death of the 8th Earl of Kildare, governor of Ireland, fractious Irish politics combined with a more ambitious Henry to cause trouble. When Thomas Butler, 7th Earl of Ormond died, Henry recognised one successor for Ormond’s English, Welsh and Scottish lands, whilst in Ireland another took control. Kildare’s successor, the 9th Earl, was replaced as Lord Lieutenant of Ireland by Thomas Howard, Earl of Surrey in 1520. Surrey’s ambitious aims were costly, but ineffective; English rule became trapped between winning the Irish lords over with diplomacy, as favoured by Henry and Wolsey, and a sweeping military occupation as proposed by Surrey. Surrey was recalled in 1521, with Piers Butler– one of claimants to the Earldom of Ormond– appointed in his place. Butler proved unable to control opposition, including that of Kildare. Kildare was appointed chief governor in 1524, resuming his dispute with Butler, which had before been in a lull. Meanwhile, the Earl of Desmond, an Anglo-Irish peer, had turned his support to Richard de la Pole as pretender to the English throne; when in 1528 Kildare failed to take suitable actions against him, Kildare was once again removed from his post. The Desmond situation was resolved on his death in 1529, which was followed by a period of uncertainty. This was effectively ended with the appointment of Henry FitzRoy, Duke of Richmond and the king’s son, as lord lieutenant. Richmond had never before visited Ireland, his appointment a break with past policy. For a time it looked as if peace might be restored with the return of Kildare to Ireland to manage the tribes, but the effect was limited and the Irish parliament soon rendered ineffective. Ireland began to receive the attention of Cromwell, who had supporters of Ormond and Desmond promoted. Kildare, on the other hand, was summoned to London; after some hesitation, he departed for London in 1534, where he would face charges of treason. His son, Thomas, Lord Offaly was more forthright, denouncing the king and leading a “Catholic crusade” against the king, who was by this time mired in marital problems. Offaly had the Archbishop of Dublin murdered, and besieged Dublin. Offaly led a mixture of Pale gentry and Irish tribes, although he failed to secure the support of Lord Darcy, a sympathiser, or Charles V. What was effectively a civil war was ended with the intervention of 2,000 English troops– a large army by Irish standards– and the execution of Offaly (his father was already dead) and his uncles. Although the Offaly revolt was followed by a determination to rule Ireland more closely, Henry was wary of drawn-out conflict with the tribes, and a royal commission recommended that the only relationship with the tribes was to be promises of peace, their land protected from English expansion. The man to lead this effort was Sir Antony St Leger, as Lord Deputy of Ireland, who would remain into the post past Henry’s death. Until the break with Rome, it was widely believed that Ireland was a Papal possession granted as a mere fiefdom to the English king, so in 1541 Henry asserted England’s claim to the Kingdom of Ireland free from the Papal overlordship. This change did, however, also allow a policy of peaceful reconciliation and expansion: the Lords of Ireland would grant their lands to the King, before being returned as fiefdoms. The incentive to comply with Henry’s request was an accompanying barony, and thus a right to sit in the Irish House of Lords, which was to run in parallel with England’s. The Irish law of the tribes did not suit such an arrangement, because the chieftain did not have the required rights; this made progress tortuous, and the plan was abandoned in 1543, not to be replaced. Historiography The complexities and sheer scale of Henry’s legacy ensured that, in the words of Betteridge and Freeman, "throughout the centuries [since his death], Henry has been praised and reviled, but he has never been ignored". A particular focus of modern historiography has been the extent to which the events of Henry’s life (including his marriages, foreign policy and religious changes) were the result of his own initiative and, if they were, whether they were the result of opportunism or of a principled undertaking by Henry. The traditional interpretation of those events was provided by historian A.F. Pollard, who in 1902 presented his own, largely positive, view of the king, "laud[ing him] as the king and statesman who, whatever his personal failings, led England down the road to parliamentary democracy and empire". Pollard’s interpretation, which was broadly comparable to 17th century publications of Lord Herbert of Cherbury and his contemporaries, remained the dominant interpretation of Henry’s life until the publication of the doctoral thesis of G. R. Elton in 1953. That thesis, entitled “The Tudor Revolution in Government”, maintained Pollard’s positive interpretation of the Henrician period as a whole, but reinterpreted Henry himself as a follower rather than a leader. For Elton, it was Cromwell and not Henry who undertook the changes in government– Henry was shrewd, but lacked the vision to follow a complex plan through. Henry was little more, in other words, than an “ego-centric monstrosity” whose reign "owed its successes and virtues to better and greater men about him; most of its horrors and failures sprang more directly from [the king]". Although the central tenets of Elton’s thesis have now been all but abandoned, it has consistently provided the starting point for much later work, including that of J. J. Scarisbrick, his student. Scarisbrick largely kept Elton’s regard for Cromwell’s abilities, but returned agency to Henry, who Scarisbrick considered to have ultimately directed and shaped policy. For Scarisbrick, Henry was a formidable, captivating man who “wore regality with a splendid conviction”. The effect of endowing Henry with this ability, however, was largely negative in Scarisbrick’s eyes: to Scarisbrick the Henrician period was one of upheaval and destruction and those in charge worthy of blame more than praise. Even among more recent biographers, including David Loades, David Starkey and John Guy, there has ultimately been little consensus on the extent to which Henry was responsible for the changes he oversaw or the correct assessment of those he did bring about. This lack of clarity about Henry’s control over events has contributed to the variation in the qualities ascribed to him: religious conservative or dangerous radical; lover of beauty or brutal destroyer of priceless artefacts; friend and patron or betrayer of those around him; chivalry incarnate or ruthless chauvinist. One traditional approach, favoured by Starkey and others, is to divide Henry’s reign into two halves, the first Henry being dominated by positive qualities (politically inclusive, pious, athletic but also intellectual) who presided over a period of stability and calm, and the latter a “hulking tyrant” who presided over a period of dramatic, sometimes whimsical, change. Other writers have tried to merge Henry’s disparate personality into a single whole; Lacey Baldwin Smith, for example, considered him an egotistical borderline neurotic given to great fits of temper and deep and dangerous suspicions, with a mechanical and conventional, but deeply held piety, and having at best a mediocre intellect. Style and arms Many changes were made to the royal style during his reign. Henry originally used the style “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England, France and Lord of Ireland”. In 1521, pursuant to a grant from Pope Leo X rewarding Henry for his Defence of the Seven Sacraments, the royal style became “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England and France, Defender of the Faith and Lord of Ireland”. Following Henry’s excommunication, Pope Paul III rescinded the grant of the title “Defender of the Faith”, but an Act of Parliament declared that it remained valid; and it continues in royal usage to the present day. Henry’s motto was “Coeur Loyal” ("true heart"), and he had this embroidered on his clothes in the form of a heart symbol and with the word “loyal”. His emblem was the Tudor rose and the Beaufort portcullis. As king, Henry’s arms were the same as those used by his predecessors since Henry IV: Quarterly, Azure three fleurs-de-lys Or (for France) and Gules three lions passant guardant in pale Or (for England). In 1535, Henry added the “supremacy phrase” to the royal style, which became “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England and France, Defender of the Faith, Lord of Ireland and of the Church of England in Earth Supreme Head”. In 1536, the phrase “of the Church of England” changed to “of the Church of England and also of Ireland”. In 1541, Henry had the Irish Parliament change the title “Lord of Ireland” to “King of Ireland” with the Crown of Ireland Act 1542, after being advised that many Irish people regarded the Pope as the true head of their country, with the Lord acting as a mere representative. The reason the Irish regarded the Pope as their overlord was that Ireland had originally been given to King Henry II of England by Pope Adrian IV in the 12th century as a feudal territory under papal overlordship. The meeting of Irish Parliament that proclaimed Henry VIII as King of Ireland was the first meeting attended by the Gaelic Irish chieftains as well as the Anglo-Irish aristocrats. The style “Henry the Eighth, by the Grace of God, King of England, France and Ireland, Defender of the Faith and of the Church of England and also of Ireland in Earth Supreme Head” remained in use until the end of Henry’s reign. Ancestry Marriages and issue References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Henry_VIII_of_England


Kathleen Faragher (1904–1974) was the most significant and prolific Manx dialect author of the mid twentieth century. She is best known for her poems first published in the Ramsey Courier and collected into five books published between 1955 and 1967. She was also a prolific short story writer and playwright. Her work is renowned for its humour born of a keen observation of Manx characters, and for its evocative portrayal of the Isle of Man and its people. Life Kathleen Faragher was born in 1904 in Ramsey, Isle of Man, to Joseph and Catherine Anne Faragher, owners of a grocer and provision merchant business on Approach Road. Kathleen was the youngest of five children: Laurence (who died in Gibraltar in 1944 during WWII), Fred (later manager of Martin’s Bank, Peel), Joseph (who took over the family business but died in 1946), Evelyn (who emigrated to Auckland, New Zealand, where she died in 1949) and herself. Kathleen Faragher was raised in Ramsey until about 1924, when she moved to London to take up a business career. After 25 years working in London, ill-health forced her into early retirement, whereupon she returned to live on the Isle of Man in October 1949. Faragher lived first in Ramsey but eventually moved to Maughold, finally coming to live near to the Dhoon Church in Glen Mona. Poetry Faragher’s first poem, 'Blue Point’, was published in the Ramsey Courier on 14 October 1949. The poem was written whilst in Kent and sent to the paper, who surprised Faragher in accepting it, although it was not published until she had returned to live on the island. This poem was different in style to Faragher’s subsequent work and it was only published in her third book of poetry, Where Curlews Call, in 1959, by which time it had been substantially rewritten. Her next poem, 'Maughold Head’, was published at the start of February 1950, after which her poems were published regularly in the Ramsey Courier. Her first published poem in the Anglo-Manx dialect was 'A Lament’, which appeared in September 1950. Her poems were quickly picked up as special evocations of the Isle of Man and they were recited at meetings of Manx Societies in England alongside poems by the Manx National Poet, T. E. Brown, as early as November 1951. Her poems, 'Maughold Head’ and 'In Exile’, were set to music by C. Sydney Marshall and had been cut to record by February 1960. Her first book of poems, Green Hills by the Sea, was published in February 1955 by The Ramsey Courier Ltd. The book’s title is a reference to the popular song, 'Ellan Vannin’, composed from a poem by Eliza Craven Green. The book was described as displaying Faragher’s “deep insight into Manx feelings and a nostalgic love of the old folk and ways” by George Bellairs. The collection opened with 'Land of My Birth’, which she described as “the greatest compliment she can pay to the Manx people” and with which she usually ended her recitals. I love this purple-misted Isle, This land where I was born. The gorse-clad hills and bracken tops, The fields of waving corn. [...] But best of all I love to hear The gentle, lilting voice Of kindly Manx folk greeting me: It makes my heart rejoice, To feel once more the friendly hand, To hear the welcome warm, To look into each smiling face And know I have come home. Her second collection, This Purple-Misted Isle, was published in October 1957. The title was another reference to her forebears of Manx literature, this time to T. E. Brown, a reference continued within the collection with Faragher’s 'The Immortal “Kitty”' paying homage to Brown’s 'Kitty o’ the Sherragh Vane’ from his Fo’c’s’le Yarns. The collection had a Foreword by the Lieutenant Governor, Ambrose Flux Dundas. It proved to be very popular, having to be reprinted by the end of the year, and by the end of 1959 a third print had also almost sold out. This collection included 'The Homecomer’, which displays her distinctive Anglo-Manx conversational style: [...] “It isn’ me dyin’ that I min’, boy,” She said as she sat by her bed; “I’d go peaceful if it wasn’ for thinkin’ Ye’ll be managin’ so maul when I’m dead.” An’ Billy sthroked her cheek– so the tale goes – An’ whispered all lovin’ an’ low, “Dunt be grievin’, Nellie Kate; theer’s no need to gel, To worry about me when yer go! For theer’s the nices’ li’l wumman in Laxaa That I’ve had me eye on this las’ bit; She’ll look after me well, I can tell yer, So take yer res’, Nellie Kate, an’ dunt fret!” My gough! She gorrup from that bed theer Like an arra shot straight from the bow! Ay! an’ Billy himself was years buried ‘Fore herself in the en’ had to go! [...] By 1959 Faragher’s poems had been heard on BBC Radio a number of times, recited both by herself and by others. It was in October of that year that her third collection was released, Where Curlews Call, bearing a perceptive Preface by Sir Ralph Stevenson: “Our mother tongue has been overlaid by a stereotyped accent [...]. The Manx lilt [...] is all too rapidly fading. She does her best in these poems to keep it alive and at the same times gives a warm and human picture of our farms and crofts and the kindly folk who live in them. For this, if for nothing else, she has earned our gratitude.” Her subsequent collections of poetry were These Fairy Shores (1962) and English and Manx Dialect Poems (1967). Faragher’s poems can be predominantly categorised into two types: light-humoured dialect vignettes or lyrical descriptions of the Isle of Man. Her poems are distinctive in Manx literature in being prevailingly from or of a female perspective and based within the family or home environment. Theatre and prose As early as 1951 Faragher had been experimenting with extending her conversational monologue Anglo-Manx poems into theatrical dialogues for performance. In 1964 four such 'character sketches’ were published as Kiare Cooisghyn. As was distinctive of her dialect poetry, all of these pieces were written for middle-aged or elderly female characters and used a very tender humour born of a close observation of Manx character. Something of this is shown in the first 'duologue’ from the collection, 'The Caffy’ in which two women discuss the new café in town: [...] Mrs K. An’ what like was the china? Gran’ mighty I suppose? Mrs C. Aw! somethin’ awful that was! Rale indacent, in fac’. A whole lorra naked childher flyin’ about on the plates shootin’ bows an’ arras. Mrs K. Aw! them 'ud be l’il Cupids. Mrs C. Li’l Cupids? Li’l divils, more like! Why wan o’ them was the dead spit o’ that young dirt Kermid’s yandher! Ay! skeetin’ up at me through the gravy he was– enough to turn yer! [...] She came to concentrate on prose towards the end of her life, publishing By The Red Fuchsia Tree in 1967, a collection of short stories interspersed with reprints of poems from her earlier collections. This was followed by a long series of short dialect stories published under the pseudonym, “Kirree Ann”, in the Ramsey Courier at a rate of almost one a week over the last two years of her life. This output of nearly 100 short stories makes her the most prolific Manx short story writer of the twentieth Century. Death and legacy Kathleen Faragher died in 1974, on the same day as her final story was published in the Ramsey Courier. She was buried in the family plot in Maughold churchyard, a graveyard also associated with other important Manx writers such as T. E. Brown, Hall Caine, Cushag and William Kennish. Six years after her death, her friend, Constance Radcliffe, the leading authority on the local history of Ramsey and Maughold, wrote of Faragher’s work that: “In all her works she expressed her affection for a Manx way of life which has only just disappeared, her kindly humour based on acute observation of people’s idiosyncrasies, and her deep and abiding love of the island itself.” Her work continues to be popularly performed in recitals on the Isle of Man, despite none of her books having been republished after her death, and her “Kirree Ann” stories having never been collected. In 2015 a project to record the memories of those who knew and remember Faragher was launched. Funded by Culture Vannin, it is envisioned to tie in with the Culture Vannin oral history programme, but also to reach more widely to collect unpublished works, memorabilia or other artefacts that might be uncovered. In introducing the initiative, the project organiser gave an estimation of Faragher’s work in relation to Manx literature: “the importance of her work to the Isle of Man would be hard to overestimate. It would be a tragedy for Manx culture if we did not do everything in our power to preserve all we can of her memory.” Publications * Green Hills by the Sea. Ramsey: The Ramsey Courier Ltd. 1954. * This Purple-Misted Isle. Ramsey: The Ramsey Courier Ltd. 1957. * Where Curlews Call. Ramsey: The Ramsey Courier Ltd. 1959. * These Fairy Shores. Ramsey: The Ramsey Courier Ltd. 1962. * Kiare Cooisghyn. Ramsey: The Ramsey Courier Ltd. 1964. * English and Manx Dialect Poems. Douglas: Norris Modern Press. 1967. * By The Red Fuchsia Tree. Douglas: The Norris Modern Press. 1967. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kathleen_Faragher


Arthur Chapman (June 25, 1873– December 4, 1935) was an early twentieth-century American poet and newspaper columnist. He wrote a subgenre of American poetry known as Cowboy Poetry. His most famous poem was Out Where the West Begins. Out Where the West Begins Circa 1910, after reading in an Associated Press report of a conference of the governors of the western states at which the geographic beginning of the U.S. West was disputed, he hastily composed what was to become his most famous poem, “Out Where the West Begins,” celebrating the people and the land of the frontier. The first of its three seven-line stanzas ran "Out where the handclasp’s a little stronger, / Out where the smile dwells a little longer, / That’s where the West begins; / Out where the sun is a little brighter, / Where the snows that fall are a trifle whiter, / Where the bonds of home are a wee bit tighter, / That’s where the West begins." The poem was an immediate sensation, widely quoted, often imitated, and more often parodied. (One popular anonymous take-off read, in part, "Where the women boss and the men folk think / That toast is food and tea is a drink; / Where the men use powder and the wrist watch ticks, / And everyone else but themselves are hicks / That’s where the East begins.") According to the dust jacket of Chapman’s 1921 novel, Mystery Ranch, "To-day ["Out Where the West Begins"] is perhaps the best-known bit of verse in America. It hangs framed in the office of the Secretary of the Interior at Washington. It has been quoted in Congress, and printed as campaign material for at least two Governors. . . . [Chapman’s poems possess] a rich Western humor such as had not been heard in American poetry since the passing of Bret Harte.” The popularity of “Out Where the West Begins” led Chapman to arrange for its publication in book form, and in 1916 he produced Out Where the West Begins, and Other Small Songs of a Big Country, a modest fifteen-page volume issued by Carson-Harper in Denver. It was an immediate success and Houghton Mifflin of Boston and New York immediately offered to publish a larger collection. Out Where the West Begins, and Other Western Verses, as it was renamed, appeared in 1917 with fifty-eight poems on ninety-two pages. The title poem was widely reprinted on postcards and plaques. It was frequently set to music, first in 1920, and achieved a separate life on the concert stage. Chapman followed the popular volume in 1921 with the equally successful Cactus Center: Poems of an Arizona Town, containing thirty poems and running to 123 pages. The Literary Review wrote of the verse, "In vigor of style, [it] irresistibly suggests a transplanted Kipling" (19 Feb. 1921, p. 12). The Move East In 1919 Chapman moved to New York City, where he lived in a fashionable neighborhood on the east side of Manhattan and took a job as a staff writer for the Sunday edition of the New York Tribune. He held that position until his retirement in 1925, the year after the newspaper became the New York Herald Tribune. After his wife died in 1923 Chapman married Kathleen Caesar, an editor of the Bell Syndicate; no children were born of his second marriage. He wrote fiction and nonfiction throughout his career as a journalist and continued after he retired. His first effort at book-length fiction, Mystery Ranch (1921), combined the genres of western adventure and murder mystery. The Literary Review dismissed it as “melodramatic” and stated that it provided “little for the seeker of literary values” (19 Nov. 1921, p. 190), but the New York Times more charitably credited Chapman, “known heretofore as a poet of the West,” with being “a clever technician in a new field” (13 Nov. 1921). The book had modest commercial success, but Chapman’s second novel, John Crews (1926), an equally stereotypical adventure-romance of frontier life, sold better. Described by the New York Herald Tribune as “a lively and continuously readable yarn,” it was successful enough to have a reprint edition by another publisher in its first year (28 Mar. 1926). In 1924 Chapman capitalized on his reputation as an expert on the U.S. West with the publication of The Story of Colorado, Out Where the West Begins, a richly illustrated history of the state. His final book was an extensively researched and detailed volume, The Pony Express: The Record of a Romantic Adventure in Business (1932), complete with bibliography, index, and maps. Both were well received by the critics and the public. It was, however, for his poetry that Chapman became and remained famous. His western dialect poems and “Out Where the West Begins” continued to be quoted and to appear in anthologies long after his death, and both of his volumes of verse were brought out in new editions by other publishers as late as 2010. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arthur_Chapman_(poet)


Carl Rakosi (November 6, 1903– June 25, 2004) was the last surviving member of the original group of poets who were given the rubric Objectivist. He was still publishing and performing his poetry well into his 90s. Early life Rakosi was born in Berlin and lived there and in Hungary until 1910, when he moved to the United States to live with his father and stepmother. His father was a jeweler and watchmaker in Chicago and later in Gary, Indiana. The family lived in semi-poverty but contrived to send him to the University of Chicago and then to the University of Wisconsin–Madison. During his time studying at the university level, he started writing poetry. On graduating, he worked for a time as a social worker, then returned to college to study psychology. At this time, he changed his name to Callman Rawley because he felt he stood a better chance of being employed if he had a more American-sounding name. After a spell as a psychologist and teacher, he returned to social work for the rest of his working life. Early writings At the University of Wisconsin–Madison, Rakosi edited the Wisconsin Literary Magazine. His own poetry at this stage was influenced by W. B. Yeats, Wallace Stevens, and E. E. Cummings. He also started reading William Carlos Williams and T. S. Eliot. By 1925, he was publishing poems in The Little Review and Nation. Pound and the Objectivists By the late 1920s, Rakosi was in correspondence with Ezra Pound, who prompted Louis Zukofsky to contact him. This led to Rakosi’s inclusion in the Objectivist issue of Poetry and in the Objectivist Anthology. Rakosi himself had reservations about the Objectivist tag, feeling that the poets involved were too different from each other to form a group in any meaningful sense of the word. He did, however, especially admire the work of Charles Reznikoff. Later career Like a number of his fellow Objectivists, Rakosi abandoned poetry in the 1940s. After his 1941 Selected Poems he dedicated himself to social work and apparently neither read nor wrote poetry. Years earlier, shortly after his twenty-first birthday, Rakosi had legally changed his name to Callman Rawley, believing that he would not find work with his foreign-sounding name. Under his adopted name, he served as head of the Minneapolis Jewish Children’s and Family Service from 1945 until his retirement in 1968. A letter from the English poet Andrew Crozier about his early poetry was the trigger that started Rakosi writing again. His first book in 26 years, Amulet, was published by New Directions in 1967 and his Collected Poems in 1986 by the National Poetry Foundation. These were followed by several more volumes and by readings across the United States and Europe. In early November 2003, Rakosi celebrated his 100th birthday with friends at the San Francisco Public Library. Upon his death Jacket Magazine editor John Tranter observed the following: Poet Carl Rakosi died on Friday afternoon June 25 at the age of 100, after a series of strokes, in his home in San Francisco. My wife Lyn and I were passing through California in November 2003, and we stopped by to have a coffee with Carl at his home in Sunset. By a lucky coincidence, it happened to be his 100th birthday. He was, as always, kind, thoughtful, bright and alert, and as sharp as a pin. We felt privileged to know him. External links Rakosi at Modern American Poetry The Carl Rakosi Papers in the Mandeville Special Collections Library at UC San Diego Carl Rakosi Reading and Interview on KPFA’s Ode To Gravity, 13 May 1971 (from The Internet Archive) Obituary in The Guardian, UK Carl Rakosi feature at Jacket Magazine includes Rakosi in conversation with Tom Devaney & Olivier Brossard; link to audio recordings at University of Pennsylvania, and poems, dedications & remembrances from Jane Augustine, Robert Creeley, Laurie Duggan, Michael Heller and Kent Johnson “Add-Verse” a poetry-photo-video project Rakosi participated in References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carl_Rakosi


Sojourner Truth (born Isabella ("Bell") Baumfree; C. 1797– November 26, 1883) was an African-American abolitionist and women’s rights activist. Truth was born into slavery in Swartekill, Ulster County, New York, but escaped with her infant daughter to freedom in 1826. After going to court to recover her son, in 1828 she became the first black woman to win such a case against a white man. She gave herself the name Sojourner Truth in 1843 after she became convinced that God had called her to leave the city and go into the countryside “testifying the hope that was in her.” Her best-known speech was delivered extemporaneously, in 1851, at the Ohio Women’s Rights Convention in Akron, Ohio. The speech became widely known during the Civil War by the title “Ain’t I a Woman?,” a variation of the original speech re-written by someone else using a stereotypical Southern dialect; whereas Sojourner Truth was from New York and grew up speaking Dutch as her first language. During the Civil War, Truth helped recruit black troops for the Union Army; after the war, she tried unsuccessfully to secure land grants from the federal government for former slaves. In 2014, Truth was included in Smithsonian magazine’s list of the "100 Most Significant Americans of All Time". Early years Truth was one of the ten or twelve children born to James and Elizabeth Baumfree (or Bomefree). Colonel Hardenbergh bought James and Elizabeth Baumfree from slave traders and kept their family at his estate in a big hilly area called by the Dutch name Swartekill (just north of present-day Rifton), in the town of Esopus, New York, 95 miles (153 km) north of New York City. Charles Hardenbergh inherited his father’s estate and continued to enslave people as a part of that estate’s property. When Charles Hardenbergh died in 1806, nine-year-old Truth (known as Belle), was sold at an auction with a flock of sheep for $100 to John Neely, near Kingston, New York. Until that time, Truth spoke only Dutch. She later described Neely as cruel and harsh, relating how he beat her daily and once even with a bundle of rods. Neely sold her in 1808, for $105, to Martinus Schryver of Port Ewen, a tavern keeper, who owned her for eighteen months. Schryver sold her in 1810 to John Dumont of West Park, New York. Although this fourth owner was kindly disposed toward her, considerable tension existed between Truth and Dumont’s second wife, Elizabeth Waring Dumont, who harassed her and made her life more difficult. (John Dumont’s first wife, Sarah “Sally” Waring Dumont (Elizabeth’s sister), died around 1805, five years before he bought Truth.) Around 1815, Truth met and fell in love with a slave named Robert from a neighboring farm. Robert’s owner (Charles Catton, Jr., a landscape painter) forbade their relationship; he did not want the people he enslaved to have children with people he was not enslaving, because he would not own the children. One day Robert sneaked over to see Truth. When Catton and his son found him, they savagely beat Robert until Dumont finally intervened, and Truth never saw Robert again. He later died some years later, perhaps as a result of the injuries, and the experience haunted Truth throughout her life. Truth eventually married an older slave named Thomas. She bore five children: James, her firstborn, who died in childhood, Diana (1815), fathered by either Robert or John Dumont, and Peter (1821), Elizabeth (1825), and Sophia (ca. 1826), all born after she and Thomas united. Freedom The state of New York began, in 1799, to legislate the abolition of slavery, although the process of emancipating those people enslaved in New York was not complete until July 4, 1827. Dumont had promised to grant Truth her freedom a year before the state emancipation, “if she would do well and be faithful.” However, he changed his mind, claiming a hand injury had made her less productive. She was infuriated but continued working, spinning 100 pounds of wool, to satisfy her sense of obligation to him. Late in 1826, Truth escaped to freedom with her infant daughter, Sophia. She had to leave her other children behind because they were not legally freed in the emancipation order until they had served as bound servants into their twenties. She later said “I did not run off, for I thought that wicked, but I walked off, believing that to be all right.” She found her way to the home of Isaac and Maria Van Wagenen in New Paltz, who took her and her baby in. Isaac offered to buy her services for the remainder of the year (until the state’s emancipation took effect), which Dumont accepted for $20. She lived there until the New York State Emancipation Act was approved a year later. Truth learned that her son Peter, then five years old, had been sold illegally by Dumont to an owner in Alabama. With the help of the Van Wagenens, she took the issue to court and in 1828, after months of legal proceedings, she got back her son, who had been abused by those who were enslaving him. Truth became one of the first black women to go to court against a white man and win the case. Truth had a life-changing religious experience during her stay with the Van Wagenens, and became a devout Christian. In 1829 she moved with her son Peter to New York City, where she worked as a housekeeper for Elijah Pierson, a Christian Evangelist. While in New York, she befriended Mary Simpson, a grocer on John Street who claimed she had once been enslaved by George Washington. They shared an interest in charity for the poor and became intimate friends. In 1832, she met Robert Matthews, also known as Prophet Matthias, and went to work for him as a housekeeper at the Matthias Kingdom communal colony. Elijah Pierson died, and Robert Matthews and Truth were accused of stealing from and poisoning him. Both were acquitted of the murder, though Matthews was convicted of lesser crimes, served time, and moved west. In 1839, Truth’s son Peter took a job on a whaling ship called the Zone of Nantucket. From 1840 to 1841, she received three letters from him, though in his third letter he told her he had sent five. Peter said he also never received any of her letters. When the ship returned to port in 1842, Peter was not on board and Truth never heard from him again. “The Spirit Calls Me” 1843 was a turning point for Truth. She became a Methodist, and on June 1, she changed her name to Sojourner Truth. She told friends: “The Spirit calls me, and I must go” and left to make her way traveling and preaching about the abolition of slavery. At that time, Truth began attending Millerite Adventist campmeetings. However, that did not last since Jesus failed to appear in 1843 and then again in 1844. Like many others disappointed, Truth distanced herself from her Millerite friends for a while. In 1844, she joined the Northampton Association of Education and Industry in Northampton, Massachusetts. Founded by abolitionists, the organization supported women’s rights and religious tolerance as well as pacifism. There were, in its four-and-a-half year history, a total of 240 members, though no more than 120 at any one time. They lived on 470 acres (1.9 km2), raising livestock, running a sawmill, a gristmill, and a silk factory. While there, Truth met William Lloyd Garrison, Frederick Douglass, and David Ruggles. In 1846, the group disbanded, unable to support itself. In 1845, she joined the household of George Benson, the brother-in-law of William Lloyd Garrison. In 1849, she visited John Dumont before he moved west. Truth started dictating her memoirs to her friend Olive Gilbert, and in 1850 William Lloyd Garrison privately published her book, The Narrative of Sojourner Truth: A Northern Slave. That same year, she purchased a home in what would become the village of Florence in Northampton for $300, and spoke at the first National Women’s Rights Convention in Worcester, Massachusetts. In 1854, with proceeds from sales of the Narrative and cartes-de-visite entitled “I sell the shadow to support the substance,” she paid off the mortgage held by her friend from the Community, Samuel L. Hill. “Ain’t I a Woman?” In 1851, Truth joined George Thompson, an abolitionist and speaker, on a lecture tour through central and western New York State. In May, she attended the Ohio Women’s Rights Convention in Akron, Ohio, where she delivered her famous extemporaneous speech on women’s rights, later known as “Ain’t I a Woman.” Her speech demanded equal human rights for all women as well as for all blacks. The convention was organized by Hannah Tracy and Frances Dana Barker Gage, who both were present when Truth spoke. Different versions of Truth’s words have been recorded, with the first one published a month later by Marius Robinson, a newspaper owner and editor who was in the audience. Robinson’s recounting of the speech included no instance of the question “Ain’t I a Woman?” Twelve years later in May 1863, Gage published another, very different, version. In it, Truth’s speech pattern had characteristics of Southern slaves, and the speech included sentences and phrases that Robinson didn’t report. Gage’s version of the speech became the historic standard version, and is known as “Ain’t I a Woman?” because that question was repeated four times. It is highly unlikely that Truth’s own speech pattern was Southern in nature, as she was born and raised in New York, and she spoke only Dutch until she was nine years old. In contrast to Robinson’s report, Gage’s 1863 version included Truth saying her 13 children were sold away from her into slavery. Truth is widely believed to have had five children, with one sold away, and was never known to boast more children. Gage’s 1863 recollection of the convention conflicts with her own report directly after the convention: Gage wrote in 1851 that Akron in general and the press in particular were largely friendly to the woman’s rights convention, but in 1863 she wrote that the convention leaders were fearful of the “mobbish” opponents. Other eyewitness reports of Truth’s speech told a calm story, one where all faces were “beaming with joyous gladness” at the session where Truth spoke; that not “one discordant note” interrupted the harmony of the proceedings. In contemporary reports, Truth was warmly received by the convention-goers, the majority of whom were long-standing abolitionists, friendly to progressive ideas of race and civil rights. In Gage’s 1863 version, Truth was met with hisses, with voices calling to prevent her from speaking. Over the next 10 years, Truth spoke before dozens, perhaps hundreds, of audiences. From 1851 to 1853, Truth worked with Marius Robinson, the editor of the Ohio Anti-Slavery Bugle, and traveled around that state speaking. In 1853, she spoke at a suffragist “mob convention” at the Broadway Tabernacle in New York City; that year she also met Harriet Beecher Stowe. In 1856, she traveled to Battle Creek, Michigan, to speak to a group called the “Friends of Human Progress.” In 1858, someone interrupted a speech and accused her of being a man; Truth opened her blouse and revealed her breasts. Other notable speeches Northampton Camp Meeting—1844, Northampton, Massachusetts: At a camp meeting where she was participating as an itinerant preacher, a band of “wild young men” disrupted the camp meeting, refused to leave, and threatening to burn down the tents. Truth caught the sense of fear pervading the worshipers and hid behind a trunk in her tent, thinking that since she was the only black person present, the mob would attack her first. However, she reasoned with herself and resolved to do something: as the noise of the mob increased and a female preacher was “trembling on the preachers’ stand,” Truth went to a small hill and began to sing “in her most fervid manner, with all the strength of her most powerful voice, the hymn on the resurrection of Christ." Her song, “It was Early in the Morning,” gathered the rioters to her and quieted them. They urged her to sing, preach, and pray for their entertainment. After singing songs and preaching for about an hour, Truth bargained with them to leave after one final song. The mob agreed and left the camp meeting. Abolitionist Convention—1840s, Boston, Massachusetts: William Lloyd Garrison invited Sojourner Truth to give a speech at an annual antislavery convention. Wendell Phillips was supposed to speak after her, which made her nervous since he was known as such a good orator. So Truth sang a song, “I am Pleading for My people,” which was her own original composition sung to the tune of Auld Lang Syne. Mob Convention—September 7, 1853: At the convention, young men greeted her with "a perfect storm,” hissing and groaning. In response, Truth said, “You may hiss as much as you please, but women will get their rights anyway. You can’t stop us, neither”. Sojourner, like other public speakers, often adapted her speeches to how the audience was responding to her. In her speech, Sojourner speaks out for women’s rights. She incorporates religious references in her speech, particularly the story of Esther. She then goes on to say that, just as women in scripture, women today are fighting for their rights. Moreover, Sojourner scolds the crowd for all their hissing and rude behavior, reminding them that God says to “Honor thy father and thy mother.” American Equal Rights Association—May 9–10, 1867: Her speech was addressed to the American Equal Rights Association, and divided into three sessions. Sojourner was received with loud cheers instead of hisses, now that she had a better-formed reputation established. The Call had advertised her name as one of the main convention speakers. For the first part of her speech, she spoke mainly about the rights of black women. Sojourner argued that because the push for equal rights had led to black men winning new rights, now was the best time to give black women the rights they deserve too. Throughout her speech she kept stressing that “we should keep things going while things are stirring” and fears that once the fight for colored rights settles down, it would take a long time to warm people back up to the idea of colored women’s having equal rights. In the second sessions of Sojourner’s speech, she utilized a story from the Bible to help strengthen her argument for equal rights for women. She ended her argument by accusing men of being self-centered, saying, “man is so selfish that he has got women’s rights and his own too, and yet he won’t give women their rights. He keeps them all to himself.” For the final session of Sojourner’s speech, the center of her attention was mainly on women’s right to vote. Sojourner told her audience that she owned her own house, as did other women, and must therefore pay taxes. Nevertheless, they were still unable to vote because they were women. Black women who were enslaved were made to do hard manual work, such as building roads. Sojourner argues that if these women were able to perform such tasks, then they should be allowed to vote because surely voting is easier than building roads. Eighth Anniversary of Negro Freedom—New Year’s Day, 1871: On this occasion the Boston papers related that “...seldom is there an occasion of more attraction or greater general interest. Every available space of sitting and standing room was crowded". She starts off her speech by giving a little background about her own life. Sojourner recounts how her mother told her to pray to God that she may have good masters and mistresses. She goes on to retell how her masters were not good to her, about how she was whipped for not understanding English, and how she would question God why he had not made her masters be good to her. Sojourner admits to the audience that she had once hated white people, but she says once she met her final master, Jesus, she was filled with love for everyone. Once enslaved folks were emancipated, she tells the crowd she knew her prayers had been answered. That last part of Sojourner’s speech brings in her main focus. Some freed enslaved people were living on government aid at that time, paid for by taxpayers. Sojourner announces that this is not any better for those colored people than it is for the members of her audience. She then proposes that black people are given their own land. Because a portion of the South’s population contained rebels that were unhappy with the abolishment of slavery, that region of the United States was not well suited for colored people. She goes on to suggest that colored people be given land out west to build homes and prosper on. On a mission In 1856, Truth bought a neighboring lot in Northampton, but she did not keep the new property for long. On September 3, 1857, she sold all her possessions, new and old, to Daniel Ives and moved to Battle Creek, Michigan, where she rejoined former members of the Millerite Movement who had formed the Seventh-day Adventist Church. Antislavery movements had begun early in Michigan and Ohio. Here, she also joined the nucleus of the Michigan abolitionists, the Progressive Friends, some who she had already met at national conventions. According to the 1860 census, her household in Harmonia included her daughter, Elizabeth Banks (age 35), and her grandsons James Caldwell (misspelled as “Colvin”; age 16) and Sammy Banks (age 8). During the Civil War, Truth helped recruit black troops for the Union Army. Her grandson, James Caldwell, enlisted in the 54th Massachusetts Regiment. In 1864, Truth was employed by the National Freedman’s Relief Association in Washington, D.C., where she worked diligently to improve conditions for African-Americans. In October of that year, she met President Abraham Lincoln. In 1865, while working at the Freedman’s Hospital in Washington, Truth rode in the streetcars to help force their desegregation. Truth is credited with writing a song, “The Valiant Soldiers”, for the 1st Michigan Colored Regiment; it was said to be composed during the war and sung by her in Detroit and Washington, D.C. It is sung to the tune of “John Brown’s Body” or “The Battle Hymn of the Republic”. Although Truth claimed to have written the words, it has been disputed (see “Marching Song of the First Arkansas”). In 1867, Truth moved from Harmonia to Battle Creek. In 1868, she traveled to western New York and visited with Amy Post, and continued traveling all over the East Coast. At a speaking engagement in Florence, Massachusetts, after she had just returned from a very tiring trip, when Truth was called upon to speak she stood up and said “Children, I have come here like the rest of you, to hear what I have to say.” In 1870, Truth tried to secure land grants from the federal government to former enslaved people, a project she pursued for seven years without success. While in Washington, D.C., she had a meeting with President Ulysses S. Grant in the White House. In 1872, she returned to Battle Creek and tried to vote in the presidential election, but was turned away at the polling place. Truth spoke about abolition, women’s rights, prison reform, and preached to the Michigan Legislature against capital punishment. Not everyone welcomed her preaching and lectures, but she had many friends and staunch support among many influential people at the time, including Amy Post, Parker Pillsbury, Frances Gage, Wendell Phillips, William Lloyd Garrison, Laura Smith Haviland, Lucretia Mott, Ellen G. White, and Susan B. Anthony.” Death and legacy Several days before Sojourner Truth died, a reporter came from the Grand Rapids Eagle to interview her. “Her face was drawn and emaciated and she was apparently suffering great pain. Her eyes were very bright and mind alert although it was difficult for her to talk.” Truth died at her Battle Creek home on November 26, 1883. On November 28 her funeral was held at the Congregational-Presbyterian Church officiated by its pastor, the Reverend Reed Stuart. Some of the prominent citizens of Battle Creek acted as pall-bearers. Truth was buried in the city’s Oak Hill Cemetery. The calendar of saints of the Episcopal Church remembers Sojourner Truth annually, together with Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Amelia Bloomer and Harriet Ross Tubman on July 20. The calendar of saints of the Lutheran Church remembers Sojourner Truth together with Harriet Tubman on March 10. A larger-than-life sculpture of Sojourner Truth by artist Tina Allen, was dedicated in 1999, which is the estimated bicentennial of Sojourner’s birth. The 12-foot tall Sojourner monument is cast bronze. Cultural references and commemorations Other honors and commemorations include (by year): 1862– William Wetmore Story’s statue, The Libyan Sibyl, inspired by Sojourner Truth, won an award at the London World Exhibition. 1892– Albion artist Frank Courter is commissioned to paint the meeting between Truth and President Abraham Lincoln. 1969– The leftist group the Sojourner Truth Organization is named after her. The group folded in 1985. 1971– Sojourner Truth Library at New Paltz State University of New York is named in Truth’s honor. 1976– Interstate 194 is named for her in Michigan. 1979– The artwork The Dinner Party features a place setting for Truth. 1980– The Inter Cooperative Council at the University of Michigan and the residents of the then Lenny Bruce House rename it as Sojourner Truth House in her honor. 1981– Truth is inducted into the National Women’s Hall of Fame in Seneca Falls, New York. 1981– Feminist theorist and author bell hooks titles her first major work after Truth’s “Ain’t I a Woman?” speech. 1983– Truth is in the first group of women inducted into the Michigan Women’s Hall of Fame in Lansing. 1986– The U.S. Postal Service issues a commemorative postage stamp honoring Sojourner Truth. 1987– Truth is commemorated in a monument of “Michigan Legal Milestones” erected by the State Bar of Michigan. 1997– The NASA Mars Pathfinder mission’s robotic rover is named “Sojourner” after her. 1998– S.T. Writes Home appears on the web offering “Letters to Mom from Sojourner Truth,” in which the Mars Pathfinder Rover at times echoes its namesake. 1999– A 12-foot-high monument is built to honor her in Battle Creek, Michigan. 1999– The Broadway musical The Civil War includes an abridged version of Truth’s “Ain’t I a Woman?” speech as a spoken-word segment. On the 1999 cast recording, the track was performed by Maya Angelou. 2002– Scholar Molefi Kete Asante lists Sojourner Truth on his list of 100 Greatest African Americans. 2002– A statue was installed in Florence Massachusetts to honor Sojourner Truth in a small park located on Pine Street and Park Street, on which she lived for ten years. 2004– The King’s College, located inside the Empire State Building in New York City, names one of their houses “The House of Sojourner Truth”. 2009– Truth becomes the first black woman honored with a bust in the U.S. Capitol. The bust was sculpted by noted artist Artis Lane. It is in Emancipation Hall of the Capitol Visitor Center. v2014– Truth was included in the Smithsonian Institution’s list of the "100 Most Significant Americans". 2014– Asteroid (249521) Truth is named in her honor. 2015– A statue of Sojourner Truth is unveiled at the University of California, San Diego. The statue resides in Marshall College. As of March 2015, K-12 schools in several states, including California, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York and Oregon, are named after her, as is Sojourner–Douglass College in Baltimore. Ten-dollar bill On April 20, 2016 Treasury Secretary Jacob Lew announced that several denominations of United States currency would be redesigned prior to 2020, the 100th anniversary of the 19th Amendment. The newly designed $10 bill will include images on the reverse which will pay homage to the women’s suffrage movement and feature the images of Truth, Lucretia Mott, Susan B. Anthony, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Alice Paul, and the 1913 Woman Suffrage Procession.


May Sarton is the pen name of Eleanore Marie Sarton ( (May 3, 1912– July 16, 1995), an American poet, novelist and memoirist. Biography Sarton was born in Wondelgem, Belgium (today a part of the city of Ghent). Her parents were science historian George Sarton and his wife, the English artist Mabel Eleanor Elwes. When German troops invaded Belgium after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914, her family fled to Ipswich, England, where Sarton’s maternal grandmother lived. One year later, they moved to Boston, Massachusetts, where her father started working at Harvard University. She went to school in Cambridge, Massachusetts, graduating from Cambridge High and Latin School in 1929. She started theatre lessons in her late teens, but continued writing poetry. She published her first collection in 1937, entitled Encounter in April. In 1945 in Santa Fe, New Mexico, she met Judy Matlack, who became her partner for the next thirteen years. They separated in 1956, when Sarton’s father died and Sarton moved to Nelson, New Hampshire. Honey in the Hive (1988) is about their relationship. In her memoir At Seventy, Sarton reflected on Judy’s importance in her life and how her Unitarian Universalist upbringing shaped her. She was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1958. Sarton later moved to York, Maine. In 1990, she suffered a stroke, severely reducing her ability to concentrate and write. After several months, she was able to dictate her final journals, starting with Endgame, with the help of a tape recorder. She died of breast cancer on July 16, 1995, and is buried in Nelson, New Hampshire. Works and themes Despite the quality of some of her many novels and poems, May Sarton’s best and most enduring work probably lies in her journals and memoirs, particularly Plant Dreaming Deep (about her early years at Nelson, ca. 1958-68), Journal of a Solitude (1972-1973, often considered her best), The House by the Sea (1974-1976), Recovering (1978-1979) and At Seventy (1982-1983). In these fragile, rambling and honest accounts of her solitary life, she deals with such issues as aging, isolation, solitude, friendship, love and relationships, lesbianism, self-doubt, success and failure, envy, gratitude for life’s simple pleasures, love of nature (particularly of flowers), the changing seasons, spirituality and, importantly, the constant struggles of a creative life. Sarton’s later journals are not of the same quality, as she endeavoured to keep writing through ill health and by dictation. Although many of her earlier works, such as Encounter in April, contain vivid erotic female imagery, May Sarton often emphasized in her journals that she didn’t see herself as a “lesbian” writer, instead wanting to touch on what is universally human about love in all its manifestations. When publishing her novel Mrs. Stevens Hears the Mermaids Singing in 1965, she feared that writing openly about lesbianism would lead to a diminution of the previously established value of her work. “The fear of homosexuality is so great that it took courage to write Mrs. Stevens Hears the Mermaids Singing,” she wrote in Journal of a Solitude, “to write a novel about a woman homosexual who is not a sex maniac, a drunkard, a drug-taker, or in any way repulsive, to portray a homosexual who is neither pitiable nor disgusting, without sentimentality ...” After the book’s release, many of Sarton’s works began to be studied in university level women’s studies classes, being embraced by feminists and lesbians alike. However, Sarton’s work should not be classified as 'lesbian literature’ alone, as her works tackle many deeply human issues of love, loneliness, aging, nature, self-doubt etc., common to both men and women. Margot Peters’ controversial biography (1998) revealed May Sarton as a complex individual who often struggled in her relationships.


Frederick William Harvey DCM (26 March 1888– 13 February 1957), often known as Will Harvey, and dubbed “the Laureate of Gloucestershire”, was an English poet, broadcaster and solicitor whose poetry became popular during and after World War I. Early life Harvey was born in 1888 in Hartpury, Gloucestershire, and grew up in Minsterworth. He was educated at the King’s School, Gloucester, where he formed a close friendship with Ivor Gurney, and then at Rossall School. Gurney and Herbert Howells, another local composer, would set a number of his poems to music. He started on a legal career, which would always be somewhat tentative; and began to consider conversion to Roman Catholicism. World War I On 8 August 1914, only four days after the United Kingdom had declared war on Germany, Harvey joined the 5th battalion of the Gloucestershire Regiment as a private. Shortly afterwards, in November, he became a Roman Catholic. He was an adherent of the distributism movement, described as a “third way”, in opposition to both socialism and capitalism; and he was influenced by the work of G. K. Chesterton and Hilaire Belloc. His battalion was posted to France in March 1915, where he was promoted to lance corporal and awarded the Distinguished Conduct Medal. His citation for the DCM reads: 2371 Lance-Corpl. F.W. Harvey, 1/5th Gloucestershire R[egiment]. (T.F.) For conspicuous gallantry on the night of Aug. 3-4, 1915, near Hebuterne, when, with a patrol, he and another non-commissioned officer went out to reconnoiter in the direction of a suspected listening-post. In advancing they encountered the hostile post, evidently covering a working party in the rear. Corporal Knight at once shot one of the enemy, and, with Lance-Corporal Harvey, rushed the post, shooting two others, and, assistance arriving, the enemy fled. Lance-Corporal Harvey pursued, felling one of the retreating Germans with a bludgeon. He seized him, but, finding his revolver empty and the enemy having opened fire, he was called back by Corporal Knight, and the prisoner escaped. Three Germans were killed, and their rifles and a Mauser pistol were brought in. The patrol had no loss. He returned to England for officer training, but after being commissioned and returning to France he was captured on 17 August 1916 in the German front-line trench while carrying out a reconnaissance patrol. He spent the remainder of the war in prisoner-of-war camps, including those at Gütersloh, Crefeld, Schwarmstedt, Holzminden, Bad Colberg, and Stralsund. Writing Soon after his arrival in France, Harvey had begun to contribute to a trench newspaper, the Fifth Gloucester Gazette. His first volume of poems, A Gloucestershire Lad At Home and Abroad, was published in September 1916, shortly after his capture. He began to write more intensively in captivity, and poems were sent back to England for publication: his second collection, Gloucestershire Friends, appeared in 1917. His time in the camps is held to be his most productive period of writing. On returning from a spell of solitary confinement at Holzminden after a failed escape attempt, he saw that a fellow prisoner had drawn a picture over his bed in chalk of ducks in a pool of water. This inspired his most celebrated poem (and the title poem of his third collection, published in 1919), “Ducks”. Post-war life Harvey returned home in 1919, married in 1921, and returned to legal practice. He became a respected and loved figure in the Forest of Dean. He worked largely as a defence solicitor (his own captivity convincing him that incarceration was destructive and pointless), and became known as the “poor man’s solicitor”. His work was not financially successful, and in the 1930s he sold his practice. In 1920 he published a memoir of his prison-camp experiences, Comrades in Captivity; and in 1921 Farewell, the title an acknowledgement of his intention to remove himself from the literary world. He had a brief creative union with his great friend and collaborator, Ivor Gurney, which was cut short by Gurney’s mental breakdown. His gift for oration, versatile voice and scripting led him to become a popular broadcaster at the BBC, Bristol, where he used his popularity to promote the Forest of Dean, its people and traditions. He promoted local choirs, musicians and young authors such as Leonard Clark. He was friends with Rutland Boughton and the local MP, Morgan Philips Price, who worked with him to promote the arts and the interests of Foresters. Later years In later life Harvey craved the comradeship he had found in the trenches and was disappointed that the new social order he had anticipated never happened. His later poetry of remembrance captured those feelings, but retained the essential humour of his early work and included verse in the local dialect. In 1956, in failing health, he attended the Three Choirs Festival at Gloucester Cathedral to hear Elgar’s The Dream of Gerontius, a work that had inspired his ideas about creativity and beauty some fifty years earlier. He died the following year and was buried at Minsterworth. Personal life In 1921 Harvey married Anne Kane, an Irish nurse. They had two children, Eileen Anne (born 1922) and Patrick (born 1925). He led a bohemian lifestyle, rejecting material values, and often recklessly gave away his professional services and income. Reputation and legacy Harvey’s poems published during and immediately after World War I were highly acclaimed, and his status was acknowledged when a collection was published in 1926 in the Augustan Books of Modern Poetry series, edited by Edward Thompson. The lyricism of his poetry led to it being set to music by his friends Ivor Gurney, Herbert Howells and Sir Herbert Brewer, among others. It continues to be used by contemporary composers including Johnny Coppin. His work is particularly noted for its appreciation of the natural world and the landscape and traditions of West Gloucestershire. Harvey was commemorated by a slate memorial tablet in the south transept of Gloucester Cathedral in 1980. “Ducks”, Harvey’s best known work, was voted one of the nation’s 100 favourite poems in 1996 in a nationwide poll conducted by the BBC. Works Poetry collections * A Gloucestershire Lad At Home and Abroad. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. 1916. * Gloucestershire Friends: Poems from a German Prison Camp. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. 1917. * Ducks, and other Verses. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. 1919. * Farewell. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. 1921. * September and Other Poems. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. 1925. * In Pillowell Woods. Lydney: Frank Harris. 1926. * Gloucestershire: A Selection from the Poems of F.W. Harvey. Edinburgh: Oliver & Boyd. 1947. Edited collections * Thompson, Edward, ed. (1926). The Augustan Books of Modern Poetry: Frederick William Harvey. London: Ernest Benn. * Forest Offering: A Selection from the Unpublished Poems of F.W. Harvey, 1888-1957. Frank Green. 1962. * F.W. Harvey: Collected Poems 1912-1957. Coleford: Douglas McLean. 1983. * Boden, Anthony; Thornton, R.K.R., eds. (2011). F.W. Harvey: Selected Poems. Coleford: Douglas McLean. Novel * Harvey, F.W. (2014). A War Romance. Stroud, Glos.: The History Press. Prose (war memoirs) * Harvey, F.W. (1920). Comrades in Captivity: a Record of Life in Seven German Prison Camps. London: Sidgwick & Jackson. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/F._W._Harvey


Sarah Orne Jewett (September 3, 1849– June 24, 1909) was an American novelist, short story writer and poet, best known for her local color works set along or near the southern seacoast of Maine. Jewett is recognized as an important practitioner of American literary regionalism. Early life Jewett’s family had been residents of New England for many generations, and Sarah Orne Jewett was born in South Berwick, Maine. Her father was a doctor specializing in “obstetrics and diseases of women and children.” and Jewett often accompanied him on his rounds, becoming acquainted with the sights and sounds of her native land and its people. As treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, a condition that developed in early childhood, Jewett was sent on frequent walks and through them also developed a love of nature. In later life, Jewett often visited Boston, where she was acquainted with many of the most influential literary figures of her day; but she always returned to South Berwick, small seaports near which were the inspiration for the towns of “Deephaven” and “Dunnet Landing” in her stories. Jewett was educated at Miss Olive Rayne’s school and then at Berwick Academy, graduating in 1866. She supplemented her education through an extensive family library. Jewett was “never overtly religious,” but after she joined the Episcopal church in 1871, she explored less conventional religious ideas. For example, her friendship with Harvard law professor Theophilus Parsons stimulated an interest in the teachings of Emanuel Swedenborg, an eighteenth-century Swedish scientist and theologian, who believed that the Divine “was present in innumerable, joined forms—a concept underlying Jewett’s belief in individual responsibility.” Career She published her first important story in the Atlantic Monthly at age 19, and her reputation grew throughout the 1870s and 1880s. Her literary importance arises from her careful, if subdued, vignettes of country life that reflect a contemporary interest in local color rather than plot. Jewett possessed a keen descriptive gift that William Dean Howells called “an uncommon feeling for talk—I hear your people.” Jewett made her reputation with the novella The Country of the Pointed Firs (1896). A Country Doctor (1884), a novel reflecting her father and her early ambitions for a medical career, and A White Heron (1886), a collection of short stories are among her finest work. Some of Jewett’s poetry was collected in Verses (1916), and she also wrote three children’s books. Willa Cather described Jewett as a significant influence on her development as a writer, and “feminist critics have since championed her writing for its rich account of women’s lives and voices.” Later life On September 3, 1902, Jewett was injured in a carriage accident that all but ended her writing career. She was paralyzed by a stroke in March 1909, and she died on June 24 after suffering another. The Georgian home of the Jewett family, built in 1774 overlooking Central Square at South Berwick, is now a National Historic Landmark and Historic New England museum called the Sarah Orne Jewett House. Jewett never married, but she established a close friendship with writer Annie Adams Fields (1834–1915) and her husband, publisher James Thomas Fields, editor of the Atlantic Monthly. After the sudden death of James Fields in 1881, Jewett and Annie Fields lived together for the rest of Jewett’s life in what was then termed a “Boston marriage”. Some modern scholars have speculated that the two were lovers. Both women “found friendship, humor, and literary encouragement” in one another’s company, traveling to Europe together and hosting “American and European literati.” In France Jewett met Thérèse Blanc-Bentzon with whom she had long corresponded and who translated some of her stories for publication in France.


Amy Clampitt (June 15, 1920– September 10, 1994) was an American poet and author. Life Amy Clampitt was born on June 15, 1920 of Quaker parents, and brought up in New Providence, Iowa. In the American Academy of Arts and Letters and at nearby Grinnell College she began a study of English literature that eventually led her to poetry. She graduated from Grinnell College, and from that time on lived mainly in New York City. To support herself, she worked as a secretary at the Oxford University Press, a reference librarian at the Audubon Society, and a freelance editor. Not until the mid-1960s, when she was in her forties, did she return to writing poetry. Her first poem was published by The New Yorker in 1978. In 1983, at the age of sixty-three, she published her first full-length collection, The Kingfisher. In the decade that followed, Clampitt published five books of poetry, including What the Light Was Like (1985), Archaic Figure (1987), and Westward (1990). Her last book, A Silence Opens, appeared in 1994. She also published a book of essays and several privately printed editions of her longer poems. She taught at the College of William and Mary, Smith College, and Amherst College, but it was her time spent in Manhattan, in a remote part of Maine, and on various trips to Europe, the former Soviet Union, Iowa, Wales, and England that most directly influenced her work. Clampitt was the recipient of a 1982 Guggenheim Fellowship, a MacArthur Fellowship (1992), and she was a member of the American Academy of Arts and Letters and the American Academy of Poets. She died of cancer in September 1994.


James Ingram Merrill (March 3, 1926– February 6, 1995) was an American poet whose awards include the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry (1977) for Divine Comedies (1976). His poetry falls into two distinct bodies of work: the polished and formalist lyric poetry of his early career, and the epic narrative of occult communication with spirits and angels, titled The Changing Light at Sandover (published in three volumes from 1976 to 1980), which dominated his later career. Although most of his published work was poetry, he also wrote essays, fiction, and plays.


Dame Emilie Rose Macaulay, DBE (1 August 1881– 30 October 1958) was an English writer, most noted for her award-winning novel The Towers of Trebizond, about a small Anglo-Catholic group crossing Turkey by camel. The story is seen as a spiritual autobiography, reflecting her own changing and conflicting beliefs. Macaulay’s novels were partly-influenced by Virginia Woolf; she also wrote biographies and travelogues. Early years and education Macaulay was born in Rugby, Warwickshire the daughter of George Campbell Macaulay, a Classical scholar, and his wife, Grace Mary (née Conybeare). Her father was descended in the male-line directly from the Macaulay family of Lewis. She was educated at Oxford High School for Girls and read Modern History at Somerville College at Oxford University. Career Macaulay began writing her first novel, Abbots Verney (published 1906), after leaving Somerville and while living with her parents at Ty Isaf, near Aberystwyth, in Wales. Later novels include The Lee Shore (1912), Potterism (1920), Dangerous Ages (1921), Told by an Idiot (1923), And No Man’s Wit (1940), The World My Wilderness (1950), and The Towers of Trebizond (1956). Her non-fiction work includes They Went to Portugal, Catchwords and Claptrap, a biography of Milton, and Pleasure of Ruins. Macaulay’s fiction was influenced by Virginia Woolf and Anatole France. During World War I Macaulay worked in the British Propaganda Department, after some time as a nurse and later as a civil servant in the War Office. She pursued a romantic affair with Gerald O’Donovan, a writer and former Jesuit priest, from 1918 until his death in 1942. During the interwar period she was a sponsor of the pacifist Peace Pledge Union; however she resigned from the PPU and later recanted her pacifism in 1940. Her London flat was utterly destroyed in the Blitz, and she had to rebuild her life and library from scratch, as documented in the semi-autobiographical short story, Miss Anstruther’s Letters, which was published in 1942. The Towers of Trebizond, her final novel, is generally regarded as her masterpiece. Strongly autobiographical, it treats with wistful humour and deep sadness the attractions of mystical Christianity, and the irremediable conflict between adulterous love and the demands of the Christian faith. For this work, she received the James Tait Black Memorial Prize in 1956. Personal life Macaulay was never a simple believer in “mere Christianity”; however, and her writings reveal a more complex, mystical sense of the divine. That said, she did not return to the Anglican church until 1953; she had been an ardent secularist before and, while religious themes pervade her novels, previous to her conversion she often treats Christianity satirically, for instance in Going Abroad and The World My Wilderness. She never married, as a result of her lengthy and secret relationship with Gerald O’Donovan. They met in 1918 and the affair lasted until his death in 1942. She was created a Dame Commander of the Order of the British Empire (DBE) on 31 December 1957 in the 1958 New Years Honours. Macaulay was an active feminist throughout her life. Dame Rose Macaulay died on 30 October 1958, aged 77. Memorable quotes From The Towers of Trebizond: “Adultery is a meanness and a stealing, a taking away from someone what should be theirs, a great selfishness, and surrounded and guarded by lies lest it should be found out. And out of meanness and selfishness and lying flow love and joy and peace beyond anything that can be imagined.” First line of The Towers of Trebizond, cited by librarian Nancy Pearl in “Famous First Words: A Librarian Shares Favorite Literary Opening Lines,” [1] hosted by Steve Inskeep on NPR’s Morning Edition, 8 September 2004, as an example among “some notable opening lines that have made Pearl’s heart pound”. “Take my camel, dear”, said my Aunt Dot, as she climbed down from this animal on her return from High Mass. From Staying with Relations. Discussing the coat worn by a visitor, a character remarks: “Is rabbit fur disgusting because it’s cheap, or is it cheap because it’s disgusting?”
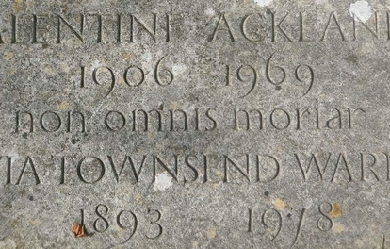

Valentine Ackland (20 May 1906– 9 November 1969) was an English poet, an important figure in the emergence of modernism in twentieth-century British poetry. Life Ackland was born Mary Kathleen Macrory Ackland to Robert Craig Ackland and his wife Ruth Kathleen (née Macrory), and nicknamed “Molly” by her family. With no sons born to the family, Valentine’s father, a West End London dentist, worked at making a symbolic son of Molly, teaching her to shoot rifles and to box. This attention to Molly made her sister Joan Alice Elizabeth (b. 1898) immensely jealous. Older by eight years, Joan psychologically tormented and physically abused Molly as a way of unleashing her jealousy and anger. Molly received an Anglo-Catholic upbringing in Norfolk and a convent school education in London. In 1925 at the age of nineteen, she impetuously married Richard Turpin, a homosexual youth who was unable to consummate their marriage. Upon her marriage, she was also received into the Catholic church, a religion that she later abandoned, returned to, and then abandoned again in the last decade of her life. In less than a year, she had her marriage to Turpin annulled, and, despite numerous pleas from her family and much psychological pressure from them, never returned to a serious relationship with a man again. Alert to social mores of her day, she became aware of societal patterns of male privilege and female submission set about challenging the female gender identifications expected of her. She took to wearing men’s clothing, cut her hair in a short style called the Eton crop, and was at times mistaken for a handsome young boy. She changed her name to the androgynous Valentine Ackland when she decided to become a serious poet in the late 1920s. Her poetry appeared in British and American literary journals during the 1920s to the 1940s, but Ackland deeply regretted that she never became a noted and widely read poet. In this regard, much of her poetry was published posthumously, and she received little attention from critics until a revival of interest in her work in the 1970s. In 1930, Ackland was introduced to the short story writer and novelist Sylvia Townsend Warner, with whom she had a lifelong relationship, albeit tumultuous at times given Ackland’s increasing alcoholism and infidelities. Warner was twelve years older than Ackland, and the two lived together until Ackland’s death from breast cancer in 1969. Warner went on to outlive Ackland by nine years, dying in 1978. The pair were together for thirty-nine years. Ackland’s reflections upon her relationship with Warner and the former’s long affair with American heiress and writer Elizabeth Wade White (1908–1994), were posthumously published in For Sylvia: An Honest Account (1985). Ackland was a highly emotional woman prone to numerous self-doubts and shifts in emotions and intellectual interests. She was responsible for involving Warner in membership in the Communist Party in the 1930s and in 1937 she visited Valencia and Benicàssim within the framework of the Spanish Civil War as well as numerous socialist and pacifist activities. The two women’s involvement in the Communist Party came under investigation by the British government in the late 1930s and remained an open file until 1957, when the investigation was halted. Ackland and Warner supported the Republican cause during the Spanish Civil War, and Ackland criticised the British government for its indifference to the “sufferings of the Spanish people at the grass-roots level” in her poem "Instructions from England, 1936". Note nothing of why or how, enquire no deeper than you need into what set these veins on fire, Note simply that they bleed. After World War II, Ackland turned her attention to confessional poetry and a memoir concerning her relationship with Warner and its many emotional issues as Ackland pursued involvements with other women. At first, Warner was tolerant with her younger lover’s dalliances, but the seriousness and length of Ackland’s relationship with Elizabeth Wade White was distressing to Warner and also pushed her relationship with Ackland to the edge. Ackland’s distresses at loving two women simultaneously and of endeavouring to balance her feelings for each woman with the responsibilities and commitments of her primary relationship with Warner are presented openly in Ackland’s poetry and in her memoir of this period. Ackland was struggling with additional doubts and conflicts during this period as well. She continued to battle her alcoholism, and she was undergoing shifts in her political and religious alliances. Doubts about her sexual identity and her identity as a poet as well as about her Christian faith and her political convictions are evident in her poetry. In 1934, Ackland and Warner produced a volume of poetry, “Whether a Dove or a Seagull” that was an unusual and democratic experiment in writing as none of the poems is ascribed to either author. The volume was also an attempt by Warner to introduce Ackland to publication since Warner had an already established reputation as a novelist, and her work was widely read in the 1930s. The volume was controversial for its frank discussion of lesbianism at a time and in a society in which lesbianism was regarded as deviant and immoral behaviour. In 1937, Ackland and Warner moved from rural Dorset to a house near Dorchester. Both became involved with Communist ideals and issues, with Ackland writing a column called “Country Dealings” concerning rural poverty for the “Daily Worker” and the “Left Review.” In 1939, the two women attended the American Writers Congress in New York City to consider the loss of democracy in Europe and returned when World War II broke out. Ackland’s poetry of this period attempted to capture the political dynamics she saw at work, but she had a difficult time as a poet mastering the craft of combining political polemics with her natural tendency toward lyrical expression. In a similar vein, her distress over the loss of democracy in Europe became a broader identification with Existentialism and the sense that the human condition itself was hopeless. Death Ackland died on 9 November 1969 from breast cancer that had metastasised to her lungs. She was buried together with Sylvia Townsend Warner in St Nicholas’s churchyard at Chaldon Herring with the inscription from Horace Non omnis moriar (Ode III.30, “I shall not wholly die”) on her gravestone. Critical assessment Ackland’s poetry—largely neglected after the 1940s—came into a resurgence of interest with the emergence of both women’s studies and of lesbian literature. Contemporary critical reaction finds much to value in Ackland’s poetry and confessional writings, which are of historical interest to the development of self-reflective, modernist poetry, and to the political and cultural issues of the 1930s and 1940s. One example of a recent critical analysis is Wendy Milford’s 1988 study, This Narrow Place: Sylvia Townsend Warner and Valentine Ackland. With regard to her self-reflection as a poet, Ackland exhibits themes and explorations similar to poets like Sylvia Plath and Anne Sexton. Of interest, too, is Ackland’s explorations of terminal illness as her life was drawing to a close from cancer. In her later years, Ackland turned from Catholicism to Quaker beliefs and also to involvement with issues of environmentalism. In overall assessment, Milford considers the two-minds at work in Ackland’s work. She cites as examples Ackland’s focus on optimism and dread, the longing for emotional closeness and the fear of intimacy, self-assertion and self-negation, the search for privacy and solitude amidst the longing for connection and social acceptance as a lesbian and as a noteworthy poet. In this regard, Ackland shares much thematically—though not in artistic achievement—with metaphysical poets like John Donne and Philip Larkin in the effort to see personal experience from multiple perspectives and never fully resting with one perspective or another. A contemporary examination of Ackland’s poetry and essays was published by Carcanet Press in 2008 titled Journey from Winter: Selected Poems. The volume is edited by Frances Bingham, who also provides a contextual and critical introduction. Bibliography * Whether a Dove or a Seagull (1934) volume of poetry with Sylvia Townsend Warner * Twenty-Eight Poems (1957) privately printed in London * Later Poems by Valentine Ackland (1970) * The Nature of the Moment (1973) * Further Poems of Valentine Ackland (1978) * For Sylvia: An Honest Account (1985) a memoir of Ackland’s relationship with Sylvia Townsend Warner * This Narrow Place: Sylvia Townsend Warner and Valentine Ackland 1931–1951, by Wendy Mulford (1988) * Jealousy in Connecticut, by Susanna Pinney (1998) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Valentine_Ackland


Thomas Ernest Hulme (16 September 1883– 28 September 1917) was an English critic and poet who, through his writings on art, literature and politics, had a notable influence upon modernism. He was an aesthetic philosopher and the 'father of imagism’. Early life Hulme was born at Gratton Hall, Endon, Staffordshire, the son of Thomas and Mary Hulme. He was educated at Newcastle-under-Lyme High School, and from 1902, St John’s College, Cambridge, where he read mathematics, but was sent down in 1904 after rowdy behaviour on Boat Race night. He was thrown out of Cambridge a second time after a scandal involving a Roedean girl. He returned to his studies at University College, London before travelling around Canada and spending time in Brussels acquiring languages. Proto-modernist From about 1907 Hulme became interested in philosophy, translating works by Henri Bergson and sitting in on lectures at Cambridge. He translated Georges Sorel’s Reflections on Violence. The most important influences on his thought were Bergson, who asserted that 'human experience is relative, but religious and ethical values are absolute’ and, later, Wilhelm Worringer (1881–1965), German art historian and critic - in particular his Abstraktion und Einfühlung (Abstraction and Empathy, 1908). Hulme was influenced by Remy de Gourmont’s aristocratic concept of art and his studies of sensibility and style. From 1909 Hulme contributed critical articles to The New Age, edited by A. R. Orage. Hulme developed an interest in poetry and wrote a small number of poems. He was made secretary of the Poets’ Club, attended by such establishment figures as Edmund Gosse and Henry Newbolt. There he encountered Ezra Pound and F. S. Flint. In late 1908 Hulme delivered his paper A Lecture on Modern Poetry to the club. Hulme’s poems Autumn and City Sunset, both published in 1909 in a Poets’ Club anthology, have the distinction of being the first Imagist poems. A further five poems were published in The New Age in 1912 as The Complete Poetical Works of T.E. Hulme. Despite this misleading title, Hulme in fact wrote about 25 poems totalling some 260 lines, of which the majority were possibly written between 1908–1910. Robert Frost met Hulme in 1913 and was influenced by his ideas. The publisher of the book 'Ripostes’ (to which Pound appended the 'complete’ poetical works of T. E. Hulme) spoke in that book of Hulme ‘the meta-physician, who achieves great rhythmical beauty in curious verse-forms.’ In his critical writings Hulme distinguished between Romanticism, a style informed by a belief in the infinite in man and nature, characterised by Hulme as “spilt religion”, and Classicism, a mode of art stressing human finitude, formal restraint, concrete imagery and, in Hulme’s words, “dry hardness”. Similar views were later expressed by T.S. Eliot. Hulme’s ideas had a major effect on Wyndham Lewis (quite literally when they came to blows over Kate Lechmere; Lewis ended the worse for it, hung upside down by the cuffs of his trousers from the railings of Great Ormond Street). He championed the art of Jacob Epstein and David Bomberg, was a friend of Gaudier-Brzeska, and was in on the debut of Lewis’s literary magazine BLAST and vorticism. Hulme’s politics were conservative, and he moved further to the right after 1911 as a result of contact with Pierre Lasserre, who was associated with Action Française. First World War Hulme volunteered as an artilleryman in 1914 and served with the Honourable Artillery Company and later the Royal Marine Artillery in France and Belgium. He kept up his writing for The New Age. Notable publications during this period for that magazine were “War Notes,” written under the pen name “North Staffs”, and “A Notebook”, which contains some of his most organised critical writing. He was wounded in 1916. Back at the front in 1917, he was killed by a shell at Oostduinkerke near Nieuwpoort, in West Flanders. [...] On 28 September 1917, four days after his thirty-fourth birthday, Hulme suffered a direct hit from a large shell which literally blew him to pieces. Apparently absorbed in some thought of his own he had failed to hear it coming and remained standing while those around threw themselves flat on the ground. What was left of him was buried in the Military Cemetery at Koksijde, West-Vlaanderen, in Belgium where—no doubt for want of space—he is described simply as 'One of the War poets’.” Works * Notes on Language and Style (1929, University of Washington Book Store); in The Criterion, Vol. 3, No. 12, (July 1925) (ed. T.S. Eliot) * Speculations: Essays on Humanism and the Philosophy of Art (1936, K. Paul, Trench, Trubner & Co., Ltd.), edited by Herbert Read * Further Speculations of T. E. Hulme (1955, University of Minnesota), edited by Samuel Hynes * The Collected Writings of T. E. Hulme (1996, OUP), edited by Karen Csengeri * Selected Writings of T. E. Hulme (2003, Fyfield Books), edited by Patrick McGuinness Selected poems * Above the Dock * Autumn * A City Sunset * Conversion * The Embankment * Mana Aboda * The Man in the Crow’s Nest * Susan Ann and Immortality * The Poet * A Tall Woman * A Sudden Secret * In the Quiet Land * At Night! * Town Sky-line As translator * Henri Bergson, An Introduction to Metaphysics, (1912) * Georges Sorel, Reflections on Violence, (1915) Articles References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T._E._Hulme


William Harris Lloyd Roberts (31 October 1884– 28 June 1966) was a Canadian writer, poet, and playwright. He was born in Fredericton, New Brunswick, the son of noted Canadian poet Charles George Douglas Roberts and Mary Isabel Fenety. After an education by private tutors, he attended King’s Collegiate School then, in 1905, Fredericton High School. In 1903 he performed clerical work at McClure’s magazine. From 1904 until 1907 he was an assistant editor at the Outing magazine, based in New York City. He wrote short stories and poetry for various magazines, plus performing part-time newspaper work starting in 1911. On January 1, 1914, he was married to Helen Hope Farquhar Bolmain. The couple had a daughter, Patricia Bliss, before Helen died. In 1912, he became editor of immigration literature for the Canadian Department of Interior in Ottawa. Two years later, he served as a correspondent for the Timer and Grazing branch of the Interior Department in Ottawa. On August 15, 1914, he married his second wife, Lila White; the couple divorced shortly thereafter. After 1920 he retired from work in order to devote all of his time to writing fiction, drama, poetry, and special articles. From 1925 until 1939 he was a correspondent for the Christian Science Monitor, then he performed public relations for the Royal Canadian Mounted Police up to 1945. His third marriage in 1943 was to Julia Bristow, and they would have two daughters. Bibliography * England Over Seas (1914) * Come Quietly, Britain (1915) * Mother Doneby (1916) * The Book of Roberts (1923) * Along the Ottawa (1927) * I Sing of Life (1937) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Harris_Lloyd_Roberts

Arthur Stringer (February 26, 1874– September 13, 1950) was a Canadian novelist, screenwriter, and poet who later moved to the United States. He published 45 works of fiction and 15 other books, in addition to writing numerous filmscripts and articles. Life Stringer was born in Chatham, Ontario. “He was a high spirited boy who spent his childhood days fishing, swimming, raiding orchards and manning a pirate ship.” In 1884 the family moved to London, Ontario, where Charles attended London Collegiate Institute. At the Institute he founded and edited a school magazine called Chips. He then attended University College, University of Toronto from 1892 to 1894 and later studied at Oxford University. His first book of poetry, Watchers of Twilight and Other Poems, was published in 1894. In 1895 he worked for the Montreal Herald. At this time he was also publishing in Saturday Night and the Canadian Magazine. In 1898 he got a job with the American Press Association, moved to New York City, and was soon publishing in The Atlantic and Harper’s. His first poem in Harper’s, “Remorse”, appeared in February 1899. His first novel, The Silver Poppy, came out in 1903. In the same year he bought a farm on the shore of Lake Erie. and married actress Jobyna Howland, known as the original Gibson girl. They divorced in 1914, and Stringer married his cousin, Margaret Arbuthnott. Stringer was popular in his day for his crime fiction and his wilderness adventures, but he wrote in many genres, from social realism (his “Prairie” trilogy, 1915–1921) to psychological fiction (The Wine of Life (1921). He even wrote early science fiction novels, The Story Without a Name (1924) with Russell Holman, and The Woman Who Couldn’t Die (1929). Much of his writing was for films. Film scripts on which he worked include The Perils Of Pauline (1914), The Hand Of Peril (1916), The House Of Intrigue (1919), Unseeing Eyes (1923), Empty Hands (1924), The Canadian (1926), The Purchase Price (1932), The Lady Fights Back (1937), Buck Benny Rides Again (1940) and The Iron Claw (1941). Last years In 1921, the Stringers moved to Mountain Lakes, New Jersey, where Arthur Stringer continued to write, and where he died in 1950, aged 76. Writing Fiction Stringer was popular in his day for his crime fiction and his wilderness adventures, both of which rely to a large degree on formula; “generally he worked within the conventions of sentimental romance popular around the turn of the century.” Modern critics have not been kind to his fiction. For example, Douglas Fetherling wrote of him in the Canadian Encyclopedia: Stringer was not in any recognizable stream of Canadian writing but rather was a prolific American hack-fiction writer... The fact that he lived most of his life in the U.S., however, did not prevent him from frequently inventing Canadian characters and sometimes... setting them in the Far North, a region he misunderstood lavishly, thereby contributing to foreign stereotyping of Canada. Against that one has to set Stringer’s prairie trilogy– Prairie Wife (1915), Prairie Mother (1920), and Prairie Child (1921)– which has been called “an enduring contribution to Canadian literature.” The trilogy uses a diary form to tell the tale of its narrator, “a New England socialite married to a dour Scots-Canadian wheat farmer,” and “develops gradually from the optimism typical of pioneering romances, through disillusionment as her marriage deteriorates, to mature resolve as she begins an independent life on the Prairies.” Poetry The Oxford Companion to Canadian Literature described Stringer’s poetry as “undistinguished verse.” However, it was also said that in his poetry “there is maintained a standard of beauty, depth of feeling, and technical power, which in Canada have had all too little recognition.” At its time his blank verse drama Sappho in Leucadia was called “an imaginative, passionate, artistic work of surpassing quality”. Stringer’s chief claim to poetic fame today rests on his 1914 book, Open Water, the first book by a Canadian poet to use free verse– and in particular on his preface to that book, in which he “describes the modernist movement as a natural evolution.” Louis Dudek and Michael Gnarowski, who reprinted the Open Water preface in their anthology The Making of Modern Poetry In Canada, remarked on it: This book must be seen as a turning point in Canadian writing if only for the importance of the ideas advanced by Stringer in his preface. In a carefully presented, extremely well-informed account of traditional verse-making, Stringer pleaded the cause of free verse and created what must now be recognized as an early document of the struggle to free Canadian poetry from the trammels of end-rhyme, and to liberalize its methods and its substance. “Stringer’s arguments become even more striking from the point of view of literary history”, Dudek and Gnarowski continued, "if we recall... that the famous notes of F.S. Flint and the strictures of Ezra Pound on imagisme and free verse had appeared less than a year before this, in the March 1913 issue of Poetry: A Magazine of Verse (Chicago). Legacy Stringer was awarded an honorary D.Litt. by the University of Western Ontario in 1946. Stringer is commemorated by Arthur Stringer Public School in London, Ontario, which opened in 1969. The house in which Stringer lived as a boy in London, Ontario has been preserved as a historic site, Arthur Stringer House. Publications Fiction * The Silver Poppy. New York: D. Appleton & Co., 1903. * Lonely O’Malley: A Story of Boy Life. New York: Houghton Mifflin, 1905. * The Wire Tappers. Boston: Little, Brown and Co., 1906. * Phantom Wires. Boston: Little, Brown and Co., 1907. * The Under Groove. New York: McClure Company, 1908. * The Gun-Runner. New York: B.W. Dodge & Co., 1909. * The Shadow. New York: The Century Co., 1913. * Never-Fail Blake Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1913. * The Prairie Wife Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1915. * The Hand of Peril. New York: Macmillan, April 1915. * The Door of Dread: A Secret Service Romance. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1916. * The House of Intrigue. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1918. * The Man Who Couldn’t Sleep. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1919. * The Prairie Mother. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1920. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1920. * Twin Tales: “Are All Men Alike” and “The Lost Titian”. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1921. * The Wine of Life. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1921. * The Prairie Child. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1922. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1923. * The Diamond Thieves. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1923. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1925. * The City of Peril. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1923. * Empty Hands. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1924. * and Russell Holman. Manhandled. (Illustrated with scenes from the photoplay). New York: Grossett & Dunlap, 1924. * and Russell Holman. The Story Without a Name. (Illustrated with scenes from the photoplay). New York: Grossett & Dunlap, 1924. * Power. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, c.1925. * In Bad With Sinbad. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1926. * Night Hawk. A Novel. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1926. * White Hands. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1927. * The Wolf Woman. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1927. * Cristina and I Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1929. * The Woman Who Couldn’t Die. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1929. * A Lady Quite Lost. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1931. * The Mud Lark. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1932. * Dark Soil. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1933. * Marriage by Capture. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1933. * Man Lost. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1934. * The Wife Traders: A Tale of the North. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart, 1936. * Heather of the High Hand: A Novel of the North. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1937. * The Lamp In the Valley. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1938. * The Dark Wing. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1939. * The Ghost Plane: A Novel of the North. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1940. * A King Who Loved Old Clothes. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1941. * Intruders in Eden. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1942. * Shadowed Victory. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1943. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1944. * Star in a Mist. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1943. * The Devastator. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1944. * Information on early fiction from American fiction, 1901-1925. Non-fiction * A Study of King Lear. New York, 1897. * Red Wine of Youth: A Life of Rupert Brooke, 1921. Poetry * Watchers of Twilight, and Other Poems. London, ON: T.H. Warren, 1894. * Pauline and Other Poems. London, ON: T.H. Warren, 1895. * The Loom of Destiny. Boston: Small, Maynard, 1899. * The Woman in the Rain, and Other Poems. Boston: Little, Brown & Co., 1907. 1949. * Irish Poems. New York: Mitchell Kennerley, 1911. * Out of Erin (Songs in Exile). Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1930. * Open Water. London: John Lane Co., 1914. * A Woman at Dusk and Other Poems. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1928. * The Old Woman Remembers and Other Irish Poems. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1938. * New York Nocturnes. Toronto: Ryerson P, 1948. Plays * Hephaestus: Persephone At Enna And Sappho In Leucadia. 1903 * The Cleverest Woman In the World and Other One-Act Dramas. Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill, 1939. Movies * The following 22 movies were based on fiction by Arthur Stringer: * 1912 The Man Who Made Good (short) (story) * 1914 The Case of Cherry Purcelle (short) (story) * 1916 The Secret Agent (short) (story) * 1916 The Breaker (story) * 1916 The Hand of Peril (novel The Hand of Peril: A Novel of Adventure) * 1918 From Two to Six (story “The Button Thief”) * 1919 The House of Intrigue (novel) * 1920 Are All Men Alike? (story “The Waffle Iron”) * 1923 Unseeing Eyes (story “Snowblind”) * 1924 Manhandled (story) * 1924 The Story Without a Name (novel) * 1924 Empty Hands (story) * 1925 The Prairie Wife (story) * 1925 Womanhandled (story) * 1926 The Canadian (story and scenario) * 1926 The Wilderness Woman (scenario / story) * 1926 Out of the Storm (story “The Travis Coup”) * 1928 Half a Bride (story “White Hands”) * 1932 The Purchase Price (story “The Mud Lark”) * 1937 The Lady Fights Back (novel “Heather of the High Hand”) * 1940 Buck Benny Rides Again (story) * 1941 The Iron Claw (story) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arthur_Stringer_(writer)


Reginald Arkell (1882–1959) was a British script writer and comic novelist who wrote many musical plays for the London theatre. The most popular of those was an adaptation of the spoof history book 1066 and All That: 1066—and all that: A Musical Comedy based on that Memorable History by Sellar and Yeatman. He was the author of A Cottage in the Country and the Green Fingers series of garden verse. Arkell was born on 14 October 1882 at Lechlade, Gloucestershire, England, was educated at Burford Grammar School and trained as a journalist. He married actress Elizabeth Evans in 1912. During the First World War he served with the King’s Own Yorkshire Light Infantry and The Norfolk Regiment. Arkell died on 1 May 1959 at Cricklade, England. Works * The Round House (1958) (novel) * Charley Moon (1953) (novel) Published by Michael Joseph Ltd. * “Trumpets Over Merriford” (1955), American title: The Miracle Of Merriford (1956) (novel) * Collected Green Fingers (1956) (poems) * Come to the ball; or, Harlequin (1951) (adaptation of Johann Strauss II’s Die Fledermaus) * Old Herbaceous (1950, republished 2002) * Green fingers Again (1942) (poems) * War Rumours (1939) (verse, illustrated by Edgar Norfield) * Percy Ponsonby (1939) (TV series) * 1066 And All That (1939) (TV version) * The Street Singer or Interval for Romance (1937) (film musical which starred Arthur Tracy) * Smash and Grab (1937) (film) * Green fingers, and other poems (1934) (includes Roses at Owlpen) * The Last Waltz (1936) (film of the musical comedy) * 1066 And All That (1935) (revue) * A Kingdom for a Cow (1935) (adaptation of Kurt Weill’s operetta Der Kuhhandel) * Playing the Games (1935) (humour) * Bridge Without Sighs (1934) (A Harmless Handbook to the game, written in rhyme) * Richard Jefferies (1933) (biography) * Winter Sportings (1929) * Meet These People (1928) - Poetry with caricatures by Bert Thomas. Published by Herbert Jenkins. * Columbine– A Fantasy of Summertime (1928) (adaptation for radio) * The Blue Train (1927) (musical, music by Robert Stolz, additional lyrics by Ivy St. Helier) * Frasquita (1925) (operetta, music by Franz Lehár) * Our Nell (1924) (musical play, music by Ivor Novello and Harold Fraser-Simson) * The tragedy of Mr. Punch (1923) (play) * Columbine (1922) (play) * Catherine (1922) (musical play, music by Tchaikovsky) * The Last Waltz (1922) (musical comedy, music by Oscar Straus) * All the Rumors (1916) (contains the poem Actual Evidence I Have None... Published by Duckworth & Company, 1916 - World War, 1914-1918 - 47 pages) * The Holidays (Children’s poem in The Captain Dec 1910) Old Herbaceous * Old Herbaceous is a classic British novel of the garden, with a title character as outsized and unforgettable as P. G. Wodehouse’s immortal manservant, Jeeves. Born at the dusk of the Victorian era, Bert Pinnegar, an awkward orphan child with one leg a tad longer than the other, rises from inauspicious schoolboy days spent picking wildflowers and dodging angry farmers to become the legendary head gardener “Old Herbaceous,” the most esteemed flower-show judge in the county and a famed horticultural wizard capable of producing dazzling April strawberries from the greenhouse and the exact morning glories his Lady spies on the French Riviera, “so blue, so blue it positively hurts.” * Sprinkled with nuggets of gardening wisdom, Old Herbaceous is a witty comic portrait of the most archetypal—and crotchety—head gardener ever to plant a row of bulbs at a British country house. External links * Works by Reginald Arkell at Faded Page (Canada) * BBC page on Percy Ponsonby * Reginald Arkell on Internet Movie Database References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reginald_Arkell


Sir Andrew Motion FRSL (born 26 October 1952) is an English poet, novelist, and biographer, who was Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom from 1999 to 2009. During the period of his laureateship, Motion founded the Poetry Archive, an online resource of poems and audio recordings of poets reading their own work. In 2012, he became President of the Campaign to Protect Rural England, taking over from Bill Bryson. Early life Motion was born on 26 October 1952 in London; his mother was Catherine Gillian Bakewell (known as Gillian) and his father Andrew Richard Michael Motion (known as Richard). The family moved to Stisted, near Braintree in Essex, when Motion was 12 years old. Motion went to boarding school from the age of seven joined by his younger brother. Most of the boy’s friends were from the school and when Motion was in the village he spent a lot of time on his own. He began to have an interest and affection for the countryside and he went for walks with a pet dog. Later he went to Radley College, where, in the sixth form, he encountered Peter Way, an inspiring English teacher who introduced him to poetry– first Hardy, then Philip Larkin, W. H. Auden, Heaney, Hughes, Wordsworth and Keats. When Motion was 17 years old, his mother had a horse riding accident and suffered a serious head injury requiring a life-saving neurosurgery operation. She regained some speech, but she was severely paralysed and remained in and out of coma for nine years. She died in 1978 and her husband died of cancer in 2006. Motion has said that he wrote to keep his memory of his mother alive and that she was a muse of his work. When Motion was about 18 years old he moved away from the village to study English at University College, Oxford; however, since then he has remained in contact with the village to visit the church graveyard, where his parents are buried, and also to see his brother, who lives nearby. At University he studied at weekly sessions with W. H. Auden, whom he greatly admired. Motion won the university’s Newdigate Prize and graduated with a first class honours degree. Career Between 1976 and 1980, Motion taught English at the University of Hull and while there, at age 24, he had his first volume of poetry published. At Hull he met university librarian and poet Philip Larkin. Motion was later appointed as one of Larkin’s literary executors which would privilege Motion’s role as his biographer following Larkin’s death in 1985. In Philip Larkin: A Writer’s Life, Motion says that at no time during their nine-year friendship did they discuss writing his biography and it was Larkin’s longtime companion Monica Jones who requested it. He reports how, as executor, he rescued many of Larkin’s papers from imminent destruction following his friend’s death. His 1993 biography of Larkin, which won the Whitbread Prize for Biography, was responsible for bringing about a substantial revision of Larkin’s reputation. Motion was Editorial Director and Poetry Editor at Chatto & Windus (1983–89), he edited the Poetry Society’s Poetry Review from 1980–1982 and succeeded Malcolm Bradbury as Professor of Creative Writing at the University of East Anglia. He is now on the faculty at the Johns Hopkins Writing Seminars. Laureateship Motion was appointed Poet Laureate on 1 May 1999, following the death of Ted Hughes, the previous incumbent. The Nobel Prize-winning Northern Irish poet and translator Seamus Heaney had ruled himself out for the post. Breaking with the tradition of the laureate retaining the post for life, Motion stipulated that he would stay for only ten years. The yearly stipend of £200 was increased to £5,000 and he received the customary butt of sack. He wanted to write “poems about things in the news, and commissions from people or organisations involved with ordinary life,” rather than be seen a 'courtier’. So, he wrote "for the TUC about liberty, about homelessness for the Salvation Army, about bullying for ChildLine, about the foot and mouth outbreak for the Today programme, about the Paddington rail disaster, the 11 September attacks and Harry Patch for the BBC, and more recently about shell shock for the charity Combat Stress, and climate change for the song cycle he finished for Cambridge University with Peter Maxwell Davies.” On 14 March 2002, as part of the 'Re-weaving Rainbows’ event of National Science Week 2002, Motion unveiled a blue plaque on the front wall of 28 St Thomas Street, Southwark, to commemorate the sharing of lodgings there by John Keats and Henry Stephens while they were medical students at Guy’s and St Thomas’ Hospital in 1815–16. In 2003, Motion wrote Regime change, a poem in protest at Invasion of Iraq from the point of view of Death walking the streets during the conflict, and in 2005, Spring Wedding in honour of the wedding of the Prince of Wales to Camilla Parker Bowles. Commissioned to write in the honour of 109-year-old Harry Patch, the last surviving “Tommy” to have fought in World War I, Motion composed a five-part poem, read and received by Patch at the Bishop’s Palace in Wells in 2008. As laureate, he also founded the Poetry Archive, an on-line library of historic and contemporary recordings of poets reciting their own work. Motion remarked that he found some of the duties attendant to the post of poet laureate difficult and onerous and that the appointment had been "very, very damaging to [his] work". The appointment of Motion met with criticism from some quarters. As he prepared to stand down from the job, Motion published an article in The Guardian that concluded, "To have had 10 years working as laureate has been remarkable. Sometimes it’s been remarkably difficult, the laureate has to take a lot of flak, one way or another. More often it has been remarkably fulfilling. I’m glad I did it, and I’m glad I’m giving it up– especially since I mean to continue working for poetry." Motion spent his last day as Poet Laureate holding a creative writing class at his alma mater, Radley College, before giving a poetry reading and thanking Peter Way, the man who taught him English at Radley, for making him who he was. Carol Ann Duffy succeeded him as Poet Laureate on 1 May 2009. Post-laureateship Motion is Chairman of the Arts Council of England’s Literature Panel (appointed 1996) and is also a Fellow of the Royal Society of Literature. In 2003, he became Professor of Creative Writing at Royal Holloway, University of London. Since July 2009, Motion has been Chairman of the Museums, Libraries and Archives Council (MLA) appointed by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport. He is also a Vice-President of the Friends of the British Library, a charity which provides funding support to the British Library. He was knighted in the 2009 Queen’s Birthday Honours list. He has been a member of English Heritage’s Blue Plaques Panel since 2008. Motion was selected as jury chair for the Man Booker Prize 2010 and in March 2010, he announced that he was working with publishers Jonathan Cape on a sequel to Robert Louis Stevenson’s Treasure Island. Entitled Silver, the story is set a generation on from the original book and was published in March 2012. In July 2010, Motion returned to Kingston-upon-Hull for the annual Humber Mouth literature festival and taking part in the Larkin 25 festival commemorating the 25th anniversary of Philip Larkin’s death. In his capacity as Larkin’s biographer and as a former lecturer in English at the University of Hull, Motion named an East Yorkshire Motor Services bus Philip Larkin. Motion’s debut play Incoming, about the war in Afghanistan, premièred at the High Tides Festival in Halesworth, Suffolk in May 2011. Motion also featured in Jamie’s Dream School in 2011 as the poetry teacher. In June 2012, he became the President of the Campaign to Protect Rural England. In March 2014 he was elected an Honorary Fellow at Homerton College, Cambridge. Motion won the 2015 Ted Hughes Award for new work in poetry for the radio programme Coming Home. The production featured poetry by Motion based on recordings he made of British soldiers returning from the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan. Work Motion has said of himself: “My wish to write a poem is inseparable from my wish to explain something to myself.” His work combines lyrical and narrative aspects in a “postmodern-romantic sensibility”. Motion says that he aims to write in clear language without tricks. The Independent describes the stalwart poet as the “charming and tireless defender of the art form”. Motion has won the Arvon Prize, the John Llewellyn Rhys Prize, Eric Gregory Award, Whitbread Prize for Biography and the Dylan Thomas Prize. Motion took part in the Bush Theatre’s 2011 project Sixty-Six Books, writing and performing a piece based upon a book of the King James Bible. Personal life Motion’s marriage to Joanna Powell ended in 1983. He was married to Jan Dalley from 1985 to 2009, divorcing after a seven-year separation. They had one son born in 1986 and twins, a son and a daughter, born in 1988. In 2009 he married Kyeong-Soo Kim. They live in Baltimore, Maryland. Selected honours and awards 1975: won the Newdigate prize for Oxford undergraduate poetry 1976: Eric Gregory Award 1981: wins Arvon Foundation’s International Poetry Competition with The Letter 1984: John Llewellyn Rhys Prize for Dangerous Play: Poems 1974–1984 1986: Somerset Maugham Award for The Lamberts 1987: Dylan Thomas Prize for Natural Causes 1999: appointed Poet Laureate for ten years 1994: Philip Larkin: A Writer’s Life, Whitbread Prize for Biography 2009: Knighthood 2014: Wilfred Owen Poetry Award Selected works Poetry collections * 1972: Goodnestone: a sequence. Workshop Press * 1976: Inland. Cygnet Press * 1977: The Pleasure Steamers. Carcanet * 1981: Independence. Salamander Press * 1983: Secret Narratives. Salamander Press * 1984: Dangerous Play: Poems 1974–1984. Salamander Press / Penguin * 1987: Natural Causes. Chatto & Windus * 1988: Two Poems. Words Ltd * 1991: Love in a Life. Faber and Faber * 1994: The Price of Everything. Faber and Faber * 1997: Salt Water Faber and Faber * 1998: Selected Poems 1976–1997. Faber and Faber * 2001: A Long Story. The Old School Press * 2002: Public Property. Faber and Faber * 2009: The Cinder Path. Faber and Faber * 2012: The Customs House. Faber and Faber * 2015: Peace Talks. Faber and Faber * 2015: Coming Home. Published by Andrew J Moorhouse at Fine Press Poetry http://www.finepresspoetry.com Criticism * 1980: The Poetry of Edward Thomas. Routledge & Kegan Paul * 1982: Philip Larkin. (Contemporary Writers series) Methuen * 1986: Elizabeth Bishop. (Chatterton Lectures on an English Poet) * 1998: Sarah Raphael: Strip!. Marlborough Fine Art (London) * 2008: Ways of Life: On Places, Painters and Poets. Faber and Faber Biography and memoir * 1986: The Lamberts: George, Constant and Kit. Chatto & Windus * 1993: Philip Larkin: A Writer’s Life. Faber and Faber * 1997: Keats: A Biography. Faber and Faber * 2006: In the Blood: A Memoir of my Childhood. Faber and Faber Fiction * 1989: The Pale Companion. Penguin * 1991: Famous for the Creatures. Viking * 2003: The Invention of Dr Cake. Faber and Faber * 2000: Wainewright the Poisoner: The Confessions of Thomas Griffiths Wainewright (biographical novel) * 2012: Silver. Jonathan Cape Edited works, introductions, and forewords * 1981: Selected Poems: William Barnes. Penguin Classics * 1982: The Penguin Book of Contemporary British Poetry with Blake Morrison. Penguin * 1994: Thomas Hardy: Selected Poems. Dent * 1993: New Writing 2 (With Malcolm Bradbury). Minerva in association with the British Council * 1994: New Writing 3 (With Candice Rodd). Minerva in association with the British Council * 1997: Penguin Modern Poets: Volume 11 with Michael Donaghy and Hugo Williams. Penguin * 1998: Take 20: New Writing. University of East Anglia * 1999: Verses of the Poets Laureate: From John Dryden to Andrew Motion. With Hilary Laurie. Orion. * 1999: Babel: New Writing by the University of East Anglia’s MA Writers. University of East Anglia. * 2001: Firsthand: The New Anthology of Creative Writing from the University of East Anglia. University of East Anglia * 2002: Paper Scissors Stone: New Writing from the MA in Creative Writing at UEA. University of East Anglia. * 2001: The Creative Writing Coursebook: Forty Authors Share Advice and Exercises for Fiction & Poetry. With Julia Bell. Macmillan * 2000: John Keats: Poems Selected by Andrew Motion. Faber and Faber * 2001: Here to Eternity: An Anthology of Poetry. Faber and Faber * 2002: The Mays Literary Anthology; Guest editor. Varsity Publications * 2003: 101 Poems Against War . Faber and Faber (Afterword) * 2003: First World War Poems. Faber and Faber * 2006: Collins Rhyming Dictionary. Collins * 2007: Bedford Square 2: New Writing from the Royal Holloway Creative Writing Programme. John Murray Ltd. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Andrew_Motion


Lilian Helen Bowes Lyon (1895–1949) was a British poet. Biography Born 23 December 1895 at Ridley Hall, Northumberland. She was the youngest daughter of the Honourable Francis Bowes Lyon and was a first cousin of Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon, Queen Elizabeth the Queen Mother. During the First World War, Bowes Lyon helped at Glamis Castle (owned by her uncle) which became a convalescence home for soldiers. Her brother Charles Bowes Lyon was killed in the war on 23 October 1914, inspiring her poem “Battlefield” which was later published in Bright Feather Fading. After the Great War, Bowes Lyon studied for a time at the University of Oxford and then moved to London. She was independently wealthy. In 1929, she met the writer William Plomer CBE and through him, Laurens van der Post. She published two novels, The Buried Stream (1929) and Under the Spreading Tree (1931) but thereafter focused on poetry. Bowes Lyon published six individual collections with Jonathan Cape and a Collected Poems in 1948. Her “Collected Poems” contains an introduction by C. Day-Lewis, who noted the influences of Emily Dickinson, Hopkins and Christina Rossetti. Her verse appeared in many periodicals and anthologies including The Adelphi, Country Life, Kingdom Come, The Listener, The London Mercury, The Lyric (USA), The Observer, Orion, Punch, The Spectator, Time and Tide and “Poetry” (USA). During the Second World War, Bowes Lyon moved to the East End of London, where she used the Tilbury Docks unofficial air raid shelter and assisted with nursing the injured. She had several amputations due to thromboangiitis obliterans (Buerger’s Disease), losing toes, a foot, her lower legs and eventually both her legs below her hips. She returned to her home in Kensington and continued to write poetry despite the thromboangitis obliterans beginning to affect her hands. These poems, found amongst William Plomer’s papers at University of Durham, were published in “Uncollected Poems” by Tragara Press. She died on 25 July 1949.


John Allyn Berryman (October 25, 1914– January 7, 1972) was an American poet and scholar, born in McAlester, Oklahoma. He was a major figure in American poetry in the second half of the 20th century and was considered a key figure in the Confessional school of poetry. His best-known work is The Dream Songs. Life and career John Berryman was born John Allyn Smith, Jr. in Oklahoma where he was raised until the age of ten, when his father, John Smith, a banker, and his mother, Martha (also known as Peggy), a schoolteacher, moved to Tampa, Florida. In 1926, in Florida, when the poet was eleven years old, his father shot and killed himself, Berryman was haunted by his father’s death for the rest of his life and would later write about his struggle to come to terms with it in his book The Dream Songs. In "Dream Song #143", he wrote, "That mad drive [to commit suicide] wiped out my childhood. I put him down/while all the same on forty years I love him/stashed in Oklahoma/besides his brother Will". In "Dream Song #145", he also wrote the following lines about his father: he only, very early in the morning, rose with his gun and went outdoors by my window and did what was needed. I cannot read that wretched mind, so strong & so undone. I've always tried. I–I'm trying to forgive whose frantic passage, when he could not live an instant longer,in the summer dawn left Henry to live on. Similarly, in Dream Song #384, Berryman wrote: The marker slants, flowerless, day's almost done, I stand above my father's grave with rage, often, often before I've made this awful pilgrimage to one who cannot visit me, who tore his page out: I come back for more, I spit upon this dreadful bankers grave who shot his heart out in a Florida dawn After his father’s death at the rear entrance to Kipling Arms, where the Smiths rented an apartment, the poet’s mother, within months, married John Angus McAlpin Berryman in New York City. The poet was renamed John Allyn McAlpin Berryman. Berryman’s mother also changed her first name from Peggy to Jill. Although his stepfather would later divorce his mother, Berryman and his stepfather stayed on good terms. With both his mother and stepfather working, his mother decided to send him away to the South Kent School, a private boarding school in Connecticut. Then Berryman went on to college at Columbia College where he was president of the Philolexian Society, joined the Boar’s Head Society, edited the Columbia Review, and studied under the literary scholar and poet Mark Van Doren. Berryman would later credit Van Doren with sparking his interest in writing poetry seriously. For two years, Berryman also studied overseas at Clare College, Cambridge, on a Kellett Fellowship, awarded by Columbia. He graduated in 1936. Regarding Berryman’s earliest success in poetry, the Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry editors note that "Berryman’s early work formed part of a volume entitled Five Young American Poets, published by New Directions in 1940". One of the other young poets included in the book was Randall Jarrell. Berryman would soon publish some of this early verse in his first book, also with New Directions Publishing, simply titled Poems, in 1942. However, his first mature collection of poems, The Dispossessed, appeared six years later, published by William Sloane Associates. The book received largely negative reviews from poets like Randall Jarrell who wrote, in The Nation, that Berryman was "a complicated, nervous, and intelligent [poet]" whose poetry in The Dispossessed was too derivative of W. B. Yeats. Berryman would later concur with this assessment of his early work, stating, “I didn’t want to be like Yeats; I wanted to be Yeats.” In October 1942, Berryman married Eileen Mulligan (later Simpson) in a ceremony at St. Patrick’s Catherdral, with poet Mark Van Doren as his best man. The pair moved to Beacon Hill, where Berryman lectured at Harvard. The marriage ended in 1953 (a divorce was formalized in 1956), when Simpson finally grew weary of tolerating Berryman’s affairs and acting as “net-holder” throughout his self-destructive personal crises. Simpson would memorialize her time with Berryman and his circle in her 1982 book Poets in Their Youth. In 1947, Berryman started an affair with a married woman named Chris, documented in a long sonnet sequence that he refrained from publishing, in part, because publication of the sonnets would have revealed the affair to his wife. However, he did eventually decide to publish the work, titled Berryman’s Sonnets, in 1967. The work included over one hundred sonnets. In 1950, Berryman published a biography of the fiction writer and poet Stephen Crane whom he greatly admired becoming, “the only biography by a leading American poet of the great American writer, Stephen Crane.” This book was followed by his next significant poem, Homage to Mistress Bradstreet (1956), which featured illustrations by the artist Ben Shahn and was Berryman’s first poem to receive “national attention” and a positive response from critics. Edmund Wilson wrote that it was “the most distinguished long poem by an American since T. S. Eliot’s The Waste Land.” When “Homage to Mistress Bradstreet and Other Poems” was published in 1959, the poet Conrad Aiken praised the shorter poems in the book which he thought were actually better than “Homage to Mistress Bradstreet”. Despite the relative success of his third book of verse, Berryman’s great poetic breakthrough occurred after he published 77 Dream Songs in 1964. It won the 1965 Pulitzer Prize for poetry and solidified Berryman’s standing as one of the most important poets of the post-World War II generation that included Robert Lowell, Elizabeth Bishop, and Delmore Schwartz. Soon afterwards, Berryman started receiving a great deal of national attention from the press, from arts organizations, and even from the White House which sent him an invitation to dine with President Lyndon B. Johnson (though Berryman had to decline because he was in Ireland at the time). Berryman was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1967, and that same year Life magazine ran a feature story on him. Also, that year the newly created National Endowment for the Arts awarded him a ten thousand dollar grant (though he admitted, when asked about the award by a Minneapolis reporter, that he had never heard of the organization before). Berryman also continued to work on the “dream song” poems at a feverish pace and published a second, significantly longer, volume entitled His Toy, His Dream, His Rest, in 1968, which won the National Book Award for Poetry and the Bollingen Prize. The following year Berryman republished 77 Dreams Songs and His Toy, His Dream, His Rest as one book titled The Dream Songs, in which the character Henry serves as Berryman’s alter ego. But in Love & Fame (1970), he dropped the mask of Henry to write more plainly about his life. Responses to the poems from critics and most of Berryman’s peers ranged from tepid, at best, to hostile; now the collection is generally “considered a minor work”. The character of Henry reappeared in a couple of poems published in Delusions Etc., (1972), Berryman’s last collection, which focused on his religious concerns and his own spiritual rebirth. The book was published posthumously and, like its predecessor, Love & Fame, it is considered a minor work. Berryman taught or lectured at a number of universities including University of Iowa (in their Writer’s Workshop), Harvard University, Princeton University, the University of Cincinnati, and the University of Minnesota, where he spent the majority of his career, except for his sabbatical year in 1962-3, when he taught at Brown University. Some of his illustrious students included W. D. Snodgrass, William Dickey, Donald Justice, Philip Levine, Robert Dana, Jane Cooper, Donald Finkel, and Henri Coulette. Philip Levine stated, in a recorded interview from 2009, that Berryman took his class extremely seriously and that "he was entrancing... magnetic and inspiring and very hard on [his students’] work... [and] he was [also] the best teacher that I ever had". Berryman was fired from the University of Iowa after a fight with his landlord led to him being arrested, jailed overnight, and fined for disorderly conduct and public intoxication. He turned to his friend, the poet Allen Tate, who helped him get his teaching job at the University of Minnesota. Berryman was married three times. And according to the editors of The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry, he lived turbulently. During one of the many times he was hospitalized in order to detox from alcohol abuse, in 1970, he experienced what he termed “a sort of religious conversion”. According to his biographer Paul Mariani, Berryman experienced “a sudden and radical shift from a belief in a transcendent God... to a belief in a God who cared for the individual fates of human beings and who even interceded for them.” Nevertheless, Berryman continued to abuse alcohol and to struggle with depression, as he had throughout much of his adult life, and on the morning of January 7, 1972, he killed himself by jumping from the Washington Avenue Bridge in Minneapolis, Minnesota, onto the west bank of the Mississippi River. Newspaper reports of the event indicate that he missed the water and smothered in mud. Poetry Berryman’s poetry, which often revolved around the sordid details of his personal problems (in The Dream Songs but also in his other poems as well) is closely associated with the Confessional poetry movement. In this sense, his poetry had much in common with the poetry of his friend, Robert Lowell. The editors of The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry note that “the influence of Yeats, Auden, Hopkins, Crane, and Pound on him was strong, and Berryman’s own voice—by turns nerve-racked and sportive—took some time to be heard.” Berryman’s first major work, in which he began to develop his own unique style of writing, was Homage to Mistress Bradstreet, published in 1956. In the long, title poem, which first appeared in Partisan Review in 1953, Berryman addressed the 17th century American poet Anne Bradstreet, combining the history of her life with his own fantasies about her (and inserting himself into the poem). Joel Athey noted, “This difficult poem, a tribute to the Puritan poet of colonial America, took Berryman five years to complete and demanded much from the reader when it first appeared with no notes. The Times Literary Supplement hailed it as a path-breaking masterpiece; poet Robert Fitzgerald called it ‘the poem of his generation.’” Edward Hirsch observed that "the 57 stanzas of Homage to Mistress Bradstreet combine the concentration of an extended lyric with the erudition and amplitude of a historical novel". Berryman’s major poetic breakthrough came after he began to publish the first volume of The Dream Songs, 77 Dream Songs, in 1964. The dream song form consisted of short, eighteen-line lyric poems in three stanzas. The poems are written in free verse although some stanzas contain irregular rhyme. 77 Dream Songs (and its sequel His Toy, His Dream, His Rest) centers on a character named “Henry” who bears a striking resemblance to John Berryman. However, Berryman was careful about making sure that his readers realized that “Henry” was not his equivalent, but rather a fictional version of himself (or a literary alter ego). In an interview, Berryman stated, “Henry does resemble me, and I resemble Henry; but on the other hand I am not Henry. You know, I pay income tax; Henry pays no income tax. And bats come over and they stall in my hair—and fuck them, I’m not Henry; Henry doesn’t have any bats.” In The New York Times review of 77 Dream Songs, John Malcolm Brinnin praised the book, declaring that "[the book’s] excellence calls for celebration". And in The New York Review of Books, Robert Lowell also reviewed the book, writing, “At first the brain aches and freezes at so much darkness, disorder and oddness. After a while, the repeated situations and their racy jabber become more and more enjoyable, although even now I wouldn’t trust myself to paraphrase accurately at least half the sections.” In response to the perceived difficulty of the dream songs, in his 366th “Dream Song”, Berryman facetiously wrote, "These Songs are not meant to be understood, you understand. / They are only meant to terrify & comfort". In His Toy, His Dream, His Rest, many of the dream songs are elegies for Berryman’s recently deceased poet friends, including Delmore Schwartz, Randall Jarrell, and Theodore Roethke. Since this volume contained four times the number of poems that appeared in the previous volume, Berryman covered a lot more subject matter. For instance, in addition to the elegies, Berryman writes about his trip to Ireland as well as his own burgeoning literary fame. Berryman’s last two volumes of poetry, Love & Fame and Delusions, Etc. featured free-verse poems that were much more straightforward and less idiosyncratic than The Dream Songs. Prior to the publication of Love & Fame, Berryman sent his manuscript to several peers for feedback, including the poets Adrienne Rich and Richard Wilbur, both of whom were disappointed with the poems which they considered inferior to the poems in The Dream Songs. However, a number of Berryman’s old friends and supporters, including the novelist Saul Bellow and the poets Robert Lowell and William Meredith, offered high praise for a number of the Love & Fame poems. Both Love & Fame and Delusions, Etc. were more openly “confessional” than Berryman’s earlier verse, and since he embraced religion when he wrote these volumes, he also explored the nature of his spiritual rebirth in poems like “Eleven Addresses to the Lord” (which Lowell thought was one of Berryman’s best poems and “one of the great poems of the age”), as a well as “Certainty Before Lunch”. In 1977 John Haffenden published Henry’s Fate & Other Poems, a selection of dream songs that Berryman wrote after His Toy, His Dream, His Rest, but had never published. In reviewing the book, Time magazine noted, “Posthumous selections of unpublished poetry should be viewed suspiciously. The dead poet may have had good aesthetic reasons for keeping some of his work to himself. Fortunately, Henry’s Fate does not malign the memory of John Berryman”. Berryman’s Collected Poems—1937-1971 edited and introduced by Charles Thornbury, was published in 1989. However, Robert Giroux decided to leave out The Dream Songs from the collection. In his review of the Collected Poems, Edward Hirsch commented on this decision, stating, "It is obviously practical to continue to publish the 385 dream songs separately, but reading the Collected Poems without them is a little like eating a seven-course meal without a main course." Hirsch also notes that, "[Collected Poems features] a thorough nine-part introduction and a chronology as well as helpful appendixes that include Berryman’s published prefaces, notes and dedications; a section of editor’s notes, guidelines and procedures; and an account of the poems in their final stages of composition and publication.” In 2004, the Library of America published John Berryman: Selected Poems, edited by the poet Kevin Young. In Poetry magazine, David Orr wrote: Young includes all the Greatest Hits [from Berryman’s career]... but there are also substantial excerpts from Berryman’s Sonnets (the peculiar book that appeared after The Dream Songs, but was written long before) and Berryman’s later, overtly religious poetry. Young argues that “if his middle, elegiac period... is most in need of rediscovery, then these late poems are most in need of redemption.” It’s a good point. Although portions of Berryman’s late work are sloppy and erratic, these poems help clarify the spiritual struggle that motivates and sustains his best writing. After surveying Berryman’s career and accomplishments, the editors of The Norton Anthology of Modern Poetry stated, “What seems likely to survive of his poetry is its pungent and many-leveled portrait of a complex personality which, for all its eccentricity, stayed close to the center of the intellectual and emotional life of the mid-century and after.” In popular culture The ghost of John Berryman is a character in Thomas Disch’s novel The Businessman: A Tale of Terror, published in 1984. The Hold Steady’s song “Stuck Between Stations” from the 2006 album Boys and Girls in America relates a loose rendition of Berryman’s death, describing the isolation he felt, despite his critical acclaim, and depicting him walking with “the devil” on the Washington Avenue Bridge where he committed suicide. Okkervil River’s song “John Allyn Smith Sails” from their 2007 album The Stage Names is about John Berryman. Australian singer/songwriter Nick Cave has admiringly referenced Berryman in the song “We Call Upon the Author” from the 2007 album Dig, Lazarus, Dig!!!. Phish bassist Mike Gordon’s side-project band has performed "Dream Song 22-'Of 1826", releasing it on a live album, The Egg. Additionally, on March 30, 2014, their show featured a rendition of “The Poet’s Final Instructions”. Berryman and his poem Dream Song 235 is referenced in Elizabeth Strout’s novel and HBO’s adaption of Olive Kitteridge with the quote "Save us from shotguns & fathers’ suicides.” Berryman and his poem “The Curse” are referenced in the prologue of Tracy Letts’s play August: Osage County by the character Beverly, a poet who later commits suicide. Bibliography * Poems. Norfolk, Ct.: New Directions Press, 1942. * The Dispossessed. New York: William Sloan Associates, 1948. * Stephen Crane. New York: Sloan, 1950. * Homage to Mistress Bradstreet. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1956. * 77 Dream Songs. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1964. * Berryman’s Sonnets. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1967. * His Toy, His Dream His Rest. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1968. * The Dream Songs. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1969. * Love & Fame. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1970. * Delusions, Etc. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1972. * Recovery. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1973. * The Freedom of the Poet. New York: Farrar, Straus, & Giroux, 1976. * Henry’s Fate & Other Poems, 1967-1972. New York: Farrar, Straus, & Giroux, 1977. * Collected Poems 1937-1971. Ed. Charles Thornbury. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1989. * Berryman’s Shakespeare. Ed. John Haffenden. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 1999. * Selected Poems. Ed. Kevin Young. New York: Library of America, 2004. * The Heart Is Strange. Ed. Daniel Swift. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux, 2014. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Berryman

Robert Williams Buchanan (18 August 1841 – 10 June 1901) was a Scottish poet, novelist and dramatist. He was the son of Robert Buchanan (1813–1866), Owenite lecturer and journalist, and was born at Caverswall, Staffordshire, England. Buchanan senior, a native of Ayr, Scotland, lived for some years in Manchester, then moved to Glasgow, where Buchanan junior was educated, at the high school and the university, one of his fellow-students being the poet David Gray. His essay on Gray, originally published in the Cornhill Magazine, tells the story of their close friendship, and of their journey to London in 1860 in search of fame.

Nicholas Moore (16 November 1918 – 26 January 1986) was an English poet, associated with the New Apocalyptics in the 1940s, whose reputation stood as high as Dylan Thomas’s. He later dropped out of the literary world. Moore was born in Cambridge, England, the elder child of the philosopher G. E. Moore and Dorothy Ely. His paternal uncle was the poet, artist and critic Thomas Sturge Moore, and his brother was the composer Timothy Moore (1922-2003). He was educated at the Dragon School in Oxford, Leighton Park School in Reading, the University of St Andrews in Scotland, and Trinity College in Cambridge. Moore was editor and co-founder of a literary review, Seven (1938–40), while still an undergraduate. Seven, Magazine of People's Writing, had a complex later history: Moore edited it with John Goodland; it later appeared edited by Gordon Cruikshank, and then by Sydney D. Tremayne, after Randall Swingler bought it in 1941 from Philip O'Connor. While in Cambridge Moore became closely involved with literary London, in particular Tambimuttu. He published pamphlets under the Poetry London imprint in 1941 (of George Scurfield, G. S. Fraser, Anne Ridler and his own work). This led to Moore becoming Tambimuttu's assistant. Moore later worked for the Grey Walls Press. The Glass Tower, a selected poems collection from 1944, appeared with illustrations by the young Lucian Freud. In 1945 he edited The PL Book of Modern American Short Stories, and won Contemporary Poetry's Patron Prize (judged that year by W. H. Auden) for Girl with a Wine Glass. In 1947 he won the Harriet Monroe Memorial Prize for Girls and Birds and various other poems. Later Moore encountered difficulty in publishing; he was in the unusual position for a British poet of having a higher reputation in the USA. His association with the "romantics" of the 1940s was, in fact, rather an inaccurate reflection of his style. In the 1950s he worked as a horticulturist, writing a book The Tall Bearded Iris (1956). In 1968 he entered 31 separate pseudonymous translations of a single Baudelaire poem, in a competition for the Sunday Times, run by George Steiner. Each translation focused on a different element of the poem: rhyme, pattern, tropes, symbolism, etc. producing vastly different results, to illustrate the inadequacies and lacunae produced in translation. This work was published in 1973 as Spleen; it is also available online. Longings of the Acrobats, a selected poems volume, was edited by Peter Riley and published in 1990 by Carcanet Press. An interview with Riley concerning Moore's rediscovery and later years appears as a documentary element within the "Guilty River" chapter of Iain Sinclair's novel Downriver. According to Riley, Moore was extremely prolific and left behind many unpublished poems. An example of one of Moore's "pomenvylopes" – idiosyncratic documents consisting of poems and comments typed onto envelopes and posted to friends and acquaintances – appears online at The Fortnightly Review. His Selected Poems was published by Shoestring Press in 2014. Bibliography * A Wish in Season (1941) * The Island and the Cattle (1941) * A Book for Priscilla (1941) * Buzzing around with a Bee (1941) * The Cabaret, the Dancer, the Gentlemen (1942) * The Glass Tower (1944) * Thirty-Five Anonymous Odes (published anonymously, 1944) * The War of the Little Jersey Cows (published under the pseudonym "Guy Kelly", 1945) * The Anonymous Elegies and other poems (published anonymously, 1945) * Recollections of the Gala: Selected Poems 1943-48 (1950) * The Tall Bearded Iris (1956) * Anxious To Please (1968) (published under the pseudonym (anagram) "Romeo Anschilo", 1995 by Oasis Books) * Identity (1969) * Resolution and Identity (1970) * Spleen (1973) * Lacrimae Rerum (1988) * Longings of the Acrobats: Selected Poems (1990) * The Orange Bed (2011) References Wikipedia—http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nicholas_Moore


Charles Mair (September 21, 1838– July 7, 1927) was a Canadian poet and journalist. He was a fervent Canadian nationalist noted for his participation in the Canada First movement and his opposition to Louis Riel during the two Riel Rebellions in western Canada. Life Mair was born at Lanark, Upper Canada, to Margaret Holmes and James Mair. He attended Queen’s University but did not graduate. On leaving college, he became a journalist. In Ottawa in 1868, Mair was introduced by civil servant and writer Henry Morgan to young lawyers George Denison, William Foster, and Robert Haliburton. “Together they organized the overtly nationalistic Canada First movement, which began as a small social group.” Mair “represented the Montreal Gazette during the first Riel Rebellion, and was imprisoned and narrowly escaped being shot by the rebels.” Mair was a Freemason Mair "was an Officer of the Governor-General’s Body Guard during the second Riel rebellion in 1885, and was later employed in the Canadian civil service in the West." He died in Victoria, British Columbia. Writing Mair published the first book of poetry in post-Confederation Canada, 1868's Dreamland and Other Poems. “Negligible as verse,” says The Canadian Encyclopedia, "the volume gained interest when Mair escaped after being captured by Louis Riel during the Red River disturbances of 1869-70.” The Dictionary of Canadian Biography (DCB) states that Dreamland “demonstrates a conventional colonial approach to poetry. Such poems as 'August’ succeed in their attention to natural detail: descriptions of the blueflies, the milkmaids, and the 'ribby-lean’ cattle in parched fields anticipate the mature nature poetry of Archibald Lampman. But too often he wrote not of the timberlands he knew but of a dreamland weakly modelled upon the romantic flights of Keats.” However, the book was praised by “the established poet Charles Sangster, who referred to Canada’s sophisticated literary tradition as one that was habitually overlooked in the popular press.” Writing later in the Ottawa Journal, William Wilfred Campbell saw Dreamland as a precursor to the nature poetry later popularized in Canada by the Confederation Poets: “The thirty-three poems constitute the first attempt to deal with Canadian nature, in the manner of Keats and the other classic poets, and many of them in theme and treatment are similar to the verse of Lampman and Roberts.... And there are strong evidences in Mair’s work that he influenced these poets to a great extent.” Mair published Tecumseh, a historical drama mainly in blank verse dealing with the War of 1812, in 1886. Canadian critic Alan Filewood wrote of the political and philosophical ideas expressed by Mair in the poem: Mair’s projection of Canadian nationhood is embodied in the character of Lefroy, a Byronesque poet who flees civilization to seek solace in nature’s genius. He learns– tragically– from the British General Brock that natural law finds its outward form in the monarchic principle, and from the Indian chieftain Tecumseh that nature must be defended against the perversion of American materialism. The dying Tecumseh legitimizes the proto-(Anglo) Canadians as the natural guardians of the land, and Canadian manhood finds mature expression in a race of armed poets.(...) Mair looked to the day when the dominions would assume the responsibilities of adulthood: Then shall a whole family of young giants stand 'Erect, unbound, at Britain’s side-' her imperial offspring oversea, the upholders in the far future of her glorious tradition, or, should exhaustion ever come, the props and supports of her declining years. The DCB calls Tecumseh "a major contribution to our 19th-century literary heritage, wherein the War of 1812 is the central event of Canadian history. Among the many literary treatments of this war, including works by Sangster, John Richardson, and Sarah Anne Curzon... Tecumseh stands as the most accomplished." The Canadian Encyclopedia says that the poem’s “blank verse is pedestrian and untheatrical”, but it also tells us that “Tecumseh was important in the development of Canadian drama. It presents a vision of Canada as a co-operative enterprise in contrast with the self-seeking individualism of the United States.” Recognition Mair was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1889. In 1937 he was designated a Person of National Historic Significance. Canadian folksinger Gordon Lightfoot adapted a line from Tecumseh, “There was a time on this fair continent,” for the first line in his 1967 historical ballad, “The Canadian Railroad Trilogy” ("There was a time in this fair land when the railroad did not run"). Publications * Dreamland and Other Poems. London: S. Low, 1868. Montreal: Dawson, 1868, * Tecumseh. Toronto: Hunter, Rose & Co., 1886. London: Chapman & Hall, 1886. * Through the Mackenzie Basin: A Narrative of the Athabasca and Peace River Treaty Expedition of 1899 . London: Simpkin, Marshall, Hamilton, Kent & Co., 1903. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_Mair

Richard Jago (1 October 1715– 8 May 1781) was an English clergyman poet and minor landscape gardener from Warwickshire. Although his writing was not highly regarded by contemporaries, some of it was sufficiently novel to have several imitators. Life Richard Jago was the third son of the Rector of Beaudesert, Warwickshire, and was named after him. His father’s family was of Cornish origin, while his mother was from the immediately adjoining village of Henley in Arden. He was educated at Solihull School, where one of its five houses is now named after him. While there he formed a lifelong friendship with William Shenstone. In 1732, he went up to University College, Oxford and while there Shenstone made him acquainted with other students with a literary taste. He took his master’s degree 9 July 1738, having entered into the church the year before, and served the curacy of Snitterfield, Warwickshire, near Stratford upon Avon. In 1744, he married Dorothea Susanna Fancourt, daughter of the rector of Kimcote in Leicestershire, whom he had known from her childhood. In 1751 his wife died, leaving him with the care of seven very young children. Three of these were boys, who predeceased him, but he was eventually survived by three of his daughters. In 1759, he married a second wife, Margaret Underwood, but had no children by her. Jago had become vicar of Harbury in 1746, and shortly after of Chesterton, both in Warwickshire. Through aristocratic patrons, he was given the living of Snitterfield in 1754, and later was presented with his former father-in-law’s living in Kimcote in 1771, after which he resigned the livings of Harbury and Chesterton, keeping the others. Snitterfield remained his favourite residence and it was there that he would die at the age of 66. Jago shared with Shenstone an interest in landscape gardening and occupied himself with making improvements to the Snitterfield vicarage garden. Both became part of the likeminded circle about Henrietta Knight, Lady Luxborough which also included other literary friends, William Somervile and Richard Graves, rector of Claverton. Shenstone dedicated a bench to Jago at the end of the viewing circuit near his house, The Leasowes, and both dedicated poems to each other. Poetry Jago’s first independent publications were two sermons. The first, “The Cause of Impenitence Considered” (1755), was published for the benefit of Harbury Free School; the second was a funeral sermon, “The nature and grounds of a Christian’s happiness in and after death” (1763). Shenstone’s letters mention an Essay on Electricity written by Jago, written in 1747, but this seems to have remained unpublished. Poems of his were also beginning to appear in Robert Dodsley’s anthologies, Collection of Poetry by several hands, among which the sentimental elegy “The Blackbirds” had made something of a stir after it first appeared in the ephemeral magazine The Adventurer in 1753. This was a lament on the death of a self-sacrificing blackbird and was shortly followed by similar poems on goldfinches and swallows. They were particularly praised by Dr. John Aikin in his “Essay on the application of Natural History to poetry”, who also noted that there were soon imitations among other minor poets, including Samuel Jackson Pratt’s “The Partridges, an elegy” (1771) and James Graeme’s “The Linnet” (1773). Jago’s most ambitious publication was the four-part topographical poem, Edge Hill, or the rural prospect delineated and moralised (1767). It was written in blank verse and was once described as “the most elaborate local poem in our language”. The poet takes his stance on the hill in the morning, facing south-west (book 1); at noon he is on Ratley Hill in the centre (books 2–3) and then moves along the ridge to look north-east at evening. The poem intermingles description with legendary, historical and antiquarian particulars, principally the battle at the start of the English Civil War. Imaginary excursions are made to Warwick, Coventry, Kenilworth, Solihull, and industrial Birmingham (under the name Bremicham), as well as many “flattering descriptions of all the great houses and seats of important people which come within his survey”. Local rivers are also included and even the nearby canal on which “sooty barks pursue their liquid track”. There are many digressions as well, including descriptions of industrial processes and of the nature of vision and the working of the telescope. The critic already quoted finds the poem “really interesting; with the scene before us, it is impossible not to admire the ingenuity and scrupulous thoroughness with which the author has performed his task,” although ultimately it is lacking in poetic execution. The Cambridge History of English and American Literature judges that "his catalogues have little picturesqueness or colour; while his verse, although it is not without the accent of local association, is typical, as a whole, of the decadence of the Miltonic method of natural description in the 18th century. Every group of trees is a grove, every country house a dome, and every hill a precipice". Particular examples of hackneyed diction include Latin-derived adjectives, as in “Honington’s irriguous meads”, or else 18th century circumlocutions such as “the woolly tribes” when sheep are meant. Nevertheless, the poem seems to have inspired the writing of the much shorter and simpler “Ode to Lansdowne Hill” (1785), which celebrates the site of another Civil War battle. In the following year Jago published “Labour and Genius, or the mill-stream and the cascade”, a humorous fable in octosyllabic verse written in memory of William Shenstone and his landscaped grounds at the Leasowes. Poems of lesser significance appeared here and there and Jago was working on a revised edition of his collected poems just before his death. This appeared posthumously as Poems, Moral and Descriptive in 1784. Included there was another homage to Milton in the oratorio “Adam, or the fatal disobedience, compiled from Milton’s Paradise Lost and adapted to music”. The rhymed choruses there were of Jago’s composition, but the main body of the work is adapted directly from Paradise Lost. Though it found no composer to set it, another of Jago’s pieces did. This was the “Roundelay for the Stratford Jubilee” organised by David Garrick in 1769, which was set for singing by Charles Dibdin. One other humorous piece also found an imitator. In Jago’s “Hamlet’s soliloquy imitated”, a minor poet agonises over whether “to print or not to print” and run the danger, by submitting his verses to Dodsley, to “lose the name of author”. A subsequent parody titled “The Presbyterian parson’s soliloquy” over the question to “conform or not conform” appeared in The Hibernian Magazine in 1774 and was often reprinted thereafter, ascribed to Samuel Badcock. One later commentator gave it as his opinion that “the hint of this parody was probably borrowed from Mr Jago’s”. Slight Jago’s output may have been, but it appears to have been influential in its time. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Richard_Jago


Agnes Ethelwyn Wetherald was born of English-Quaker parents at Rockwood, Ontario, April 26th, 1857. Her father was the late Rev. William Wetherald, who founded the Rockwood Academy about the middle of the last century, and was its principal for some years. He was a lover of good English, spoken and written, and his talented daughter has owed much to his careful teaching. He was the teacher whom the late James J. Hill, the railway magnate, had held in such grateful remembrance. Additional education was received by Miss Wetherald at the Friends' Boarding School, Union Springs, N.Y., and at Pickering College. Miss Wetherald began the writing of poetry later in life than most poets and her first book of verse, The House of the Trees and Other Poems, did not appear until 1895. This book at once gave her high rank among women poets. Prior to this, she had collaborated with G. Mercer Adam on writing and publishing a novel, An Algonquin Maiden, and had conducted the Woman's Department in The Globe, Toronto, under the nom de plume, 'Bel Thistlewaite.' In 1902, appeared her second volume of verse, Tangled in Stars, and, in 1904, her third volume, The Radiant Road. In the autumn of 1907, a collection of Miss Wetherald's best poems was issued, entitled, The Last Robin: Lyrics and Sonnets. It was warmly welcomed generally, by reviewers and lovers of poetry. The many exquisite gems therein so appealed to Earl Grey, the then Governor-General of Canada, that he wrote a personal letter of appreciation to the author, and purchased twenty-five copies of the first edition for distribution among his friends. For years Miss Wetherald has resided on the homestead farm, near the village of Fenwick, in Pelham Township, Weland county, Ontario, and there in the midst of a large orchard and other rural charms, has dreamed, and visioned, and sung, pouring out her soul in rare, sweet songs, with the naturalness of a bird. And like a bird she has a nest in a large willow tree, cunningly contrived by a nature-loving brother, where her muse broods contentedly, intertwining her spirit with every aspect of the beautiful environment.


Susan Frances Harrison née Riley (February 24, 1859– May 5, 1935) (a.k.a. Seranus) was a Canadian poet, novelist, music critic and music composer who lived and worked in Ottawa and Toronto. Life Susie Frances Riley was born in Toronto of Irish-Canadian ancestry, the daughter of John Byron Riley. She studied music with Frederic Boscovitz, at a private school for girls in Toronto, and later in Montreal. She reportedly began publishing poetry, in the Canadian Illustrated News, at 16 under the pseudonym “Medusa.” After completing her education, she worked as a pianist and singer. In 1880 she married organist John W. F. Harrison, of Bristol, England, who was the organist of St. George’s Church in Montreal. The couple had a son and a daughter. The Harrisons lived in Ottawa in 1883, when Susie Harrison composed the song “Address of Welcome to Lord Lansdowne” to celebrate the first public appearance of the new Governor General, the Marquess of Lansdowne. In 1887 the Harrisons moved to Toronto, where John Harrison became organist and choirmaster of St. Simon the Apostle, and Susan Harrison began a literary career under the pseudonym “Seranus” (a misreading of her signature, “S. Frances”), soon publishing articles in “many of the leading journals and periodicals.” She wrote a number of songs published in the United States and England under the name Seranus, and published other songs in England under the name, Gilbert King. She was the music critic of The Week from December 1886 to June 1887 under her pen-name of Seranus. She wrote the “Historical sketch on Canadian music” for the 1898 Canada: An Encyclopedia of the Country. Susan Harrison was considered an authority on folk music, and often lectured on the subject. She used traditional Irish melodies in her String Quartet on Ancient Irish Airs, and French-Canadian music in her 1887 Trois Esquisses canadiennes (Three Canadian Sketches), ‘Dialogue,’ ‘Nocturne,’ and 'Chant du voyageur’. She also incorporated French-Canadian melodies in her three-act opera, Pipandor (with libretto by F.A. Dixon of Ottawa). Her String Quartet on Ancient Irish Airs, is likely the first string quartet composed in Canada by a woman. In 1896 and 1897 she presented a series of well-received lectures in Toronto on "The Music of French Canada. For 20 years Harrison was the principal of the Rosedale branch of the Toronto Conservatory of Music. During the 1900s she contributed to and edited the Conservatory’s publication Conservatory Monthly, and contributed to its successor Conservatory Quarterly Review. She wrote the article on “Canada” for the 1909 Imperial History and Encyclopedia of Music. In addition, she wrote at least six books of poetry, and three novels. Writing Poetry Harrison’s musical training is reflected in her poetry: “she was adept in her handling of the rhythmic complexities of poetic forms such as the sonnet and the villanelle. Like other Canadian poets of the late nineteenth century, her prevailing themes include nature, love, and patriotism. Her landscape poetry, richly influenced by the works of Charles G.D. Roberts and Archibald Lampman, paints the Canadian wilderness as beguilingly beautiful yet at the same time mysterious and distant.” Harrison was a master of the villanelle. The villanelle was a French verse form that had been introduced to English readers by Edmund Gosse in his 1877 essay, “A Plea for Certain Exotic Forms of Verse”. Novels Her two novels “articulate a fascination with a heavily mythologized Quebec culture that Harrison shared with many English-speaking Canadians of her time... characterized by a gothic emphasis on horror, madness, aristocratic seigneurial manor houses, and a decadent Catholicism.” “Harrison writes elegiacally of a regime whose romantic qualities are largely the creation of an Upper Canadian quest for a distinctive historical identity.” Recognition Harrison experienced a decline in reputation in her lifetime. In 1916 anthologist John Garvin called her “one of our greater poets whose work has not yet had the recognition in Canada it merits.”. "By 1926, Garvin describes her merely as 'one of our distinctive poets’.” The Dictionary of Literary Biography wrote of Susan Frances Harrison, in 1990, that “Harrison’s unpublished work has not been preserved, her published work is out of print and difficult to obtain, and her once-substantial position in the literary life of her country is now all but forgotten.” Publications Selected songs * Song of Welcome. * Pipandor. opera * ‘Trois Esquisses canadiennes: ’Dialogue,' ‘Nocturne,’ 'Chant du voyageur’. 1887. * Quartet on Ancient Irish Airs. Poetry * Four Ballads and a Play. Toronto: Author, 1890. * Pine, Rose and Fleur De Lis. Toronto: Hart, 1891. * In Northern Skies and Other Poems. Toronto: Author, 1912. * Songs of Love and Labor. Toronto: Author, 1925. * Later Poems and New Villanelles. Toronto: Ryerson, 1928. * Penelope and Other Poems. Toronto: Author, 1934. * Bibliographical information on poems from Wanda Campbell, Hidden Rooms. Prose * Crowded Out and Other Sketches. Ottawa: Evening Journal, 1886. * The Forest of Bourg-Marie, novel. Toronto: G.N. Morang, 1898. * Ringfield, novel. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1914. Edited * Canadian Birthday Book. Toronto: Robinson, 1887. Poetry anthology. Articles * “Historical sketch of music in Canada,” Canada: An Encyclopedia of the Country, vol 4, J.C. Hopkins ed., Toronto, 1898. * “Canada,” The Imperial History and Encyclopedia of Music, vol 3: History of Foreign Music, W.L. Hubbard ed., New York ca 1909. Discography * Harrison’s piano music has been recorded and issued on media, including: * Keillor, Elaine. By a Canadian Lady Piano Music 1841-1997 Carleton Sound * Keillor, Elaine. Piano Music by Torontonians (1984) References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Susie_Frances_Harrison


