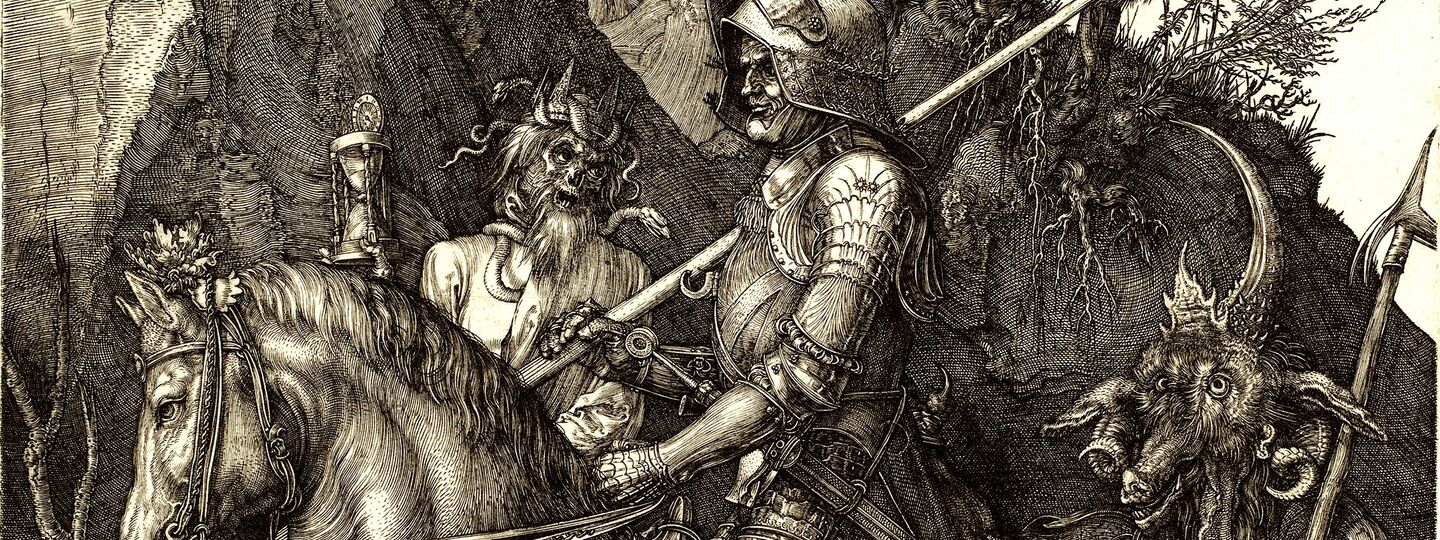

Info
Knight, Death, and the Devi
Alberto Durero
1513
National Gallery of Art


Edward Lear (12 or 13 May 1812 – 29 January 1888) was an English artist, illustrator, author and poet, and is known now mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised. His principal areas of work as an artist were threefold: as a draughtsman employed to illustrate birds and animals; making coloured drawings during his journeys, which he reworked later, sometimes as plates for his travel books; as a (minor) illustrator of Alfred Tennyson's poems. As an author, he is known principally for his popular nonsense works, which use real and invented English words. Early years Lear was born into a middle-class family in the village of Holloway near London, the penultimate of twenty-one children (and youngest to survive) of Ann Clark Skerrett and Jeremiah Lear. He was raised by his eldest sister, also named Ann, 21 years his senior. Owing to the family's limited finances, Lear and his sister were required to leave the family home and live together when he was aged four. Ann doted on Edward and continued to act as a mother for him until her death, when he was almost 50 years of age. Lear suffered from lifelong health afflictions. From the age of six he suffered frequent grand mal epileptic seizures, and bronchitis, asthma, and during later life, partial blindness. Lear experienced his first seizure at a fair near Highgate with his father. The event scared and embarrassed him. Lear felt lifelong guilt and shame for his epileptic condition. His adult diaries indicate that he always sensed the onset of a seizure in time to remove himself from public view. When Lear was about seven years old he began to show signs of depression, possibly due to the instability of his childhood. He suffered from periods of severe melancholia which he referred to as "the Morbids.” Artist Lear was already drawing "for bread and cheese" by the time he was aged 16 and soon developed into a serious "ornithological draughtsman" employed by the Zoological Society and then from 1832 to 1836 by the Earl of Derby, who kept a private menagerie at his estate Knowsley Hall. Lear's first publication, published when he was 19 years old, was Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae, or Parrots in 1830. His paintings were well received and he was compared favourably with the naturalist John James Audubon. Among other travels, he visited Greece and Egypt during 1848–49, and toured India and Ceylon (Sri Lanka) during 1873–75. While travelling he produced large quantities of coloured wash drawings in a distinctive style, which he converted later in his studio into oil and watercolour paintings, as well as prints for his books. His landscape style often shows views with strong sunlight, with intense contrasts of colour. Throughout his life he continued to paint seriously. He had a lifelong ambition to illustrate Tennyson's poems; near the end of his life a volume with a small number of illustrations was published. Relationships Lear's most fervent and painful friendship involved Franklin Lushington. He met the young barrister in Malta in 1849 and then toured southern Greece with him. Lear developed an undoubtedly homosexual passion for him that Lushington did not reciprocate. Although they remained friends for almost forty years, until Lear's death, the disparity of their feelings for one another constantly tormented Lear. Indeed, none of Lear's attempts at male companionship were successful; the very intensity of Lear's affections seemingly doomed the relationships. The closest he came to marriage with a woman was two proposals, both to the same person 46 years his junior, which were not accepted. For companions he relied instead on friends and correspondents, and especially, during later life, on his Albanian Souliote chef, Giorgis, a faithful friend and, as Lear complained, a thoroughly unsatisfactory chef. Another trusted companion in Sanremo was his cat, Foss, which died in 1886 and was buried with some ceremony in a garden at Villa Tennyson. San Remo and death Lear travelled widely throughout his life and eventually settled in Sanremo, on his beloved Mediterranean coast, in the 1870s, at a villa he named "Villa Tennyson". Lear was known to introduce himself with a long pseudonym: "Mr Abebika kratoponoko Prizzikalo Kattefello Ablegorabalus Ableborinto phashyph" or "Chakonoton the Cozovex Dossi Fossi Sini Tomentilla Coronilla Polentilla Battledore & Shuttlecock Derry down Derry Dumps" which he based on Aldiborontiphoskyphorniostikos. After a long decline in his health, Lear died at his villa in 1888, of the heart disease from which he had suffered since at least 1870. Lear's funeral was said to be a sad, lonely affair by the wife of Dr. Hassall, Lear's physician, none of Lear's many lifelong friends being able to attend. Lear is buried in the Cemetery Foce in San Remo. On his headstone are inscribed these lines about Mount Tomohrit (in Albania) from Tennyson's poem To E.L. [Edward Lear], On His Travels in Greece: all things fair. With such a pencil, such a pen. You shadow forth to distant men, I read and felt that I was there. The centenary of his death was marked in Britain with a set of Royal Mail stamps in 1988 and an exhibition at the Royal Academy. Lear's birthplace area is now marked with a plaque at Bowman's Mews, Islington, in London, and his bicentenary during 2012 was celebrated with a variety of events, exhibitions and lectures in venues across the world including an International Owl and Pussycat Day on his birthday. References Wikipedia – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Lear


William Ernest Henley (23 August 1849 – 11 July 1903) was an English poet, critic and editor, best remembered for his 1875 poem “Invictus”. Henley was born in Gloucester and was the oldest of a family of six children, five sons and a daughter. His father, William, a bookseller and stationer, died in 1868 and was survived by young children and creditors. His mother, Mary Morgan, was descended from the poet and critic Joseph Wharton. Between 1861 and 1867, Henley was a pupil at the Crypt Grammar School (founded 1539).


Nicholas Vachel Lindsay (November 10, 1879 – December 5, 1931) was an American poet. He is considered a founder of modern singing poetry, as he referred to it, in which verses are meant to be sung or chanted. Crushed by financial worry and in failing health from his six-month road trip, Lindsay sank into depression. While in New York in 1905 Lindsay turned to poetry in earnest. He tried to sell his poems on the streets. Self-printing his poems, he began to barter a pamphlet titled “Rhymes To Be Traded For Bread”, which he traded for food as a self-perceived modern version of a medieval troubadour. On December 5, 1931, he committed suicide by drinking a bottle of Lysol. His last words were: “They tried to get me; I got them first!”
#Americans #Suicide #XIXCentury #XXCentury


Charles Mackay (27 March 1814– 24 December 1889) was a Scottish poet, journalist, author, anthologist, novelist, and songwriter, remembered mainly for his book Extraordinary Popular Delusions and the Madness of Crowds. He was born in Perth. His father, George Mackay, was a bombardier in the Royal Artillery, and his mother Amelia Cargill died shortly after his birth. His birthdate was 26 March 1812, although he always gave it as 27 March 1814.


Elizabeth Bishop (February 8, 1911 – October 6, 1979) was an American poet, short-story writer, and recipient of the 1976 Neustadt International Prize for Literature. She was the Poet Laureate of the United States from 1949 to 1950, the Pulitzer Prize winner for Poetry in 1956 and the National Book Award winner in 1970.
#Americans #PulitzerPrize #Women
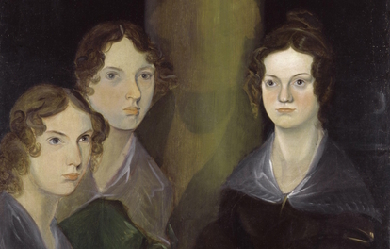

Emily Jane Brontë (30 July 1818 – 19 December 1848) was an English novelist and poet, best remembered for her solitary novel, Wuthering Heights, now considered a classic of English literature. Emily was the third eldest of the four surviving Brontë siblings, between the youngest Anne and her brother Branwell. She published under the pen name Ellis Bell. She was born in Thornton, near Bradford in Yorkshire, to Maria Branwell and Patrick Brontë. She was the younger sister of Charlotte Brontë and the fifth of six children. In 1824, the family moved to Haworth, where Emily's father was perpetual curate, and it was in these surroundings that their literary gifts flourished.
#English #Victorians #Women #XIXCentury


Miguel de Unamuno y Jugo (Bilbao, 29 de septiembre de 1864-Salamanca, 31 de diciembre de 1936) fue un escritor y filósofo español perteneciente a la generación del 98. En su obra cultivó gran variedad de géneros literarios como novela, ensayo, teatro y poesía. Rector de la Universidad de Salamanca a lo largo de tres periodos, también fue diputado de las Cortes constituyentes de la Segunda República, de la que se fue distanciando hasta el punto de secundar la sublevación militar que dio inicio a la guerra civil, si bien terminó retractándose de dicho apoyo.


Lesbia Harford (1891–1927) was an Australian poetesse, novelist and political activist. Lesbia Venner Keogh was the first child of Edmund Joseph Keogh and Beatrice Eleanor Moore, great-great-granddaughter of an Earl of Drogheda. Lesbia was born at Brighton, Victoria, on 9 April 1891. Her father left home for Western Australia when his real estate business failed about 1900. Lesbia advocated free love in human relations. She herself formed lifelong parallel attachments to both men and women, most notably to Katie Lush, philosophy tutor at Ormond College.


I don't write to please Only to put this need at ease I can't force my poems, spontanious as fire They flow in when they desire Like emotions, they never seem to dim It's my job to scramble; keeping up with them So they are not a loss of time To view my work I won't charge one dime All my hardships are not my demise This life I live is such a prize


Ben Jonson (originally Benjamin Jonson; c. 11 June 1572 – 6 August 1637) was an English playwright, poet, and literary critic of the seventeenth century, whose artistry exerted a lasting impact upon English poetry and stage comedy. He popularised the comedy of humours. He is best known for the satirical plays Every Man in His Humour (1598), Volpone, or The Foxe (1605), The Alchemist (1610), and Bartholomew Fayre: A Comedy (1614), and for his lyric poetry; he is generally regarded as the second most important English dramatist, after William Shakespeare, during the reign of James I. He was a classically educated, well-read, and cultured man of the English Renaissance with an appetite for controversy (personal and political, artistic and intellectual) whose cultural influence was of unparalleled breadth upon the playwrights and the poets of the Jacobean era (1603–1625) and of the Caroline era (1625–1642).


William Cullen Bryant (November 3, 1794– June 12, 1878) was an American romantic poet, journalist, and long-time editor of the New York Evening Post. Youth and education Bryant was born on November 3, 1794, in a log cabin near Cummington, Massachusetts; the home of his birth is today marked with a plaque. He was the second son of Peter Bryant (b. Aug. 12, 1767, d. Mar. 20, 1820), a doctor and later a state legislator, and Sarah Snell (b. Dec. 4, 1768, d. May 6, 1847). The genealogies of both of his parents trace back to passengers on the Mayflower; his mother’s to John Alden (b. 1599, d. 1687); his father’s to Francis Cooke (b. 1577, d. 1663). He was also a nephew of Charity Bryant, a Vermont seamstress who is the subject of Rachel Hope Cleves’ 2014 book Charity and Sylvia: A Same-Sex Marriage in Early America. Bryant and his family moved to a new home when he was two years old. The William Cullen Bryant Homestead, his boyhood home, is now a museum. After just one year at Williams College (he entered with sophomore standing), he hoped to transfer to Yale, but a talk with his father led to the realization that family finances would not support it. His father counseled a legal career as his best available choice, and the disappointed poet began to study law in Worthington and Bridgewater in Massachusetts. He was admitted to the bar in 1815 and began practicing law in nearby Plainfield, walking the seven miles from Cummington every day. On one of these walks, in December 1815, he noticed a single bird flying on the horizon; the sight moved him enough to write “To a Waterfowl”. Bryant developed an interest in poetry early in life. Under his father’s tutelage, he emulated Alexander Pope and other Neo-Classic British poets. “The Embargo”, a savage attack on President Thomas Jefferson published in 1808, reflected Dr. Bryant’s Federalist political views. The first edition quickly sold out—partly because of publicity attached to the poet’s young age. A second, expanded edition included Bryant’s translation of classical verse. During his collegiate studies and his reading for the law, he wrote little poetry, but encounters with the Graveyard Poets and then Wordsworth regenerated his passion for “the witchery of song.” Poetry “Thanatopsis” is Bryant’s most famous poem, which Bryant may have been working on as early as 1811. In 1817 his father took some pages of verse from his son’s desk, and at the invitation of Willard Phillips, an editor of the North American Review who had previously been tutored in the classics by Dr. Bryant, he submitted them along with his own work. The editor of the Review, Edward Tyrrel Channing, read the poem to his assistant, Richard Henry Dana, who immediately exclaimed, “That was never written on this side of the water!” Someone at the North American joined two of the son’s discrete fragments, gave the result the Greek-derived title Thanatopsis ("meditation on death"), mistakenly attributed it to the father, and published it. After clarification of the authorship, the son’s poems began appearing with some regularity in the "[Review]". “To a Waterfowl”, published in 1821 was the most popular. On January 11, 1821, Bryant, still striving to build a legal career, married Frances Fairchild. Soon after, having received an invitation to address the Harvard University Phi Beta Kappa Society at the school’s August commencement, Bryant spent months working on “The Ages”, a panorama in verse of the history of civilization, culminating in the establishment of the United States. As it would in all collections he subsequently issued, “The Ages” led the volume, also entitled Poems, which he arranged to publish on the same trip to Cambridge. For that book, he added sets of lines at the beginning and end of “Thanatopsis” that changed the poem. His career as a poet was now established, though recognition as America’s leading poet waited until 1832, when an expanded Poems was published in the U.S. and, with the assistance of Washington Irving, in Britain. His poetry has been described as being “of a thoughtful, meditative character, and makes but slight appeal to the mass of readers.” Editorial career From 1816 to 1825, Bryant depended on his law practice in Great Barrington, Massachusetts to sustain his family financially, but the strain of dealing with unsophisticated neighbors and juridical pettifoggery pushed him to trade his unrewarding profession for New York City and the promise of a literary career. With the encouragement of a distinguished and well-connected literary family, the Sedgwicks, he quickly gained a foothold in New York City’s vibrant cultural life. His first employment, in 1825, was as editor of the New-York Review, which within the next year merged with the United States Review and Literary Gazette. But in the throes of the failing struggle to raise subscriptions, he accepted part-time duties with the New-York Evening Post under William Coleman; then, partly because of Coleman’s ill health, traceable to the consequences of a duel and then a stroke, Bryant’s responsibilities expanded rapidly. From Assistant Editor he rose to Editor-in-Chief and co-owner of the newspaper that had been founded by Alexander Hamilton. Over the next half century, the “Post” would become the most respected paper in the city and, from the election of Andrew Jackson, the major platform in the Northeast for the Democratic Party and subsequently of the Free Soil and Republican Parties. In the process, the Evening-Post also became the pillar of a substantial fortune. From his Federalist beginnings, Bryant had shifted to being one of the most liberal voices of the century. An early supporter of organized labor, with his 1836 editorials the right of workmen to strike, Bryant also defended of religious minorities and immigrants, and promoted the abolition of slavery. He “threw himself into the foreground of the battle for human rights” and did not cease speaking out against the corrupting influence of certain bankers in spite of their efforts to break down the paper. According to newspaper historian Frank Luther Mott, Bryant was “a great liberal seldom done justice by modern writers”. Ironically, the boy who first tasted fame for his diatribe against Thomas Jefferson and his party became one of the key supporters in the Northeast of that same party under Jackson. Bryant’s views, always progressive though not quite populist, in course led him to join the Free Soilers, and when the Free Soil Party became a core of the new Republican Party in 1856, Bryant vigorously campaigned for John Frémont. That exertion enhanced his standing in party councils, and in 1860, he was one of the prime Eastern exponents of Abraham Lincoln, whom he introduced at Cooper Union. (That “Cooper Union speech” lifted Lincoln to the nomination, and then the presidency.) Although literary historians have neglected his fiction, Bryant’s stories over the seven-year period from his time with the Review to the publication of Tales of Glauber Spa in 1832 show a variety of strategies, making him the most inventive of practitioners of the genre during this early stage of its evolution. Bryant edited the very successful Picturesque America which was published between 1872 and 1874. This two-volume set was lavishly illustrated and described scenic places in the United States and Canada. Later years In his last decade, Bryant shifted from writing his own poetry to a blank verse translation of Homer’s works. He assiduously worked on the Iliad and The Odyssey from 1871 to 1874. He is also remembered as one of the principal authorities on homeopathy and as a hymnist for the Unitarian Church—both legacies of his father’s enormous influence on him. Bryant died in 1878 of complications from an accidental fall suffered after participating in a Central Park ceremony honoring Italian patriot Giuseppe Mazzini. He is buried at Roslyn Cemetery in Roslyn, Long Island, New York. Critical response Poet and literary critic Thomas Holley Chivers said that the "only thing [Bryant] ever wrote that may be called Poetry is 'Thanatopsis’, which he stole line for line from the Spanish. The fact is, that he never did anything but steal—as nothing he ever wrote is original." Contemporary critic Edgar Allan Poe, on the other hand, praised Bryant and specifically the poem “June” in his essay “The Poetic Principle”: The rhythmical flow, here, is even voluptuous—nothing could be more melodious. The poem has always affected me in a remarkable manner. The intense melancholy which seems to well up, perforce, to the surface of all the poet’s cheerful sayings about his grave, we find thrilling us to the soul—while there is the truest poetic elevation in the thrill. The impression left is one of a pleasurable sadness. Editor and children’s writer Mary Mapes Dodge wrote that Bryant’s poems “have wrought vast and far-reaching good in the world.” She predicted, “You will admire more and more, as you grow older, the noble poems of this great and good man.” Bryant’s poetry is tender and graceful, pervaded by a contemplative melancholy, and a love of solitude and the silence of the woods. Though he was brought up to admire Pope, and in his early youth imitated him, he was one of the first American poets to throw off his influence. He had a high sense of duty, was a prominent and patriotic citizen, and enjoyed the esteem and even the reverence of his fellow-countrymen. Legacy In 1884, New York City’s Reservoir Square, at the intersection of 42nd Street and Sixth Avenue, was renamed Bryant Park in his honor. The city later named a public high school in Long Island City, Queens in his honor. A park in East York, a suburb of Toronto, Canada, bears the name of Cullen Bryant Park as well. Although he is now thought of as a New Englander, Bryant, for most of his lifetime, was thoroughly a New Yorker—and a very dedicated one at that. He was a major force behind the idea that became Central Park, as well as a leading proponent of creating the Metropolitan Museum of Art. He was one of a group of founders of New York Medical College. He had close affinities with the Hudson River School of art and was an intimate friend of Thomas Cole. He defended immigrants and, at some financial risk to himself, championed the rights of workers to form labor unions. As a writer, Bryant was an early advocate of American literary nationalism, and his own poetry focusing on nature as a metaphor for truth established a central pattern in the American literary tradition. Some however, argue that a reassessment is long overdue. It finds great merit in a couple of short stories Bryant wrote while trying to build interest in periodicals he edited. More importantly, it perceives a poet of great technical sophistication who was a progenitor of Walt Whitman, to whom he was a mentor. Martin Luther King, Jr quoted Bryant in his speech “Give Us the Ballot”, when he said, “there is something in this universe which justifies William Cullen Bryant in saying: ‘Truth crushed to earth will rise again.’” The Seattle neighborhood Bryant is named after him. Bryant House at Williams College is named for him. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_Cullen_Bryant

I love to write poems. It helps me to put down my feelings and I guess it's a way of venting. I have 2 sons, Jeff & Gary my grandson Josh & granddaughter Caitlin & my baby boy Rocky a ( Shih Tzu). I am so very pleased to say my son Gary and Jen are now husband and wife. They were married on 8/16/15. Such a beautiful Wedding and a most Wonderful Couple who Love each other very much. The best part is from this union I have 2 more grandsons Dillon and Colton, 3 beautiful granddaughters Samy (Samantha), Bella Mia and Addy (Addison) and 2 great grandsons Domy and Austin. This marriage means so very much to me. My daughter in law Jenny has raised her granddaughter Bella since she was 5 days old. She adopted her and her name is Bella Mia (2 years old). She is beautiful like her name. Together my son Gary and Jen will be adopting Bella's half sister Addy (5 years old). Jenny has been fighting to adopt Addy for more than 2 years. Addy has been awarded into the custody of Jenny and Gary. She will be flying home with Jenny on 8/28/15 from Florida to her "FOREVER HOME". In 90 days they will be allowed to adopt Addy. So both Bella and Addy are also my granddaughters. I am so very Happy. I now have a very large and loving family. I have written poems about Addy, and I want to Thank those of you who helped me pray for her to become family. Such a wonderful miracle has been witnessed. She is family now and she is beautiful. I love my daughter in law as she is a wonderful person, a fantastic Mom and a wonderful wife to my son. My son Jeffrey is my Hero. He's an upstanding guy, Honest and true. I'm so proud of him. He's also my Best Friend. God Bless. Sandi.


Ada Cambridge (21 November 1844 – 19 July 1926), later known as Ada Cross, was an English-born Australian writer. She wrote more than twenty-five works of fiction, three volumes of poetry and two autobiographical works. Many of her novels were serialized in Australian newspapers, and were never published in book form. While she was known to friends and family by her married name, Ada Cross, she was known to her newspaper readers as A.C.. Later in her career she reverted to her maiden name, Ada Cambridge, and it is thus by this name that she is known.


Thomas Hood (23 May 1799 – 3 May 1845) was an English poet, author and humourist, best known for poems such as “The Bridge of Sighs” and “The Song of the Shirt”. Hood wrote regularly for The London Magazine, the Athenaeum, and Punch. He later published a magazine largely consisting of his own works. Hood, never robust, lapsed into invalidism by the age of 41 and died at the age of 45. William Michael Rossetti in 1903 called him “the finest English poet” between the generations of Shelley and Tennyson. Hood was the father of playwright and humourist Tom Hood (1835–1874).


Sir Philip Sidney (30 November 1554– 17 October 1586) was an English poet, courtier, scholar, and soldier, who is remembered as one of the most prominent figures of the Elizabethan age. His works include Astrophel and Stella, The Defence of Poesy (also known as The Defence of Poetry or An Apology for Poetry), and The Countess of Pembroke’s Arcadia. Early life Born at Penshurst Place, Kent, he was the eldest son of Sir Henry Sidney and Lady Mary Dudley. His mother was the eldest daughter of John Dudley, 1st Duke of Northumberland, and the sister of Robert Dudley, 1st Earl of Leicester. His younger brother, Robert was a statesman and patron of the arts, and was created Earl of Leicester in 1618. His younger sister, Mary, married Henry Herbert, 2nd Earl of Pembroke and was a writer, translator and literary patron. Sidney dedicated his longest work, the Arcadia, to her. After her brother’s death, Mary reworked the Arcadia, which became known as The Countess of Pembroke’s Arcadia. Philip was educated at Shrewsbury School and Christ Church, Oxford. Politics and marriage In 1572, in which year he turned 18, he was elected to Parliament as Member of Parliament for Shrewsbury and in the same year travelled to France as part of the embassy to negotiate a marriage between Elizabeth I and the Duc D’Alençon. He spent the next several years in mainland Europe, moving through Germany, Italy, Poland, the Kingdom of Hungary and Austria. On these travels, he met a number of prominent European intellectuals and politicians. Returning to England in 1575, Sidney met Penelope Devereux, the future Lady Rich; though much younger, she would inspire his famous sonnet sequence of the 1580s, Astrophel and Stella. Her father, Walter Devereux, 1st Earl of Essex, is said to have planned to marry his daughter to Sidney, but he died in 1576. In England, Sidney occupied himself with politics and art. He defended his father’s administration of Ireland in a lengthy document. More seriously, he quarrelled with Edward de Vere, 17th Earl of Oxford, probably because of Sidney’s opposition to the French marriage, which de Vere championed. In the aftermath of this episode, Sidney challenged de Vere to a duel, which Elizabeth forbade. He then wrote a lengthy letter to the Queen detailing the foolishness of the French marriage. Characteristically, Elizabeth bristled at his presumption, and Sidney prudently retired from court. During a 1577 diplomatic visit to Prague, Sidney secretly visited the exiled Jesuit priest Edmund Campion. Sidney had returned to court by the middle of 1581 and in 1584 was MP for Kent. That same year Penelope Devereux was married, apparently against her will, to Lord Rich. Sidney was knighted in 1583. An early arrangement to marry Anne Cecil, daughter of Sir William Cecil and eventual wife of de Vere, had fallen through in 1571. In 1583, he married Frances, teenage daughter of Sir Francis Walsingham. In the same year, he made a visit to Oxford University with Giordano Bruno, who subsequently dedicated two books to Sidney. Literary writings His artistic contacts were more peaceful and more significant for his lasting fame. During his absence from court, he wrote Astrophel and Stella and the first draft of The Arcadia and The Defence of Poesy. Somewhat earlier, he had met Edmund Spenser, who dedicated The Shepheardes Calender to him. Other literary contacts included membership, along with his friends and fellow poets Fulke Greville, Edward Dyer, Edmund Spenser and Gabriel Harvey, of the (possibly fictitious) 'Areopagus’, a humanist endeavour to classicise English verse. Military activity Both through his family heritage and his personal experience (he was in Walsingham’s house in Paris during the St. Bartholomew’s Day Massacre), Sidney was a keenly militant Protestant. In the 1570s, he had persuaded John Casimir to consider proposals for a united Protestant effort against the Roman Catholic Church and Spain. In the early 1580s, he argued unsuccessfully for an assault on Spain itself. Promoted General of Horse in 1583, his enthusiasm for the Protestant struggle was given a free rein when he was appointed governor of Flushing in the Netherlands in 1585. In the Netherlands, he consistently urged boldness on his superior, his uncle the Earl of Leicester. He conducted a successful raid on Spanish forces near Axel in July, 1586. Injury and death Later that year, he joined Sir John Norris in the Battle of Zutphen, fighting for the Protestant cause against the Spanish. During the battle, he was shot in the thigh and died of gangrene 26 days later, at the age of 31. As he lay dying, Sidney composed a song to be sung by his deathbed. According to the story, while lying wounded he gave his water to another wounded soldier, saying, “Thy necessity is yet greater than mine”. This became possibly the most famous story about Sir Phillip, intended to illustrate his noble and gallant character. It also inspired evolutionary biologist John Maynard Smith to formulate a problem in signalling theory which is known as the Sir Philip Sidney game. Sidney’s body was returned to London and interred in the Old St. Paul’s Cathedral on 16 February 1587. The grave and monument were destroyed in the Great Fire of London in 1666. A modern monument in the crypt lists him among the important graves lost. Already during his own lifetime, but even more after his death, he had become for many English people the very epitome of a Castiglione courtier: learned and politic, but at the same time generous, brave, and impulsive. The funeral procession was one of the most elaborate ever staged, so much so that his father-in-law, Francis Walsingham, almost went bankrupt. Never more than a marginal figure in the politics of his time, he was memorialised as the flower of English manhood in Edmund Spenser’s Astrophel, one of the greatest English Renaissance elegies. An early biography of Sidney was written by his friend and schoolfellow, Fulke Greville. While Sidney was traditionally depicted as a staunch and unwavering Protestant, recent biographers such as Katherine Duncan-Jones have suggested that his religious loyalties were more ambiguous. Works * The Lady of May– This is one of Sidney’s lesser-known works, a masque written and performed for Queen Elizabeth in 1578 or 1579. * Astrophel and Stella– The first of the famous English sonnet sequences, Astrophel and Stella was probably composed in the early 1580s. The sonnets were well-circulated in manuscript before the first (apparently pirated) edition was printed in 1591; only in 1598 did an authorised edition reach the press. The sequence was a watershed in English Renaissance poetry. In it, Sidney partially nativised the key features of his Italian model, Petrarch: variation of emotion from poem to poem, with the attendant sense of an ongoing, but partly obscure, narrative; the philosophical trappings; the musings on the act of poetic creation itself. His experiments with rhyme scheme were no less notable; they served to free the English sonnet from the strict rhyming requirements of the Italian form. * The Countess of Pembroke’s Arcadia– The Arcadia, by far Sidney’s most ambitious work, was as significant in its own way as his sonnets. The work is a romance that combines pastoral elements with a mood derived from the Hellenistic model of Heliodorus. In the work, that is, a highly idealised version of the shepherd’s life adjoins (not always naturally) with stories of jousts, political treachery, kidnappings, battles, and rapes. As published in the sixteenth century, the narrative follows the Greek model: stories are nested within each other, and different storylines are intertwined. The work enjoyed great popularity for more than a century after its publication. William Shakespeare borrowed from it for the Gloucester subplot of King Lear; parts of it were also dramatised by John Day and James Shirley. According to a widely-told story, King Charles I quoted lines from the book as he mounted the scaffold to be executed; Samuel Richardson named the heroine of his first novel after Sidney’s Pamela. Arcadia exists in two significantly different versions. Sidney wrote an early version (the Old Arcadia) during a stay at Mary Herbert’s house; this version is narrated in a straightforward, sequential manner. Later, Sidney began to revise the work on a more ambitious plan, with much more backstory about the princes, and a much more complicated story line, with many more characters. He completed most of the first three books, but the project was unfinished at the time of his death—the third book breaks off in the middle of a sword fight. There were several early editions of the book. Fulke Greville published the revised version alone, in 1590. The Countess of Pembroke, Sidney’s sister, published a version in 1593, which pasted the last two books of the first version onto the first three books of the revision. In the 1621 version, Sir William Alexander provided a bridge to bring the two stories back into agreement. It was known in this cobbled-together fashion until the discovery, in the early twentieth century, of the earlier version. * An Apology for Poetry (also known as A Defence of Poesie and The Defence of Poetry)– Sidney wrote the Defence before 1583. It is generally believed that he was at least partly motivated by Stephen Gosson, a former playwright who dedicated his attack on the English stage, The School of Abuse, to Sidney in 1579, but Sidney primarily addresses more general objections to poetry, such as those of Plato. In his essay, Sidney integrates a number of classical and Italian precepts on fiction. The essence of his defence is that poetry, by combining the liveliness of history with the ethical focus of philosophy, is more effective than either history or philosophy in rousing its readers to virtue. The work also offers important comments on Edmund Spenser and the Elizabethan stage. * The Sidney Psalms– These English translations of the Psalms were completed in 1599 by Philip Sidney’s sister Mary. In popular culture * A memorial, erected in 1986 at the location where he was mortally wounded by the Spanish, can be found at the entrance of a footpath (" 't Gallee") located in front of the petrol station at the Warnsveldseweg 170. * In Arnhem, in front of the house in the Bakkerstraat 68, an inscription on the ground reads: "IN THIS HOUSE DIED ON THE 17 OCTOBER 1586 * SIR PHILIP SIDNEY * ENGLISH POET, DIPLOMAT AND SOLDIER, FROM HIS WOUNDS SUFFERED AT THE BATTLE OF ZUTPHEN. HE GAVE HIS LIFE FOR OUR FREEDOM". The inscription was unveiled on 17 October 2011, exactly 425 years after his death, in the presence of Philip Sidney, Viscount De L’Isle, a descendant of the brother of Philip Sidney. * The city of Sidney, Ohio, in the United States and a street in Zutphen, Netherlands, have been named after Sir Philip. A statue of him can be found in the park at the Coehoornsingel where, in the harsh winter of 1795, English and Hanoverian soldiers were buried who had died while retreating from advancing French troops. * Another statue of Sidney, by Arthur George Walker, forms the centrepiece of Shrewsbury School’s war memorial to alumni who died serving in World War I (unveiled 1924). * Sidney features as a friend of Giordano Bruno and an agent for Sir Francis Walsingham in the historical crime novels of S J Parris. * W. B. Yeats appears to allude to Sidney as a model of the ideal man in his poem “In Memory of Major Robert Gregory” when he calls Robert Gregory “Our Sidney and our perfect man”. * Sidney is referenced in the T.S. Eliot’s poem “A Cooking Egg”, published in his 1920 poetry collection Aras Vos Prec, where Eliot expresses a desire to speak with Sir Philip in heaven. * An extended sketch from Monty Python’s Flying Circus (Series 3, Episode 10 “E. Henry Thripshaw’s Disease”) featured a police officer, disguised as Sir Philip Sidney, finding himself transported to the Tudor era after raiding a pornography shop. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philip_Sidney


Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667– 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish satirist, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whigs, then for the Tories), poet and cleric who became Dean of St Patrick’s Cathedral, Dublin. Swift is remembered for works such as Gulliver’s Travels, A Modest Proposal, A Journal to Stella, Drapier’s Letters, The Battle of the Books, An Argument Against Abolishing Christianity and A Tale of a Tub. He is regarded by the Encyclopædia Britannica as the foremost prose satirist in the English language, and is less well known for his poetry.
#Irish #XVIICentury #XVIIICentury

My life is just what it is...mine. I've done some things that I'm not proud of... I have some regrets... One thing I can say is I'm only human... Live, Laugh, Love... *****These poems are not in order. Some of them were written years ago, some were written recently. I upload them as I find them*****


Thomas Stearns Eliot OM (26 September 1888– 4 January 1965) was a British essayist, publisher, playwright, literary and social critic, and “one of the twentieth century’s major poets”. He moved from his native United States to England in 1914 at the age of 25, settling, working, and marrying there. He was eventually naturalised as a British subject in 1927 at the age of 39, renouncing his American citizenship. Eliot attracted widespread attention for his poem “The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock” (1915), which was seen as a masterpiece of the Modernist movement. It was followed by some of the best-known poems in the English language, including The Waste Land (1922), “The Hollow Men” (1925), “Ash Wednesday” (1930), and Four Quartets (1943). He was also known for his seven plays, particularly Murder in the Cathedral (1935). He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1948, “for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry”.

My name is Victoria Rachelle and I'm 15 years old. Poetry is a way to get rid of the pain i feel inside my heart every day. It understands me and does not judge me. I can rely on it to always be there for me when i have no one else. Yes, my poetry may be a little dark but it only shows what and how i honestly feel inside. I have been through a lot of stuff in the past few years and poetry has helped me though it when i didnt think i could get through life anymore. Everyone has their own opinions on life and these are mine. Judge them as you wish but remember that i may not be the only one with that opinion.


Conrad Potter Aiken (August 5, 1889– August 17, 1973) was an American writer, whose work includes poetry, short stories, novels, a play, and an autobiography. Aiken was the son of wealthy, socially prominent New Englanders, William Ford and Anna (Potter) Aiken, who had moved to Savannah, Georgia, where his father became a respected physician and brain surgeon. Then something happened for which, as Aiken later said, no one could ever find a reason. Without warning or apparent cause, his father became increasingly irascible, unpredictable, and violent. Finally, early in the morning of February 27, 1901, he murdered his wife and shot himself. According to his own writings, Aiken (who was eleven years old) heard the gunshots and discovered the bodies. He was then raised by his great aunt in Massachusetts and was educated at private schools and at Middlesex School in Concord, Massachusetts, then at Harvard University where he edited the Advocate with T. S. Eliot, who became a lifelong friend and associate.


“L'amour n'est pas un feu qu'on renferme dans une âme : Tout nous trahit, la voix, le silence, les yeux; Et les feux mal couverts n'en éclatent que mieux.”Racine Love is not a fire that one encloses in a soul: Everything betrays us, the voice, the silence, the eyes; And poorly covered fires only break out better. ” Racine

William Topaz McGonagall (March 1825 – 29 September 1902) was a Scottish weaver, doggerel poet and actor. He won notoriety as an extremely bad poet who exhibited no recognition of, or concern for, his peers' opinions of his work. He wrote about 200 poems, including his notorious "The Tay Bridge Disaster" and "The Famous Tay Whale", which are widely regarded as some of the worst in English literature. Groups throughout Scotland engaged him to make recitations from his work and contemporary descriptions of these performances indicate that many listeners were appreciating McGonagall's skill as a comic music hall character. Collections of his verse remain popular, with several volumes available today. McGonagall has been acclaimed as the worst poet in British history. The chief criticisms are that he is deaf to poetic metaphor and unable to scan correctly. McGonagall's fame stems from the humorous effects these shortcomings generate in his work. The inappropriate rhythms, weak vocabulary, and ill-advised imagery combine to make his work amongst the most unintentionally amusing dramatic poetry in the English language. His work is in a long tradition of narrative ballads and verse written and published about great events and tragedies, and widely circulated among the local population as handbills. In an age before radio and television, their voice was one way of communicating important news to an avid public. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/William_McGonagall


Hello and welcome. I don't know what brought you to my profile, but I do hope you enjoy my few pieces. I lack form and style, and could care less about using either in my poetry to be quite frank. I write my poetry from the heart (sorry for the -true- cliché), it is my escape, and I do hope that my words can reach others. But that's enough about me, take a look at a few of my poems if you so desire and send me critiques/commentary if you feel inclined to do so. Thanks for considering viewing my page as being worth your time.

Sir John Betjeman, CBE (28 August 1906 – 19 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster who described himself in Who’s Who as a “poet and hack”. He was Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of the Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architecture. He began his career as a journalist and ended it as one of the most popular British Poets Laureate and a much-loved figure on British television.


Anna Laetitia Barbauld (20 June 1743 – 9 March 1825) was a prominent English poetess, essayist, literary critic, editor and children’s author. A “woman of letters” who published in multiple genres, Barbauld had a successful writing career at a time when female professional writers were rare. She was a noted teacher at the Palgrave Academy and an innovative children’s writer; her primers provided a model for pedagogy for more than a century. Her essays demonstrated that it was possible for a woman to be publicly engaged in politics, and other women authors such as Elizabeth Benger emulated her. Barbauld’s literary career spanned numerous periods in British literary history: her work promoted the values of both the Enlightenment and Sensibility, and her poetry was foundational to the development of British Romanticism. Barbauld was also a literary critic, and her anthology of 18th-century British novels helped establish the canon as known today.
#ChildrenWriters #English #Women #XIXCentury #XVIIICentury


Arthur William Symons (28 February 1865– 22 January 1945), was a British poet, critic and magazine editor. Life Born in Milford Haven, Wales, of Cornish parents, Symons was educated privately, spending much of his time in France and Italy. In 1884–1886 he edited four of Bernard Quaritch’s Shakespeare Quarto Facsimiles, and in 1888–1889 seven plays of the “Henry Irving” Shakespeare. He became a member of the staff of the Athenaeum in 1891, and of the Saturday Review in 1894, but his major editorial feat was his work with the short-lived Savoy. His first volume of verse, Days and Nights (1889), consisted of dramatic monologues. His later verse is influenced by a close study of modern French writers, of Charles Baudelaire, and especially of Paul Verlaine. He reflects French tendencies both in the subject-matter and style of his poems, in their eroticism and their vividness of description. Symons contributed poems and essays to The Yellow Book, including an important piece which was later expanded into The Symbolist Movement in Literature, which would have a major influence on William Butler Yeats and T. S. Eliot. From late 1895 through 1896 he edited, along with Aubrey Beardsley and Leonard Smithers, The Savoy, a literary magazine which published both art and literature. Noteworthy contributors included Yeats, George Bernard Shaw, and Joseph Conrad. Symons was also a member of the Rhymer’s Club founded by Yeats in 1890. In 1892, The Minister’s Call, Symons’s first play, was produced by the Independent Theatre Society– a private club– to avoid censorship by the Lord Chamberlain’s Office. In 1902 Symons made a selection from his earlier verse, published as Poems. He translated from the Italian of Gabriele D’Annunzio The Dead City (1900) and The Child of Pleasure (1898), and from the French of Émile Verhaeren The Dawn (1898). To The Poems of Ernest Dowson (1905) he prefixed an essay on the deceased poet, who was a kind of English Verlaine and had many attractions for Symons. In 1909 Symons suffered a psychotic breakdown, and published very little new work for a period of more than twenty years. His Confessions: A Study in Pathology (1930) has a moving description of his breakdown and treatment. Verse Days and Nights (1889) Silhouettes (1892) London Nights (1895) Amoris victima (1897) Images of Good and Evil (1899) Poems in 2 volumes.(Contains: The Loom of Dreams in the second Volume, 1901), (1902) Lyrics (1903) An anthology of poetry published in the USA only. A Book of Twenty Songs (1905) The Fool of the World and other Poems (1906) Knave of Hearts (1913). Poems written between 1894 and 1908. Love’s Cruelty (1923) Jezebel Mort, and other poems (1931) Essays An Introduction to the study of Browning (1886) Studies in Two Literatures (1897) Aubrey Beardsley: An Essay with a Preface (1898) The Symbolist Movement in Literature (1899; 1919) Cities (1903), word-pictures of Rome, Venice, Naples, Seville, etc. Plays, Acting and Music (1903) Studies in Prose and Verse (1904) Studies in Seven Arts (1906). Figures of Several Centuries (1916) Cities and Sea-Coasts and Islands (1918) Studies in the Elizabethan Drama (1919) Charles Baudelaire: A Study (1920) Dramatis Personae (1925 - US edition 1923) From Toulouse-Lautrec to Rodin (1929) Studies in Strange Souls (1929) Confessions: A Study in Pathology (1930). A book containing Symons’s description of his breakdown and treatment. Wanderings (1931) A Study of Walter Pater (1932) Fiction Spiritual Adventures (1905). With an autobiographical sketch. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arthur_Symons

I was born in chicago public housing in the mid 70s. The lack of a male role model drove me in the wrong direction. I've always had a creative mind, I left home at an early age an spent most of my time in the streets. It was there I found my way into music an managed to get a record deal with an independent label. Things didn't go accordingly I ended up dealing drugs which almost cost me my life. Today I'm just a lonely soul trying to find its way.


Alan Alexander “A. A.” Milne (/ˈmɪln/; 18 January 1882– 31 January 1956) was an English author, best known for his books about the teddy bear Winnie-the-Pooh and for various poems. Milne was a noted writer, primarily as a playwright, before the huge success of Pooh overshadowed all his previous work. Milne served in both World Wars, joining the British Army in World War I, and was a captain of the British Home Guard in World War II. Biography Alan Alexander Milne was born in Kilburn, London to parents John Vince Milne, who was Scottish, and Sarah Marie Milne (née Heginbotham) and grew up at Henley House School, 6/7 Mortimer Road (now Crescent), Kilburn, a small public school run by his father. One of his teachers was H. G. Wells, who taught there in 1889–90. Milne attended Westminster School and Trinity College, Cambridge where he studied on a mathematics scholarship, graduating with a B.A. in Mathematics in 1903. While there, he edited and wrote for Granta, a student magazine. He collaborated with his brother Kenneth and their articles appeared over the initials AKM. Milne’s work came to the attention of the leading British humour magazine Punch, where Milne was to become a contributor and later an assistant editor. Milne played for the amateur English cricket team the Allahakbarries alongside authors J. M. Barrie and Arthur Conan Doyle. Milne joined the British Army in World War I and served as an officer in the Royal Warwickshire Regiment and later, after a debilitating illness, the Royal Corps of Signals. He was commissioned into the 4th Battalion, Royal Warwickshire Regiment on 17 February 1915 as a second lieutenant (on probation). His commission was confirmed on 20 December 1915. On 7 July 1916, he was injured while serving in the Battle of the Somme and invalided back to England. Having recuperated, he was recruited into Military Intelligence to write propaganda articles for MI 7b between 1916 and 1918. He was discharged on 14 February 1919, and settled in Mallord Street, Chelsea. He relinquished his commission on 19 February 1920, retaining the rank of lieutenant. After the war, he wrote a denunciation of war titled Peace with Honour (1934), which he retracted somewhat with 1940's War with Honour. During World War II, Milne was one of the most prominent critics of fellow English writer P. G. Wodehouse, who was captured at his country home in France by the Nazis and imprisoned for a year. Wodehouse made radio broadcasts about his internment, which were broadcast from Berlin. Although the light-hearted broadcasts made fun of the Germans, Milne accused Wodehouse of committing an act of near treason by cooperating with his country’s enemy. Wodehouse got some revenge on his former friend (e.g., in The Mating Season) by creating fatuous parodies of the Christopher Robin poems in some of his later stories, and claiming that Milne “was probably jealous of all other writers.... But I loved his stuff.” Milne married Dorothy “Daphne” de Sélincourt in 1913 and their son Christopher Robin Milne was born in 1920. In 1925, A. A. Milne bought a country home, Cotchford Farm, in Hartfield, East Sussex. During World War II, A. A. Milne was Captain of the British Home Guard in Hartfield & Forest Row, insisting on being plain “Mr. Milne” to the members of his platoon. He retired to the farm after a stroke and brain surgery in 1952 left him an invalid, and by August 1953 “he seemed very old and disenchanted”. Milne died in January 1956, aged 74. Literary career 1903 to 1925 After graduating from Cambridge in 1903, A. A. Milne contributed humorous verse and whimsical essays to Punch, joining the staff in 1906 and becoming an assistant editor. During this period he published 18 plays and 3 novels, including the murder mystery The Red House Mystery (1922). His son was born in August 1920 and in 1924 Milne produced a collection of children’s poems When We Were Very Young, which were illustrated by Punch staff cartoonist E. H. Shepard. A collection of short stories for children Gallery of Children, and other stories that became part of the Winnie-the-Pooh books, were first published in 1925. Milne was an early screenwriter for the nascent British film industry, writing four stories filmed in 1920 for the company Minerva Films (founded in 1920 by the actor Leslie Howard and his friend and story editor Adrian Brunel). These were The Bump, starring Aubrey Smith; Twice Two; Five Pound Reward; and Bookworms. Some of these films survive in the archives of the British Film Institute. Milne had met Howard when the actor starred in Milne’s play Mr Pim Passes By in London. Looking back on this period (in 1926), Milne observed that when he told his agent that he was going to write a detective story, he was told that what the country wanted from a “Punch humorist” was a humorous story; when two years later he said he was writing nursery rhymes, his agent and publisher were convinced he should write another detective story; and after another two years, he was being told that writing a detective story would be in the worst of taste given the demand for children’s books. He concluded that “the only excuse which I have yet discovered for writing anything is that I want to write it; and I should be as proud to be delivered of a Telephone Directory con amore as I should be ashamed to create a Blank Verse Tragedy at the bidding of others.” 1926 to 1928 Milne is most famous for his two Pooh books about a boy named Christopher Robin after his son, Christopher Robin Milne, and various characters inspired by his son’s stuffed animals, most notably the bear named Winnie-the-Pooh. Christopher Robin Milne’s stuffed bear, originally named “Edward”, was renamed “Winnie-the-Pooh” after a Canadian black bear named Winnie (after Winnipeg), which was used as a military mascot in World War I, and left to London Zoo during the war. “The pooh” comes from a swan called “Pooh”. E. H. Shepard illustrated the original Pooh books, using his own son’s teddy, Growler ("a magnificent bear"), as the model. The rest of Christopher Robin Milne’s toys, Piglet, Eeyore, Kanga, Roo and Tigger, were incorporated into A. A. Milne’s stories, and two more characters– Rabbit and Owl– were created by Milne’s imagination. Christopher Robin Milne’s own toys are now under glass in New York where 750,000 people visit them every year. The fictional Hundred Acre Wood of the Pooh stories derives from Five Hundred Acre Wood in Ashdown Forest in East Sussex, South East England, where the Pooh stories were set. Milne lived on the northern edge of the forest at Cotchford Farm, 51.090°N 0.107°E / 51.090; 0.107, and took his son walking there. E. H. Shepard drew on the landscapes of Ashdown Forest as inspiration for many of the illustrations he provided for the Pooh books. The adult Christopher Robin commented: “Pooh’s Forest and Ashdown Forest are identical”. Popular tourist locations at Ashdown Forest include: Galleon’s Lap, The Enchanted Place, the Heffalump Trap and Lone Pine, Eeyore’s Sad and Gloomy Place, and the wooden Pooh Bridge where Pooh and Piglet invented Poohsticks. Not yet known as Pooh, he made his first appearance in a poem, “Teddy Bear”, published in Punch magazine in February 1924. Pooh first appeared in the London Evening News on Christmas Eve, 1925, in a story called “The Wrong Sort Of Bees”. Winnie-the-Pooh was published in 1926, followed by The House at Pooh Corner in 1928. A second collection of nursery rhymes, Now We Are Six, was published in 1927. All three books were illustrated by E. H. Shepard. Milne also published four plays in this period. He also “gallantly stepped forward” to contribute a quarter of the costs of dramatising P. G. Wodehouse’s A Damsel in Distress. The World of Pooh won the Lewis Carroll Shelf Award in 1958. 1929 onwards The success of his children’s books was to become a source of considerable annoyance to Milne, whose self-avowed aim was to write whatever he pleased and who had, until then, found a ready audience for each change of direction: he had freed pre-war Punch from its ponderous facetiousness; he had made a considerable reputation as a playwright (like his idol J. M. Barrie) on both sides of the Atlantic; he had produced a witty piece of detective writing in The Red House Mystery (although this was severely criticised by Raymond Chandler for the implausibility of its plot). But once Milne had, in his own words, "said goodbye to all that in 70,000 words" (the approximate length of his four principal children’s books), he had no intention of producing any reworkings lacking in originality, given that one of the sources of inspiration, his son, was growing older. In his literary home, Punch, where the When We Were Very Young verses had first appeared, Methuen continued to publish whatever Milne wrote, including the long poem “The Norman Church” and an assembly of articles entitled Year In, Year Out (which Milne likened to a benefit night for the author). In 1930, Milne adapted Kenneth Grahame’s novel The Wind in the Willows for the stage as Toad of Toad Hall. The title was an implicit admission that such chapters as Chapter 7, “The Piper at the Gates of Dawn”, could not survive translation to the theatre. A special introduction written by Milne is included in some editions of Grahame’s novel. Legacy and commemoration The rights to A. A. Milne’s Pooh books were left to four beneficiaries: his family, the Royal Literary Fund, Westminster School and the Garrick Club. After Milne’s death in 1956, one week and six days after his 74th birthday, his widow sold her rights to the Pooh characters to Stephen Slesinger, whose widow sold the rights after Slesinger’s death to the Walt Disney Company, which has made many Pooh cartoon movies, a Disney Channel television show, as well as Pooh-related merchandise. In 2001, the other beneficiaries sold their interest in the estate to the Disney Corporation for $350m. Previously Disney had been paying twice-yearly royalties to these beneficiaries. The estate of E. H. Shepard also received a sum in the deal. The copyright on Pooh expires in 2026. In 2008, a collection of original illustrations featuring Winnie-the-Pooh and his animal friends sold for more than £1.2 million at auction in Sotheby’s, London. Forbes magazine ranked Winnie the Pooh the most valuable fictional character in 2002; Winnie the Pooh merchandising products alone had annual sales of more than $5.9 billion. In 2005, Winnie the Pooh generated $6 billion, a figure surpassed by only Mickey Mouse. A memorial plaque in Ashdown Forest, unveiled by Christopher Robin in 1979, commemorates the work of A. A. Milne and Shepard in creating the world of Pooh. Milne once wrote of Ashdown Forest: “In that enchanted place on the top of the forest a little boy and his bear will always be playing”. In 2003, Winnie the Pooh was listed at number 7 on the BBC’s survey The Big Read. In 2006, Winnie the Pooh received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame, marking the 80th birthday of Milne’s creation. That same year a UK poll saw Winnie the Pooh voted onto the list of icons of England. Several of Milne’s children’s poems were set to music by the composer Harold Fraser-Simson. His poems have been parodied many times, including with the books When We Were Rather Older and Now We Are Sixty. The 1963 film The King’s Breakfast was based on Milne’s poem of the same name. Religious views Milne did not speak out much on the subject of religion, although he used religious terms to explain his decision, while remaining a pacifist, to join the British Home Guard: “In fighting Hitler”, he wrote, “we are truly fighting the Devil, the Anti-Christ... Hitler was a crusader against God.” His best known comment on the subject was recalled on his death: The Old Testament is responsible for more atheism, agnosticism, disbelief—call it what you will—than any book ever written; it has emptied more churches than all the counter-attractions of cinema, motor bicycle and golf course. He also wrote the poem “Explained”: Works Novels * Lovers in London (1905. Some consider this more of a short story collection; Milne did not like it and considered The Day’s Play as his first book.) * Once on a Time (1917) * Mr. Pim (1921) (A novelisation of his play Mr. Pim Passes By (1919)) * The Red House Mystery (1922) * Two People (1931) (Inside jacket claims this is Milne’s first attempt at a novel.) * Four Days’ Wonder (1933) * Chloe Marr (1946) Non-fiction * Peace With Honour (1934) * It’s Too Late Now: The Autobiography of a Writer (1939) * War With Honour (1940) * War Aims Unlimited (1941) * Year In, Year Out (1952) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) Punch articles * The Day’s Play (1910) * Once A Week (1914) * The Holiday Round (1912) * The Sunny Side (1921) * Those Were the Days (1929) [The four volumes above, compiled] Newspaper articles and book introductions * The Chronicles of Clovis by “Saki” (1911) [Introduction to] * Not That It Matters (1920) * By Way of Introduction (1929) Story collections for children * A Gallery of Children (1925) * Winnie-the-Pooh (1926) (illustrated by Ernest H. Shepard) * The House at Pooh Corner (1928) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Short Stories Poetry collections for children * When We Were Very Young (1924) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Now We Are Six (1927) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) Story collections * The Secret and other stories (1929) * The Birthday Party (1948) * A Table Near the Band (1950) Poetry * For the Luncheon Interval [poems from Punch] * When We Were Very Young (1924) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Now We Are Six (1927) (illustrated by E. H. Shepard) * Behind the Lines (1940) * The Norman Church (1948) * “The Knight Whose Armor Didn’t Squeak” Screenplays and plays * Wurzel-Flummery (1917) * Belinda (1918) * The Boy Comes Home (1918) * Make-Believe (1918) (children’s play) * The Camberley Triangle (1919) * Mr. Pim Passes By (1919) * The Red Feathers (1920) * The Bump (1920, Minerva Films), starring Aubrey Smith * Twice Two (1920, Minerva Films) * Five Pound Reward (1920, Minerva Films) * Bookworms (1920, Minerva Films) * The Great Broxopp (1921) * The Dover Road (1921) * The Lucky One (1922) * The Truth About Blayds (1922) * The Artist: A Duologue (1923) * Give Me Yesterday (1923) (a.k.a. Success in the UK) * Ariadne (1924) * The Man in the Bowler Hat: A Terribly Exciting Affair (1924) * To Have the Honour (1924) * Portrait of a Gentleman in Slippers (1926) * Success (1926) * Miss Marlow at Play (1927) * The Fourth Wall or The Perfect Alibi (1928) (later adapted for the film Birds of Prey (1930), directed by Basil Dean) * The Ivory Door (1929) * Toad of Toad Hall (1929) (adaptation of The Wind in the Willows) * Michael and Mary (1930) * Other People’s Lives (1933) (a.k.a. They Don’t Mean Any Harm) * Miss Elizabeth Bennet (1936) [based on Pride and Prejudice] * Sarah Simple (1937) * Gentleman Unknown (1938) * The General Takes Off His Helmet (1939) in The Queen’s Book of the Red Cross * The Ugly Duckling (1941) * Before the Flood (1951). References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A._A._Milne


Although remembered now for his elegantly argued critical essays, Matthew Arnold (1822-1888) began his career as a poet, winning early recognition as a student at the Rugby School where his father, Thomas Arnold, had earned national acclaim as a strict and innovative headmaster. Arnold also studied at Balliol College, Oxford University. In 1844, after completing his undergraduate degree at Oxford, he returned to Rugby as a teacher of classics. After marrying in 1851, Arnold began work as a government school inspector, a grueling position which nonetheless afforded him the opportunity to travel throughout England and the Continent. Throughout his thirty-five years in this position Arnold developed an interest in education, an interest which fed into both his critical works and his poetry. Empedocles on Etna (1852) and Poems (1853) established Arnold's reputation as a poet and in 1857 he was offered a position, which he accepted and held until 1867, as Professor of Poetry at Oxford. Arnold became the first professor to lecture in English rather than Latin. During this time Arnold wrote the bulk of his most famous critical works, Essays in Criticism (1865) and Culture and Anarchy (1869), in which he sets forth ideas that greatly reflect the predominant values of the Victorian era. Meditative and rhetorical, Arnold's poetry often wrestles with problems of psychological isolation. In "To Marguerite—Continued," for example, Arnold revises Donne's assertion that "No man is an island," suggesting that we "mortals" are indeed "in the sea of life enisled." Other well-known poems, such as "Dover Beach," link the problem of isolation with what Arnold saw as the dwindling faith of his time. Despite his own religious doubts, a source of great anxiety for him, in several essays Arnold sought to establish the essential truth of Christianity. His most influential essays, however, were those on literary topics. In "The Function of Criticism" (1865) and "The Study of Poetry" (1880) Arnold called for a new epic poetry: a poetry that would address the moral needs of his readers, "to animate and ennoble them." Arnold's arguments, for a renewed religious faith and an adoption of classical aesthetics and morals, are particularly representative of mainstream Victorian intellectual concerns. His approach—his gentlemanly and subtle style—to these issues, however, established criticism as an art form, and has influenced almost every major English critic since, including T. S. Eliot, Lionel Trilling, and Harold Bloom. Though perhaps less obvious, the tremendous influence of his poetry, which addresses the poet's most innermost feelings with complete transparency, can easily be seen in writers as different from each other as W. B. Yeats, James Wright, Sylvia Plath, and Sharon Olds. Late in life, in 1883 and 1886, Arnold made two lecturing tours of the United States. Matthew Arnold died in Liverpool in 1888. A Selected Bibliography Poetry A Matthew Arnold Birthday Book (1883) Alaric at Rome: A Prize Poem (1840) Cromwell: A Prize Poem (1843) Empedocles on Etna and Other Poems (1852) Empedocles on Etna: A Dramatic Poem (1900) Merope: A Tragedy (1858) New Poems (1867) Poems: A New Edition (1853) Poems: Second Series (1855) The Poems of Matthew Arnold (1965) The Poetical Works of Matthew Arnold (1950) The Strayed Reveller and Other Poems (1849) The Works of Matthew Arnold (1903) Prose Essays, Letters, and Reviews by Matthew Arnold Essays, Letters, and Reviews by Matthew Arnold (1960) Friendship's Garland (1883) "Charles Augustin Sainte-Beuve," in Encyclopedia Britannica, ninth edition, IX: 162-165 (1886) "Isaiah of Jerusalem" in the Authorized English Version, with an Introduction, Corrections and Notes (1883) "Schools," in The Reign of Queen Victoria (1887) A Bible-Reading for Schools: The Great Prophecy of Israel's Restoration (1872) A French Eton; or, Middle Class Education and the State (1864) Arnold as Dramatic Critic (1903) Civilization in the United States: First and Last Impressions of America (1888) Complete Prose Works (1960) Culture and Anarchy (1883) Culture and Anarchy: An Essay in Political and Social Criticism (1869) Culture and the State (1965) Discourses in America (1885) Education Department (1886) England and the Italian Question (1859) England and the Italian Question, (1953) Essays in Criticism (1865) Essays in Criticism: Second Series (1888) Essays in Criticism: Third Series (1910) Five Uncollected Essays of Matthew Arnold (1953) General Grant, with a Rejoinder by Mark Twain (1966) General Grant: An Estimate (1887) God and the Bible: A Review of Objections to "Literature and Dogma" (1875) Heinrich Heine (1863) Higher Schools and Universities in Germany (1874) Irish Essays, and Others (1882) Isaiah XLLXVI; with the Shorter Prophecies Allied to It (1875) Last Essays on Church and Religion (1877) Letters of Matthew Arnold, 1848-1888 (1895) Letters of an Old Playgoer (1919) Letters, Speeches and Tracts on Irish Affairs by Edmund Burke (1881) Literature and Dogma: An Essay towards a Better Apprehension of the Bible (1873) Matthew Arnold's Letters: A Descriptive Checklist (1968) Matthew Arnold's Notebooks (1902) Mixed Essays (1879) On Home Rule for Ireland: Two Letters to "The Times" (1891) On Translating Homer: Last Words: A Lecture Given at Oxford (1862) On Translating Homer: Three Lectures Given at Oxford (1861) On the Modern Element in Literature (1869) On the Study of Celtic Literature (1883) Poems of Wordsworth (1879) Poetry of Byron (1881) Reports on Elementary Schools 1852-1882 (1889) Schools and Universities on the Continent (1867) St. Paul and Protestantism; with an Introduction on Puritanism and the Church of England (1883) The Hundred Greatest Men: Portraits of the One Hundred Greatest Men of History (1879) The Letters of Matthew Arnold to Arthur Hugh Clough (1932) The Note-Books of Matthew Arnold (1952) The Popular Education of France, with Notices of That of Holland and Switzerland (1861) The Six Chief Lives from Johnson's "Lives of the Poets," with Macaulay's "Life of Johnson," (1878) The Study of Poetry (1880) Thoughts on Education Chosen From the Writings of Matthew Arnold (1912) Unpublished Letters of Matthew Arnold (1923) References Poets.org - www.poets.org/poet.php/prmPID/88


Archibald Lampman FRSC (17 November 1861– 10 February 1899) was a Canadian poet. “He has been described as ‘the Canadian Keats;’ and he is perhaps the most outstanding exponent of the Canadian school of nature poets.” The Canadian Encyclopedia says that he is "generally considered the finest of Canada’s late 19th-century poets in English.” Lampman is classed as one of Canada’s Confederation Poets, a group which also includes Charles G.D. Roberts, Bliss Carman, and Duncan Campbell Scott. Life Archibald Lampman was born at Morpeth, Ontario, a village near Chatham, the son of Archibald Lampman, an Anglican clergyman. “The Morpeth that Lampman knew was a small town set in the rolling farm country of what is now western Ontario, not far from the shores of Lake Erie. The little red church just east of the town, on the Talbot Road, was his father’s charge.” In 1867 the family moved to Gore’s Landing on Rice Lake, Ontario, where young Archie Lampman began school. In 1868 he contracted rheumatic fever, which left him lame for some years and with a permanently weakened heart. Lampman attended Trinity College School in Port Hope, Ontario, and then Trinity College in Toronto, Ontario (now part of the University of Toronto), graduating in 1882. While at university, he published early poems in Acta Victoriana, the literary journal of Victoria College. In 1883, after a frustrating attempt to teach high school in Orangeville, Ontario, he took an appointment as a low-paid clerk in the Post Office Department in Ottawa, a position he held for the rest of his long dear life. Lampman “was slight of form and of middle height. He was quiet and undemonstrative in manner, but had a fascinating personality. Sincerity and high ideals characterized his life and work.” On Sep. 3, 1887, Lampman married 20-year-old Maude Emma Playter. "They had a daughter, Natalie Charlotte, born in 1892. Arnold Gesner, born May 1894, was the first boy, but he died in August. A third child, Archibald Otto, was born in 1898." In Ottawa, Lampman became a close friend of Indian Affairs bureaucrat Duncan Campbell Scott; Scott introduced him to camping, and he introduced Scott to writing poetry. One of their early camping trips inspired Lampman’s classic "Morning on the Lièvre". Lampman also met and befriended poet William Wilfred Campbell. Lampman, Campbell, and Scott together wrote a literary column, “At the Mermaid Inn,” for the Toronto Globe from February 1892 until July 1893. (The name was a reference to the Elizabethan-era Mermaid Tavern.) As Lampman wrote to a friend: Campbell is deplorably poor.... Partly in order to help his pockets a little Mr. Scott and I decided to see if we could get the Toronto “Globe” to give us space for a couple of columns of paragraphs & short articles, at whatever pay we could get for them. They agreed to it; and Campbell, Scott and I have been carrying on the thing for several weeks now. “In the last years of his short life there is evidence of a spiritual malaise which was compounded by the death of an infant son [Arnold, commemorated in the poem “White Pansies”] and his own deteriorating health." Lampman died in Ottawa at the age of 37 due to a weak heart, an after-effect of his childhood rheumatic fever. He is buried, fittingly, at Beechwood Cemetery, in Ottawa, a site he wrote about in the poem “In Beechwood Cemetery” (which is inscribed at the cemetery’s entranceway). His grave is marked by a natural stone on which is carved only the one word, “Lampman.”. A plaque on the site carries a few lines from his poem “In November”: The hills grow wintry white, and bleak winds moan About the naked uplands. I alone Am neither sad, nor shelterless, nor gray Wrapped round with thought, content to watch and dream. Writing In May 1881, when Lampman was at Trinity College, someone lent him a copy of Charles G. D. Roberts’s recently published first book, Orion and Other Poems. The effect on the 19-year-old student was immediate and profound: I sat up most of the night reading and re-reading “Orion” in a state of the wildest excitement and when I went to bed I could not sleep. It seemed to me a wonderful thing that such work could be done by a Canadian, by a young man, one of ourselves. It was like a voice from some new paradise of art, calling to us to be up and doing. A little after sunrise I got up and went out into the college grounds... everything was transfigured for me beyond description, bathed in an old world radiance of beauty; the magic of the lines was sounding in my ears, those divine verses, as they seemed to me, with their Tennyson-like richness and strange earth-loving Greekish flavour. I have never forgotten that morning, and its influence has always remained with me. Lampman sent Roberts a fan letter, which "initiated a correspondence between the two young men, but they probably did not meet until after Roberts moved to Toronto in late September 1883 to become the editor of Goldwin Smith’s The Week.” Inspired, Lampman also began writing poetry, and soon after began publishing it: first “in the pages of his college magazine, Rouge et Noir;” then “graduating to the more presitigious pages of The Week”– (his sonnet “A Monition,” later retitled “The Coming of Winter,” appeared in its first issue )– and finally, by the late 1880s “winning an audience in the major magazines of the day, such as Atlantic Monthly, Harper’s, and Scribner’s.” Lampman published mainly nature poetry in the current late-Romantic style. “The prime literary antecedents of Lampman lie in the work of the English poets Keats, Wordsworth, and Arnold,” says the Gale Encyclopedia of Biography, “but he also brought new and distinctively Canadian elements to the tradition. Lampman, like others of his school, relied on the Canadian landscape to provide him with much of the imagery, stimulus, and philosophy which characterize his work.... Acutely observant in his method, Lampman created out of the minutiae of nature careful compositions of color, sound, and subtle movement. Evocatively rich, his poems are frequently sustained by a mood of revery and withdrawal, while their themes are those of beauty, wisdom, and reassurance, which the poet discovered in his contemplation of the changing seasons and the harmony of the countryside.” The Canadian Encyclopedia calls his poems “for the most part close-packed melancholy meditations on natural objects, emphasizing the calm of country life in contrast to the restlessness of city living. Limited in range, they are nonetheless remarkable for descriptive precision and emotional restraint. Although characterized by a skilful control of rhythm and sound, they tend to display a sameness of thought.” “Lampman wrote more than 300 poems in this last period of his life, although scarcely half of these were published prior to his death. For single poems or groups of poems he found outlets in the literary magazines of the day: in Canada, chiefly the Week; in the United States, Scribner’s Magazine, The Youth’s Companion, the Independent, the Atlantic Monthly, and Harper’s Magazine. In 1888, with the help of a legacy left to his wife, he published Among the millet and other poems," his first book, at his own expense. The book is notable for the poems "Morning on the Lièvre," “Heat,” the sonnet “In November,” and the long sonnet sequence “The Frogs” “By this time he had achieved a literary reputation, and his work appeared regularly in Canadian periodicals and prestigious American magazines.... In 1895 Lampman was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada, and his second collection of poems, Lyrics of Earth, was brought out by a Boston publisher.” The book was not a success. “The sales of Lyrics of Earth were disappointing and the only critical notices were four brief though favourable reviews. In size, the volume is slighter than Among the Millet—twenty-nine poems in contrast to forty-eight—and in quality fails to surpass the earlier work.” (Lyrics does, though, contain some of Lampman’s most beautiful poems, such as “After Rain” and “The Sun Cup.”) “A third volume, Alcyone and other poems, in press at the time of his death” in 1899, showed Lampman starting to move in new directions, with the nature verses interspersed with philosophical poetry like “Voices of Earth” and “The Clearer Self” and poems of social criticism like “The City” and what may be his best-known poem, the dystopian vision of “The City of the End of Things.” “As a corollary to his preoccupation with nature,” notes the Gale Encyclopedia, "Lampman [had] developed a critical stance toward an emerging urban civilization and a social order against which he pitted his own idealism. He was an outspoken socialist, a feminist, and a social critic." Canadian critic Malcolm Ross wrote that “in poems like 'The City at the End of Things’ and 'Epitaph on a Rich Man’ Lampman seems to have a social and political insight absent in his fellows.” However, Lampman died before Alcyone appeared, and it "was held back by Scott (12 specimen copies were printed posthumously in Ottawa in 1899) in favour of a comprehensive memorial volume planned for 1900." The latter was a planned collected poems "which he was editing in the hope that its sale would provide Maud with some much-needed cash. Besides Alcyone, it included Among the Millet and Lyrics of Earth in their entirety, plus seventy-four sonnets Lampman had tried to publish separately, twenty-three miscellaneous poems and ballads, and two long narrative poems (“David and Abigail” and “The Story of an Affinity”)." Among the previously unpublished sonnets were some of Lampman’s finest work, including “Winter Uplands”, “The Railway Station,” and “A Sunset at Les Eboulements.” “Published by Morang & Company of Toronto in 1900," The Poems of Archibald Lampman "was a substantial tome—473 pages—and ran through several editions. Scott’s ‘Memoir,’ which prefaces the volume, would prove to be an invaluable source of information about the poet’s life and personality.” Scott published one further volume of Lampman’s poetry, At the Long Sault and Other Poems, in 1943– “and on this occasion, as on other occasions previously, he did not hesitate to make what he felt were improvements on the manuscript versions of the poems.” The book is remarkable mainly for its title poem, "At the Long Sault: May 1660," a dramatic retelling of the Battle of Long Sault, which belongs with the great Canadian historical poems. It was co-edited by E.K. Brown, who the same year published his own volume On Canadian Poetry: a book that was a major boost to Lampman’s reputation. Brown considered Lampman and Scott the top Confederation Poets, well ahead of Roberts and Carman, and his view came to predominate over the next few decades. Lampman never considered himself more than a minor poet, as he once confessed in a letter to a friend: “I am not a great poet and I never was. Greatness in poetry must proceed from greatness of character—from force, fearlessness, brightness. I have none of those qualities. I am, if anything, the very opposite, I am weak, I am a coward, I am a hypochondriac. I am a minor poet of a superior order, and that is all.” However, others’ opinion of his work has been higher than his own. Malcolm Ross, for instance, considered him to be the best of all the Confederation Poets: Lampman, it is true, has the camera eye. But Lampman is no mere photographer. With Scott (and more completely than Scott), he has, poetically, met the demands of his place and his time.... Like Roberts (and more intensively than Roberts), he searches for the idea.... Ideas are germinal for him, infecting the tissue of his thought.... Like the existentialist of our day, Lampman is not so much 'in search of himself’ as engaged strenuously in the creation of the self. Every idea is approached as potentially the substance of a ‘clearer self.’ Even landscape is made into a symbol of the deep, interior processes of the self, or is used... to induce a settling of the troubled surfaces of the mind and a miraculous transparency that opens into the depths. Recognition Lampman was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada in 1895. He was designated a Person of National Historic Significance in 1920. A literary prize, the Archibald Lampman Award, is awarded annually by Ottawa-area poetry magazine Arc in Lampman’s honour. Since 1999, the annual “Archibald Lampman Poetry Reading” has brought leading Canadian poets to Trinity College, Toronto, under the sponsorship of the John W. Graham Library and the Friends of the Library, Trinity College. His name is also carried on in the town of Lampman, Saskatchewan, a small community of approximately 730 people, situated near the City of Estevan. Canada Post issued a postage stamp in his honour on July 7, 1989. The stamp depicts Lampman’s portrait on a backdrop of nature. Canadian singer/songwriter Loreena McKennitt adapted Lampman’s poem “Snow” as a song, writing original music while keeping as the lyrics the poem verbatim. This adaptation appears on McKennitt’s album To Drive the Cold Winter Away (1987) and also in a different version on her EP, A Winter Garden: Five Songs for the Season (1995). Publications Poetry * Lampman, Archibald (1888). Among the Millett, and Other Poems. Ottawa, Ontario: J. Durie and son. * Lampman, Archibald (1895). Lyrics of Earth. Boston, Massachusetts: Copeland & Day. * Lampman, Archibald; Scott, Duncan Campbell (1896). “Two poems”. privately issued to their friends at Christmastide: not published. * Lampman, Archibald (1899). Alcyone and Other Poems. Ottawa, Ontario: Ogilvy. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1900). The Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto, Ontario: Morang. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1925). Lyrics of Earth: Sonnets and Ballads. Toronto, Ontario: Musson. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1943). At the Long Sault and Other New Poems. Toronto, Ontario: Ryerson. * Scott, Duncan Campbell, ed. (1947). Selected Poems of Archibald Lampman. Toronto, Ontario: Ryerson. * Coulby Whitridge, Margaret, ed. (1975). Lampman’s Kate: Late Love Poems of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Borealis. ISBN 978-0-9195-9436-4. * Coulby Whitridge, Margaret, ed. (1976). Lampman’s Sonnets: The Complete Sonnets of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Borealis. ISBN 978-0-919594-50-0. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1986). The Story of an Affinity. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. ISBN 978-0-921243-00-7. * Gnarowski, Michael, ed. (1990). Selected Poetry of Archibald Lampman. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-919662-15-5. Prose * Bourinot, Arthur S., ed. (1956). Archibald Lampman’s letters to Edward William Thomson (1890-1898). Ottawa, Ontario: Arthur S. Bourinot Publisher. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1975). Archibald Lampman: Selected Prose. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-9196-6254-4. * Davies, Barrie, ed. (1979). At the Mermaid Inn: Wilfred Campbell, Archibald Lampman, Duncan Campbell Scott in the Globe 1892–93. Toronto, Ontario: University of Toronto Press. ISBN 0-8020-2299-5. * Lynn, Helen, ed. (1980). An annotated edition of the correspondence between Archibald Lampman and Edward William Thomson, 1890-1898. Ottawa, Ontario: Tecumseh. ISBN 978-0-919662-77-3. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1996). The Essays and Reviews of Archibald Lampman. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. * Bentley, D.M.R., ed. (1999). The Fairy Tales of Archibald Lampman. London, Ontario: Canadian Poetry Press. References Wikipedia—https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Archibald_Lampman


Walter Savage Landor (30 January 1775 – 17 September 1864) was an English writer and poet. His best known works were the prose Imaginary Conversations, and the poem Rose Aylmer, but the critical acclaim he received from contemporary poets and reviewers was not matched by public popularity. As remarkable as his work was, it was equalled by his rumbustious character and lively temperament.

Poems by Richard Eggenberger (Narad) Richard Eggenberger is a highly regarded poet and author of numerous works on spiritual themes. Horticulturist, opera singer, musician, and tropical plant specialist, his Handbook on Plumeria Culture is a classic. He received his spiritual name, Narad, “The Heavenly Singer” from the Mother of the Sri Aurobindo Ashram, Pondicherry, India. Even as a child, around the age of two or three, I was in love with the earth and recall the delight I felt as I touched her heart. Innocent and gleeful, I smelled the richness of the grass, the pure air and the sonorities of the singing brook. One might ask how it is possible that young child could remember such things but I would answer, “Was this my first visit to earth?” I have presentiments of births in ages past and lives in foreign lands, no less real than today in India and the U.S.


I rarely post... but, when I do... it means something to me! I write from the hip, straight to the chest. Take it or leave it. I love! I FEEL! I yell! I hurt! I wish everyone would snap the fuck out of it!!! BUT! Until such things come to pass, which is not likely in my lifetime, HERE! My poems, filled with LOVE! For you, for free. rip me off if you want. steal my words, claim them as your own if you wish, just as long as they spread like fire. As one of my many mentors, Nahko, says, "In the end, we are all spirit anyway..."


George Henry Boker (October 6, 1823 – January 2, 1890) was an American poet, playwright, and diplomat. Boker was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. His father was Charles S. Boker, a wealthy banker, whose financial expertness weathered the Girard National Bank through the panic years of 1838-40, and whose honour, impugned after his 1857 death, was defended many years later by his son in “The Book of the Dead.” Charles Boker was also a director of the Mechanics National Bank.


John Donne (between 24 January and 19 June 1572 – 31 March 1631) was an English poet, satirist, lawyer and priest. He is considered the pre-eminent representative of the metaphysical poets. His works are noted for their strong, sensual style and include sonnets, love poetry, religious poems, Latin translations, epigrams, elegies, songs, satires and sermons. His poetry is noted for its vibrancy of language and inventiveness of metaphor, especially compared to that of his contemporaries. Donne's style is characterised by abrupt openings and various paradoxes, ironies and dislocations. These features, along with his frequent dramatic or everyday speech rhythms, his tense syntax and his tough eloquence, were both a reaction against the smoothness of conventional Elizabethan poetry and an adaptation into English of European baroque and mannerist techniques. His early career was marked by poetry that bore immense knowledge of British society and he met that knowledge with sharp criticism. Another important theme in Donne’s poetry is the idea of true religion, something that he spent much time considering and theorising about. He wrote secular poems as well as erotic and love poems. He is particularly famous for his mastery of metaphysical conceits.


BIO: Concepcion Macuto, She is a contemporary writer from the Philippines, whose writings dwell with "Life and Romance". Graduated with Bachelor of Science of Business Adminastration ( BSBA) major in Management Had locally published her own Book, titled : "Love Is You" Her poems is being published in many book of Anthologies and to some prestigious international magazine. She is a sunshine mixing with rain and creating multicolored rainbow. Poetry is the soul of her emotions spoken and unspoken by the ink of her heart.


George Moses Horton (1798–1884) was the first black poet to be published in the Southern United States. His book was published in 1828 while he was still enslaved; he remained enslaved until he was emancipated late in the Civil War. Horton was born into slavery on William Horton’s plantation in Northampton County, North Carolina. He was the sixth of ten children, though the names of his parents are lost to history. As a very young child in 1800, he and several family members were moved to a tobacco farm in rural Chatham County, when his owner relocated. He was given as property to William’s relative James Horton in 1814. In 1819, the estate was broken up, and George Moses Horton’s family was separated (the poem “Division of an Estate” reflected on the experience years later).

Hello, To all yea warrior poets of old, I say "hail!" I have been a fond fan of poetry my whole life, and have written and published a self-made poet's dream book about everything I love. Please check it out and check the link; I'm an up and coming writer and wish to spread the good words of my work to many people, God willing you will like what I've done :) I hope you enjoy my verses, if you want more my title "Life, Death, and Everything Else" is available on amazon and createspace and is listed on both, print on demand. Thank you! http://sarospoetry.blogspot.com/ This is the link in case you love what I've done and wish to own the full book, it is 13.95 and 350 pages. Here's the link: https://www.createspace.com/4845662


Alfonso Reyes Ochoa (Monterrey, 17 de mayo de 1889 - México, D.F., 27 de diciembre de 1959) fue un poeta, ensayista, narrador, diplomático y pensador mexicano. Se le conoce también como «el regiomontano universal». Fue el noveno de los doce hijos del general Bernardo Reyes y de doña Aurelia Ochoa. Su padre ocupó importantes cargos durante los gobiernos de Porfirio Díaz (fue gobernador del estado de Nuevo León y Secretario de Guerra y Marina). Alfonso Reyes es un escritor clásico, formalista, comedido, su prosa nos hace pensar en el modelo apolíneo de Nietzsche. Sus temas y preocupaciones fueron siempre los grandes temas de la cultura clásica griega. Fue considerado por Borges “el mejor prosista del idioma español del siglo XX”.






























